Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
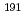 Pt-labeled platinum complex and evaluation of its biodistribution in healthy mice
Pt-labeled platinum complex and evaluation of its biodistribution in healthy miceOmokawa, Marina*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Kawashima, Hidekazu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Yagi, Yusuke*; Naito, Yuki*; Yasui, Hiroyuki*
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 97, p.117557_1 - 117557_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Suzuki, Hiroaki*; Morita, Yoshihiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00450_1 - 19-00450_17, 2020/06
In this study, the SAMPSON code was modified to evaluate severe accidents in a spent fuel pool (SFP). Air oxidation models based on oxidation data obtained on the Zircaroy-4 cladding (ANL model) and the Zircaroy-2 cladding (JAEA model) were included in the modified SAMPSON code. Experiments done by Sandia National Laboratory using simulated fuel assemblies equivalent to those of an actual BWR plant were analyzed by the modified SAMPSON code to confirm the functions for analysis of the severe SFP accidents. The rapid fuel rod temperature rise due to the Zr air oxidation reaction could be reasonably evaluated by the SAMPSON analysis. The SFP accident analyses were conducted with different initial water levels which were no water, water level at bottom of active fuel, and water level at half of active fuel. The present analysis showed that the earliest temperature rise of the fuel rod surface occurred when there was no water in the SFP and natural circulation of air became possible.
Morita, Yoshihiro*; Suzuki, Hiroaki*; Naito, Masanori*; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2019/05
In this study, the SAMPSON code was modified to evaluate severe accidents in a spent fuel pool (SFP). Not only the SFP but also upper spaces of the SFP, walls of the reactor building, and the blowout panel were included. Air oxidation models obtained by the Zircaroy-4 cladding (ANL model) and the Zircaroy-2 cladding (JAEA model) were included in the modified SAMPSON code. Experiments done by Sandia National Laboratory using simulated fuel assemblies equivalent to those of an actual BWR plant were analyzed by the modified SAMPSON code to confirm the functions for analysis of the severe SFP accidents.
Suzuki, Hiroaki*; Morita, Yoshihiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Nagatake, Taku; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/05
In this paper, modification of the SAMPSON code was carried out to enable the analysis of spray cooling. The SAMPSON analysis of a spray cooling experiment was performed to confirm reproducibility of spray cooling behavior of fuel claddings. The modified SAMPSON code was applied to a hypothetical loss-of-coolant accident analysis of the SFP. Effectiveness of spray cooling on cladding temperature behavior was investigated. The SAMPSON analysis showed that spraying from the top of the SFP was effective for cooling the fuel assemblies exposed to the gas phase.
Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Tachibana, Shoichi*; Iwasaki, Daisuke*; Higashino, Yuji*; Yoshimi, Chiaki*; Nakagawa, Koya*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 94(11), p.115103_1 - 115103_10, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:61.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we systematically investigate three-dimensional(3D) momentum-resolved electronic structures of Ruddlesden-Popper-type iridium oxides Sr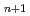 Ir
Ir O
O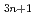 using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO
using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO -plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled
-plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled 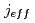 = 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO
= 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO and
and 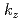 -dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr
-dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr Ir
Ir O
O . To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
. To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
Naito, Fujio*; Anami, Shozo*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Uota, Masahiko*; Ouchi, Toshikatsu*; Onishi, Takahiro*; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Obina, Takashi*; Kawamura, Masato*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1244 - 1246, 2016/11
The proton linac installed in the Ibaraki Neutron Medical Research Center is used for production of the intense neutron flux for the Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). The linac consists of the 3-MeV RFQ and the 8-MeV DTL. Design average beam current is 10mA. Target is made of Beryllium. First neutron production from the Beryllium target was observed at the end of 2015 with the low intensity beam as a demonstration. After the observation of neutron production, a lot of improvement s was carried out in order to increase the proton beam intensity for the real beam commissioning. The beam commissioning has been started on May 2016. The status of the commissioning is summarized in this report.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Higashi, Yasuo*; Sugawara, Hirotaka*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*
Proceedings of 7th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '16) (Internet), p.906 - 909, 2016/06
An accelerator based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) facility is being planned at Okinawa institute of science and technology (OIST). The proton accelerator consists of a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a drift tube linac (DTL). The required beam power is 60 kW. The present beam energy and current are 10 MeV and 30 mA, respectively. The pulse length is 3.3 ms and the repetition rate is 60 Hz, therefore, the duty factor is 20%. In this paper, present design of this compact, medium current, high duty proton linac is presented.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Shibata, Takanori*; Nishida, Kenjiro*; Mochizuki, Shintaro*; Mattei, S.*; Lettry, J.*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02B128_1 - 02B128_3, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)A numerical model of plasma transport and electromagnetic field in the J-PARC RF ion source has been developed to understand relation between antenna coil heat loadings and plasma production/transport processes. From the calculation, the local plasma density increase is observed in the region close to the antenna coil. The magnetic field line with absolute magnetic flux density 30-120 Gauss results in the magnetization of electron which leads to high local ionization rate. The results suggest that modification of magnetic configuration can be made to reduce plasma heat flux onto the antenna.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Higashi, Yasuo*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Kurokawa, Shinichi*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.948 - 950, 2015/09
An accelerator based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) facility is being planned at Okinawa institute of science and technology (OIST). The proton accelerator consists of a radio frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac and a drift tube linac (DTL). The reqired beam power is 60 kW. The present beam energy and current are 10 MeV and 30 mA, respectively. The pulse length is 3.3 ms and the repetition rate is 60 Hz, therefore, the duty factor is 20%. In this paper, present designof this compact, midium current, high duty proton linac is presented.
Oguri, Hidetomo; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ao, Hiroyuki; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.389 - 393, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Tagawa, Akihiro; Tezuka, Masashi; Terakura, Yoshihiro*; Naito, Masayuki*; Miyajima, Kenji*
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-21) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2013/07
It is one of the most urgent issues to remediate the nuclear power plants contaminated by radioactive materials discharged following the accident at the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi NPS. Concrete walls of nuclear power plants in Japan are coated an epoxy resin coating for easily performing decontamination. We experimented a cutting test in Fugen Decommissioning Engineering Center using maximum 280 MPa pressure and 30 L/min water quantity, ultra-high pressure water jet system and 40 m /min air quantity vacuum system. We are conducting a study of decontamination technology in environmental pollution using this decontamination system. This decontamination system has achieved a decontamination factor 10 to 100. Thus, we have confirmed the change in a cutting ability by changing parameters. Parameters are the water pressure, the water quantity and air quantity. The impact force for water jet is a function that contains the test parameters. We have considered it using this function. The results of the test showed that there is a correlation between the impact force for water jet and a cutting capability. This decontamination technology can decontaminate radioactive material of the surface adhesion contamination and reduce the amount of waste generated for a thin cutting. In addition, we have experimented that the water can be recycled by chemical precipitation. After we experimented flocculation test using aluminum sulfate and zeolite flocculant, we have confirmed that it can clean water up to the level of suspended solids 5 mg/L, in turbid water using zeolite flocculant. This suspended solids concentration can be passed to the water processing system in nuclear power plant. From the test results, we found that ultra-high pressure water jet decontamination technology has a possibility that it can be used for decontamination of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant.
/min air quantity vacuum system. We are conducting a study of decontamination technology in environmental pollution using this decontamination system. This decontamination system has achieved a decontamination factor 10 to 100. Thus, we have confirmed the change in a cutting ability by changing parameters. Parameters are the water pressure, the water quantity and air quantity. The impact force for water jet is a function that contains the test parameters. We have considered it using this function. The results of the test showed that there is a correlation between the impact force for water jet and a cutting capability. This decontamination technology can decontaminate radioactive material of the surface adhesion contamination and reduce the amount of waste generated for a thin cutting. In addition, we have experimented that the water can be recycled by chemical precipitation. After we experimented flocculation test using aluminum sulfate and zeolite flocculant, we have confirmed that it can clean water up to the level of suspended solids 5 mg/L, in turbid water using zeolite flocculant. This suspended solids concentration can be passed to the water processing system in nuclear power plant. From the test results, we found that ultra-high pressure water jet decontamination technology has a possibility that it can be used for decontamination of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Hori, Toshihiko; Oguri, Hidetomo; Sato, Fumiaki; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Sugimura, Takashi*; et al.
Physical Review Special Topics; Accelerators and Beams, 16(4), p.040102_1 - 040102_8, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:68.29(Physics, Nuclear)We performed a high-power test of a new radio-frequency quadrupole (RFQ II) for the J-PARC linac. RFQ II was developed as a spare RFQ because the operating J-PARC RFQ has suffered from a sparking problem. First, the conditioning of RFQ II was carried out; after 50 h of conditioning, RFQ II became very stable with a nominal power and duty of 330 kW and 3%, respectively. Next the thermal properties were measured because the resonant frequency of RFQ II is tuned by changing the temperature of the cooling water. The frequency response was measured and compared to finite-element method simulation results, confirming that the simple two-dimensional model reproduces the experimental data well. The differences in the field distribution with changes in the rf loading and the cooling-water temperature were also measured, and no serious field distortion was observed. Therefore, we conclude that RFQ II can perform well as a high-power rf cavity.
Morita, Koji*; Zhang, S.*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Inoue, Fusao*; Yugo, Hiroaki*; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 241(12), p.4672 - 4681, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:73.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)A five-year research project has been initiated in 2005 to develop a code based on the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method for detailed analysis of key phenomena in core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The code is named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis). The key phenomena include (1) fuel pin failure and disruption, (2) molten pool boiling, (3) melt freezing and blockage formation, (4) duct wall failure, (5) low-energy disruptive core motion, (6) debris-bed coolability, (7) metal-fuel pin failure. Validation study of COMPASS is progressing for these key phenomena. In this paper, recent COMPASS results of detailed analyses for the several key phenomena are summarized. The present results demonstrate COMPASS will be useful to understand and clarify the key phenomena of CDAs in SFRs in details.
Kawamura, Masato*; Chishiro, Etsuji; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Fang, Z.*; Fukui, Yuji*; Naito, Fujio*; Yamazaki, Masayoshi*; Tsubota, Naoaki; Futatsukawa, Kenta; Sato, Fumiaki; et al.
Proceedings of 8th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), 3 Pages, 2011/08
We will report about status of linac 400 MeV upgrade program and northeast Japan earthquake restoration. On March 11, the linac suffered serious damage as consequence of the earthquake, and was shuttled down for long term. Linac RF group restores the facilities and is accomplishing 400 MeV upgrade at the same time.
Ito, Hideaki; Maeda, Shigetaka; Naito, Hiroyuki; Akiyama, Yoichi; Miyamoto, Kazuyuki; Ashida, Takashi; Noguchi, Koichi; Ito, Chikara; Aoyama, Takafumi
JAEA-Technology 2010-049, 129 Pages, 2011/03
The in-vessel gamma dose rate was measured in the experimental fast reactor Joyo to evaluate the activation of reactor structural components and the radiation exposure of the fiber scope used for in-vessel visual inspection. The measurement system, which requires a wide sensitivity range and high durability in a high-temperature environment, was specifically developed for use in the sodium cooled fast reactor. Using this system, the in-vessel gamma dose rate with cooling times of 450 and 720 days after reactor shutdown was measured in Joyo, which has been operated for 71,000 hours over approximately 30 years. The gamma dose rate was calculated using QAD-CGGP2 code with the gamma source intensity obtained by the ORIGEN2 code. The neutron flux used as input to the ORIGEN2 was evaluated by the Joyo dosimetry method. The ratio between the calculated and experimental values ranged from 1.1 to 2.4, confirming the accuracy of gamma dose rate and component activation calculation.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Uehara, Yasushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-8) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2010/10
In this paper, FY2009 results of the COMPASS code development are reported. Validation calculations for melt freezing and blockage formation, eutectic reaction of metal fuel, duct wall failure (thermal-hydraulic analysis), fuel pin failure and disruption and duct wall failure (structural analysis) are shown. Phase diagram calculations, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics were used to investigate physical properties of eutectic reactions: metallic fuel/steel and control rod material/steel. Basic studies for the particle method and SIMMER code calculations supported the COMPASS code development. COMPASS is expected to clarify the basis of experimentally-obtained correlations used in SIMMER. Combination of SIMMER and COMPASS will be useful for safety assessment of CDAs as well as optimization of the core design.
Terunuma, Akihiro; Naito, Akira; Nemoto, Koichi; Usami, Jun; Tomii, Hiroyuki; Shiraishi, Kunio; Ito, Shinichi
JAEA-Review 2010-038, 96 Pages, 2010/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has midterm plan for decommissioning the facilities being finished their role and the facilities that became unnecessary by shifting their functions to other facilities. In the first midterm plan (from the latter half of fiscal year 2005 to fiscal year 2009), decommissioning of five facilities (Ceramic Research Facility, Plutonium Research Facility No.2, Metallurgy Research Facility, Isotope Separation Research Facility and Reprocessing Test Facility) had been carried out in order to release controlled area and dismantle the facilities in Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI), JAEA. The decommissioning activity for each facility had been reported to the regulatory body and municipalities. On this report, we summarize the each activity for five facilities by reviewing the reports to the regulatory body and municipalities. We also added the knowledge obtained through the activity.
Ao, Hiroyuki; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ouchi, Nobuo; Tsubota, Naoaki; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Hirano, Koichiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Takata, Koji*; Naito, Fujio*; Yamazaki, Yoshishige
Proceedings of 7th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (DVD-ROM), p.552 - 554, 2010/08
The energy upgrade of the J-PARC linac was started from March 2009. In this project 20 Annular Coupled Structure (ACS) modules will be fabricated. The resonant frequency of the ACS module has to be tuned with mechanical machining before the final brazing. Therefore the test cells were fabricated to accumulate frequency tuning parameters. We fixed the final dimensions and the machining amount of the frequency tuning using these results. So far, the cell parts for the five ACS modules were tuned within 71.93  0.05 MHz. At the moment the first ACS module is being assembled and it will be completed in autumn 2010.
0.05 MHz. At the moment the first ACS module is being assembled and it will be completed in autumn 2010.
Oka, Kiyoshi; Seki, Takeshi*; Naito, Takehito*; Watanabe, Shinya*; Wakabayashi, Takao*; Naganawa, Akihiro*; Inui, Kazuo*; Yoshino, Junji*
Nihon Gazo Igaku Zasshi, 28(1), p.12 - 24, 2010/05
Focusing on the measurement function loaded on our rigid-typed endoscope for the fetal surgery treatment, we proposed that its combination with a generally used digestive endoscope enabled calibration of lesion size in stomach. While adding the function, with which the target size is to be easily measured, on the endoscope, we simplified the system structure as much as possible. We also tried to minimize the total cost by using the generally used endoscope, instead of making it from scratch. Combining another development, the composite-type optical fiberscope with diameter of 1.1mm, with a generally used endoscope, we proposed the following as the features: (1)acquisition of fiberscope image, (2)laser irradiation for treatments, (3)applying the real time measurement function of distance and blood flow by semiconductor laser to the generally used endoscope. We have operated the clinical study to the gastric wall of person with no health problem, using this system and confirmed it was available for practical use.