Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 X-ray synchrotron diffraction
X-ray synchrotron diffractionLi, H.*; Liu, Y.*; Zhao, W.*; Liu, B.*; Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Wei, D.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 165, p.103612_1 - 103612_20, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.7(Engineering, Mechanical)In order to clarify the strength properties of Co-free maraging steel,  tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
Miyagawa, Reina*; Kamibayashi, Daisuke*; Nakamura, Hirotaka*; Hashida, Masaki*; Zen, H.*; Somekawa, Toshihiro*; Matsuoka, Takeshi*; Ogura, Hiroyuki*; Sagae, Daisuke*; Seto, Yusuke*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12, p.20955_1 - 20955_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We evaluated Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structure (LIPSS) crystal structures using the stress imaging station at BL22XU of JAEA-BL on SPring-8. Crystallization of LIPPS was used different two types laser these are Ti:Sapphire laser (wavelength: 800 nm) and MIR-FEL (mid-infrared free electron laser, wavelength 11.4  m). These lasers are different in the laser pulse structure and the wavelength. We investigated on the effects of formed LIPSS crystallization using different kind of laser. Measured synchrotron X-ray energy is 30 keV and beam size is 20
m). These lasers are different in the laser pulse structure and the wavelength. We investigated on the effects of formed LIPSS crystallization using different kind of laser. Measured synchrotron X-ray energy is 30 keV and beam size is 20  m. Detector of diffracted X-ray is two-dimensional detector (PILATUS300K, DECTRIS). LIPSS formed using Ti:Sapphire laser has deformed structure with good crystallinity. LIPSS formed using MIR-FEL has dislocation or fault without structural stress. These results show depending on select of laser forming LIPPS structure. These information becomes important a point of the functional application of LIPSS.
m. Detector of diffracted X-ray is two-dimensional detector (PILATUS300K, DECTRIS). LIPSS formed using Ti:Sapphire laser has deformed structure with good crystallinity. LIPSS formed using MIR-FEL has dislocation or fault without structural stress. These results show depending on select of laser forming LIPPS structure. These information becomes important a point of the functional application of LIPSS.
Kumada, Takayuki; Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Morooka, Satoshi; Tominaga, Aki; Tanida, Hajime; Shobu, Takahisa; Konno, Azusa; Owada, Kenji*; Ono, Naoko*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 528, p.151890_1 - 151890_7, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have developed an anomalous small-angle X-ray scattering (ASAXS) diffractometer in SPring-8 to investigate irradiation-induced nanostructural change in ion-beam irradiated stainless steel. A thermally-aged MA956 stainless steel sample displays power-law scattering that follows the Porod law at the magnitude of scattering vector, Q, below 0.5 nm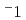 and an overlapped shoulder around 0.7 nm
and an overlapped shoulder around 0.7 nm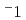 . After the ion-beam irradiation, the intensity of the shoulder remained unchanged, whereas that of the power-law scattering nearly doubled. This result indicates that none of the structural parameters of the Cr-rich nanoprecipitates, such as the number density, size, and interface roughness, were changed by the irradiation.
. After the ion-beam irradiation, the intensity of the shoulder remained unchanged, whereas that of the power-law scattering nearly doubled. This result indicates that none of the structural parameters of the Cr-rich nanoprecipitates, such as the number density, size, and interface roughness, were changed by the irradiation.
Konno, Azusa; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Kumada, Takayuki; Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Morooka, Satoshi; Ukai, Shigeharu*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Ono, Naoko*; Shobu, Takahisa; et al.
no journal, ,
Duplex stainless steels is composed by austenite and ferrite phases, offering superior toughness, high strength properties, good weldability, and corrosion-resistance. It has been used as the heat exchanger components for the chemical industrial plants and pipes for the Pressurized light-Water Reactors (PWR). However, the duplex stainless steels is also known to suffer from the embrittlement due to the phase separation into the Cr-rich phase and Fe-rich one when it is annealed at longer time at the temperature over 300 degrees. In this study, we focused on the Anomalous Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (A-SAXS) technique that can analyze "arbitrary element" by using absorption edge of a specific element and estimated the chromium separation quantitatively by utilizing the A-SAXS method, considering the availability of this new technique as the quantitative and non-destructive analysis method for microstructure in metallic material.
Tominaga, Aki; Oba, Yojiro; Shobu, Takahisa; Owada, Kenji*; Tanida, Hajime; Konno, Azusa; Morooka, Satoshi; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki
no journal, ,
In steel materials, it is known that precipitation of Cr rich phase hardens ferrite phase and decreases toughness in base material. Small angle X-ray scattering is a promising method for analysis of this precipitation process because the precipitate is nanometer size. However, it is usually difficult to separate the scattering between the Fe phase and Cr phase since Fe and Cr are close in atomic number. Therefore, in order to observe the state of phase separation of Cr, we developed an anomalous X-ray small angle scattering (A-SAXS) method at BL22XU.
Shiwaku, Hideaki; Tanida, Hajime; Tominaga, Aki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tominaga, Aki; Oba, Yojiro; Shobu, Takahisa; Tanida, Hajime; Owada, Kenji*; Konno, Azusa; Morooka, Satoshi; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki
no journal, ,
In development of oxide-dispersed ferritic steels, it is known that precipitation of Cr rich phase hardens ferrite phase and decreases toughness in base material. Small angle X-ray scattering is a promising method for analysis of this precipitation process because the precipitate is nanometer size. However, it is usually difficult to separate the scattering between the Fe phase and Cr phase since Fe and Cr are close in atomic number. Therefore, in order to observe the state of phase separation of Cr, we developed an anomalous X-ray small angle scattering (A-SAXS) method using synchrotron radiation.
Konno, Azusa; Oba, Yojiro; Tominaga, Aki; Morooka, Satoshi; Ono, Naoko*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Ukai, Shigeharu; Owada, Kenji*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; et al.
no journal, ,
An ODS alloy is one of the promising candidate materials applicable to the fusion reactor because of its high-temperature creep strength and irradiation resistance. However, the ODS ferritic stainless steel with high Cr content sometimes suffers from the embrittlement related to phase separation below 748 K for a long term using in the reactor. It is, therefore, an important issue to understand embrittlement phenomena from not only macrostructural viewpoint but also microstructural one. Anomalous Small Angle X-ray Scattering (A-SAXS) is a unique and potential evaluation method that can analyze complex microstructure. This method can extract the signal only from an element of interest to implant the X-ray of the wavelength near orbit electron of the element. In this study, we performed both the A-SAXS analysis and TEM observation for high Cr-ODS alloy in order to assess the applicability of the A-SAXS technique as a microstructure determination and compared the A-SAXS signal with the TEM micrograph. The specimen of the commercial MA956 (Fe-20Cr-4.8Al-0.4Ti-0.02C-0.4Y O
O (mass%)) were thermally-aged at 748 K for 1, 10, 100 and 1000 hrs, and measured using the A-SAXS diffractometer at BL22XU in SPring-8 and a TEM. The A-SAXS data reveal that the average size of Cr precipitations increases with increasing the aging time. Also, using the A-SAXS profiles, it was estimated that there were two cases; one is the case that the microstructure does have a distinct interface between the matrix and Cr precipitate. The other case is the microstructure does not have the distinct interface. On the other hand, in TEM observation, the periodic modulated structure was observed for 10 hrs thermally-aged sample, and the sphere precipitation was confirmed for 100 hrs thermally-aged sample. It was suggested that there would be a crucial phase separation mode from spinodal decomposition to nucleation-growth between 10 and 100 hrs.
(mass%)) were thermally-aged at 748 K for 1, 10, 100 and 1000 hrs, and measured using the A-SAXS diffractometer at BL22XU in SPring-8 and a TEM. The A-SAXS data reveal that the average size of Cr precipitations increases with increasing the aging time. Also, using the A-SAXS profiles, it was estimated that there were two cases; one is the case that the microstructure does have a distinct interface between the matrix and Cr precipitate. The other case is the microstructure does not have the distinct interface. On the other hand, in TEM observation, the periodic modulated structure was observed for 10 hrs thermally-aged sample, and the sphere precipitation was confirmed for 100 hrs thermally-aged sample. It was suggested that there would be a crucial phase separation mode from spinodal decomposition to nucleation-growth between 10 and 100 hrs.
Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Kamei, Naomitsu; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
no journal, ,
A joint exists in mechanical structure. The material used according to the use environment is also various for mechanical structure. The reliability is requested of the technology to which those are joined. Laser machining doesn't choose the material. It's expected that this is used as variety material junction technique and necessary welding technique. It's necessary to consider influence of a stress by the variety organization of the joint neighborhood, the mechanical property and the difference in the heat expansion coefficient between the variety metal together. To aim at generalization by this TAKUMI's technological calculation scientific simulation, permanent deformation spacial distribution inside the same kind material weld material between the carbon steel, the carbon steel and the variety material weld material of oxygen-free copper by a high powered fiber laser was measured and the special quality about the processing influence was estimated.
Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Nagai, Takayuki
no journal, ,
Glassy radioactive waste is a promising method for treating radioactive waste. Many kinds of elements are confined in the glass raw material. To stablish technology of confirm the stability for vitrified substances is required. We developed an analytical method for residual stress in vitrified radioactive waste samples using the analyzing from synchrotron-ray diffraction and scattering profile. We are studying application to various vitrified radioactive waste samples. We hope that this measurement method will be one of the methods for contributing to the solvation of vitrification technology.
Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Nagai, Takayuki
no journal, ,
High level radioactive vitrified materials are subject to monitoring during decades at storage facilities and over tens of thousands of years at final disposal sites. Although sufficient structural stability for long-term storage is necessary, high effluent filling which is often incompatible with mechanical and chemical integrity are required. The inhomogeneity of the glass yielded in preparation will cause the instability of the glass. Residual stress is one of the important parameters for evaluating the stability of the vitrified materials. Conventional stress measurement using a strain gauge reveal the averaged stress of whole specimen, however, local stress is also important because it can be an origin of the deformation or crack. Therefore, we developed a method using high-energy synchrotron X-ray stress measurements to clarify the local strain of the vitrified materials. Moreover, stress of each structural component such as crystalline and glass matrix can be separated by the method.
Shobu, Takahisa; Tominaga, Aki; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Nagai, Takayuki
no journal, ,
In order to ensure the long-term safety of the vitrified radioactive waste, the relationship between number of stirring and characteristics of material strength after melting the raw material glass and simulated vitrified radioactive waste were investigated by synchrotron radiation X-rays. As a result, it was clarified that the internal defects in simulated vitrified radioactive waste increased and the material strength of simulated vitrified radioactive waste was suitable as increasing the number of stirrings.
 1 surface oxidation at room temperature
1 surface oxidation at room temperatureYoshigoe, Akitaka; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Tominaga, Aki; Sakamoto, Tetsuya; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
no journal, ,
In Society 5.0, nanometer-scaled devices with high performance and low-power are required. Since silicon (Si) based metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) transistors play an important role in the application of information and communication technology, precise control and understanding of Si surface oxidation is still important. However, the debate on the Si surface oxidation by molecular oxygen still remains. In our previous study, we found that the O1s photoelectron spectra of room temperature oxidation of Si(001)2 1 surface show satellite peaks indicating molecularly adsorbed oxygen. In this study, the role of molecularly adsorbed oxygen in the oxidation reaction in relation to the translational energy of incident oxygen molecules was investigated by synchrotron radiation real-time photoemission spectroscopy. All experiments were conducted using the surface experimental station of JAEA's BL23SU at SPring-8. Even on a p-type Si(001) surface under molecular beam irradiation with the translational energy of 0.06 eV, a satellite peak was clearly observed at a binding energy of about 4.45 eV lower than the main peak (oxygen atom in Si-O-Si). The role of molecularly adsorption in the oxidation reaction will be discussed from the results of signal changes with the progress of oxidation times.
1 surface show satellite peaks indicating molecularly adsorbed oxygen. In this study, the role of molecularly adsorbed oxygen in the oxidation reaction in relation to the translational energy of incident oxygen molecules was investigated by synchrotron radiation real-time photoemission spectroscopy. All experiments were conducted using the surface experimental station of JAEA's BL23SU at SPring-8. Even on a p-type Si(001) surface under molecular beam irradiation with the translational energy of 0.06 eV, a satellite peak was clearly observed at a binding energy of about 4.45 eV lower than the main peak (oxygen atom in Si-O-Si). The role of molecularly adsorption in the oxidation reaction will be discussed from the results of signal changes with the progress of oxidation times.
Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Satou, Yukihiko; Shiro, Ayumi*; Kuwatsuru, Osamu*; Uno, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
During the fracture test of the simulated debris, the internal deformation and the strain were evaluated by X-ray CT and X-ray diffraction using synchrotron radiation source, respectively. The purpose of this study is to determine the fracture strength of the debris, the prediction of which is thought to be difficult, from the CT images and strain amounts during the fracture test. We'll report the results of measurements using synchrotron X-ray CT and diffraction at the JAEA beamline BL22XU on SPring-8. ZrO phase, Al
phase, Al O
O phase, and voids were observed in the CT image. In the strain analysis by X-ray diffraction of this sample was obtained from the average strain of the sample flat plate with the thickness of about 0.1 mm including the center of the sample. We consider that the difference between the macrostrain and microstrain is the amount of void deformation.
phase, and voids were observed in the CT image. In the strain analysis by X-ray diffraction of this sample was obtained from the average strain of the sample flat plate with the thickness of about 0.1 mm including the center of the sample. We consider that the difference between the macrostrain and microstrain is the amount of void deformation.
 1 surface oxidation at room temperature
1 surface oxidation at room temperatureYoshigoe, Akitaka; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Tominaga, Aki; Sakamoto, Tetsuya; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
no journal, ,
The basic understanding of the oxidation at Si surfaces by oxygen gas has been important to develop advanced metal-oxide-semiconductor devices. In our previous study, we succeeded to detect a satellite peak located at lower binding energy sides of the main peak (Si-O-Si) in the Si(001)2 1 surface oxidation. This peak has been considered to be due to the molecularly adsorbed oxygen. In this study, we studied the incident O
1 surface oxidation. This peak has been considered to be due to the molecularly adsorbed oxygen. In this study, we studied the incident O energy dependence of this adsorbate by using real-time photoemission spectroscopy. All experiments were conducted at the surface experimental station (SUREAC2000) at BL23SU in SPring-8. It was found that the satellite peak was clearly observed. This result also implies the existence of a precursor state of adsorbed oxygen dissociation even for 0.06 eV.
energy dependence of this adsorbate by using real-time photoemission spectroscopy. All experiments were conducted at the surface experimental station (SUREAC2000) at BL23SU in SPring-8. It was found that the satellite peak was clearly observed. This result also implies the existence of a precursor state of adsorbed oxygen dissociation even for 0.06 eV.
 ders deformation of 5Mn-0.1C steels monitored by in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction under tensile loading
ders deformation of 5Mn-0.1C steels monitored by in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction under tensile loadingMorooka, Satoshi; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Koyama, Motomichi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 /Si(001) interfacial oxidation
/Si(001) interfacial oxidationTsuda, Yasutaka; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Tominaga, Aki; Sakamoto, Tetsuya; Yamamoto, Yoshiki*; Yamamoto, Yukio*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Oba, Yojiro; Shobu, Takahisa; Tominaga, Aki; Tanida, Hajime; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to evaluate the integrity of simulated nuclear waste glass samples, a multi-scale structural analysis system has been established, covering the range from local structure to implementation scale. Synchrotron radiation XAFS was used to investigate the local structure. Since XAFS has excellent elemental selectivity, it is useful for the analysis of waste components in the glass samples which are multi-component systems. In the short range structure, we prepared glass samples with substituted boron isotopes for neutron diffraction experiments and succeeded in obtaining diffraction data with high boron fraction for the first time. In the medium range structure, the influence of platinum group elements was evaluated by PDF analysis. Small-angle scattering experiments provided insight into the phase separation of borosilicate glasses. In addition, we attempted to apply stress-strain analysis to glass samples as structural information on the implementation scale. Through these structural analyses, we will evaluate the structural integrity of the modified glass samples being developed under the contract with the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy.
Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Satou, Yukihiko; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Shiro, Ayumi*; Kuwatsuru, Osamu*; Uno, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
We focused on element selectivity, which is a feature of the imaging method and the XAFS method. The research purpose is to construct the CT-XAFS method on BL22XU. We have constructed a system that enables energy scanning near the absorption edge of target elements. In the measurement, we identified the scan energies containing many target elements. Based on the results, we built a technology to obtain information on the crystal structure and valence. The simulated debris of the measurement sample was made by melting and solidifying UO and B
and B O
O at 1800
at 1800 C using eutectic reaction. Simulated fuel debris was irradiated with synchrotron radiation, and its interior was observed using the X-ray CT method. After confirming the inside, a CT image was acquired at the energy around the U-L
C using eutectic reaction. Simulated fuel debris was irradiated with synchrotron radiation, and its interior was observed using the X-ray CT method. After confirming the inside, a CT image was acquired at the energy around the U-L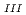 edge. In the presentation, we will report on the construction status of the measurement technology, the acquisition of XAFS spectra at specific locations inside the material from CT images, and the presence or absence of structural differences due to differences in fabrication methods.
edge. In the presentation, we will report on the construction status of the measurement technology, the acquisition of XAFS spectra at specific locations inside the material from CT images, and the presence or absence of structural differences due to differences in fabrication methods.
Shobu, Takahisa; Tominaga, Aki; Mukai, Tomohisa*; Ariki, Katsuyoshi*; Choe, H.*; Takano, Yoshiki*; Morooka, Satoshi; Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English