Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 GeP
GeP S
S by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements
by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurementsHori, Satoshi*; Kanno, Ryoji*; Kwon, O.*; Kato, Yuki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Matsuura, Masato*; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Kawakita, Yukinobu
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(22), p.9518 - 9527, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:41.53(Chemistry, Physical)Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.19(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:79.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Yasuda, Satoshi; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Terasawa, Tomoo; Yano, Masahiro; Nakajima, Hideaki*; Morimoto, Takahiro*; Okazaki, Toshiya*; Agari, Ryushi*; Takahashi, Yasufumi*; Kato, Masaru*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 124(9), p.5300 - 5307, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:60.14(Chemistry, Physical)Confinement of hydrogen molecules at graphene-substrate interface has presented significant importance from the viewpoints of development of fundamental understanding of two-dimensional material interface and energy storage system. In this study, we investigate H confinement at a graphene-Au interface by combining selective proton permeability of graphene and the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (electrochemical HER) method. After HER on a graphene/Au electrode in protonic acidic solution, scanning tunneling microscopy finds that H
confinement at a graphene-Au interface by combining selective proton permeability of graphene and the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (electrochemical HER) method. After HER on a graphene/Au electrode in protonic acidic solution, scanning tunneling microscopy finds that H nanobubble structures can be produced between graphene and the Au surface. Strain analysis by Raman spectroscopy also shows that atomic size roughness on the graphene/Au surface originating from the HER-induced strain relaxation of graphene plays significant role in formation of the nucleation site and H
nanobubble structures can be produced between graphene and the Au surface. Strain analysis by Raman spectroscopy also shows that atomic size roughness on the graphene/Au surface originating from the HER-induced strain relaxation of graphene plays significant role in formation of the nucleation site and H storage capacity.
storage capacity.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.28(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Ino, Kohei*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Yanagawa, Katsunori*; Kato, Shingo*; Sunamura, Michinari*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; et al.
ISME Journal, 12(1), p.31 - 47, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:91.33(Ecology)In this study, we found the dominance ofanaerobic methane-oxidizing archaea in groundwater enriched in sulfate and methane from a 300-m deep underground borehole in granitic rock.
Oguri, Hidetomo; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ao, Hiroyuki; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.389 - 393, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Kato, Atsushi; Kubo, Shigenobu; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Hayafune, Hiroki; Yokoi, Shinobu*; Nakata, Shuhei*; Tani, Akihiro*; Shimakawa, Yoshio*
Proceedings of 2014 International Congress on the Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2014) (CD-ROM), p.616 - 623, 2014/04
This paper focuses on loss of heat removal system (LOHRS) type event as Design Extension Condition (DEC) and describes candidates design measures to improve the decay heat removal system of JSFR against LOHRS type DEC. The design requirements are determined based on the Safety Design Criteria for Generation-IV Sodium-cooled fast reactor system. Effectiveness and reliability of the candidate design measures are discussed with preliminary evaluations.
Kato, Atsushi; Kotake, Shoji; Yoshiuji, Takahiro*
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles (FR 2009) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2012/00
Within the FaCT project, commodities shall be reduced by introducing innovative technologies. In order to evaluate the economy for the Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR), the account code named SCALLE (Sum of Cost Account Leading to future Logistics Economy) has been developed, in which the basic methodology is bottom up of component costs based on amounts of material and corresponding unit costs.
Maekawa, Fujio; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Teshigawara, Makoto; Kai, Tetsuya; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Takada, Hiroshi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 620(2-3), p.159 - 165, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:97.59(Instruments & Instrumentation)The J-PARC 1-MW pulsed spallation neutron source JSNS was successfully launched on 30th of May 2008. To demonstrate the unique features of the moderator design and the neutronic performance of JSNS the neutron spectral intensity, absolute neutron flux, and time structure of the neutron pulse shapes etc have been measured using several neutron instruments since then. The measured energy spectra clearly revealed the feature of the para-hydrogen, as expected when designing the moderator. The measured neutron flux below 0.4 eV agreed with the corresponding design value within  20%, thus suggesting that the JSNS design calculations to have been reliable. World-class high-resolution diffraction data could be recorded due to the suitability of design of the moderators and the instruments. Another world-class high-intensity neutron flux was also capable of being demonstrated due to the unique design of the large cylindrical coupled moderator.
20%, thus suggesting that the JSNS design calculations to have been reliable. World-class high-resolution diffraction data could be recorded due to the suitability of design of the moderators and the instruments. Another world-class high-intensity neutron flux was also capable of being demonstrated due to the unique design of the large cylindrical coupled moderator.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Shirai, Yasuyuki*; Shiotsu, Masahiro*; Hata, Koichi*; Kobayashi, Hiroaki*; Naruo, Yoshihiro*; Inatani, Yoshifumi*; Kato, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Kinoshita, Katsuhiro*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 234, p.032056_1 - 032056_9, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:97.04(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A thermal-hydraulics experimental system of liquid hydrogen was developed in order to investigate the forced flow heat transfer characteristics in the various cooling channels for wide ranges of subcoolings, flow velocities, and pressures up to supercritical. Forced flow through the channel is produced by adjusting the pressure difference between the tanks and the valve opening. The mass flow rate is measured from the weight change of the main tank. For the explosion protection, electrical equipments are covered with a nitrogen gas blanket layer and a remote control system has been established. The first cryogenic performance tests have confirmed that the experimental system has satisfied with the required performances. The forced convection heat transfer characteristics have been successfully measured at the pressure of 0.7 MPa for various flow velocities.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Shirai, Yasuyuki*; Hata, Koichi*; Kato, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Shiotsu, Masahiro*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 234, p.032057_1 - 032057_8, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:90.8(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Experimental research on forced convection heat transfer of subcooled liquid nitrogen ranging from the pressures of 0.3 MPa to its supercritical pressure is carried out for wide ranges of inlet temperature and flow velocity. The heat transfer coefficients in non-boiling region and the DNB heat fluxes are higher for higher flow velocity and higher subcooling. The heat transfer coefficients in the non-boiling region agree well with those by the Dittus-Boelter correlation, although they are unaffected by the flow velocity for 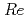
 8000. The lowest limits agree with those obtained for no forced flow. The correlation of DNB heat flux that can describe the experimental data is presented. The heat transfer characteristics of supercritical nitrogen can be predicted by authors'correlation.
8000. The lowest limits agree with those obtained for no forced flow. The correlation of DNB heat flux that can describe the experimental data is presented. The heat transfer characteristics of supercritical nitrogen can be predicted by authors'correlation.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Shirai, Yasuyuki*; Shiotsu, Masahiro*; Hata, Koichi*; Kobayashi, Hiroaki*; Naruo, Yoshihiro*; Inatani, Yoshifumi*; Kato, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Kinoshita, Katsuhiro*
Proceedings of International Cryogenic Engineering Conference 23 (ICEC-23) and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2010 (ICMC 2010), p.491 - 496, 2010/07
Forced flow heat transfers of liquid hydrogen through a vertical tube with the diameter, d, of 3.0 mm were measured at the pressure of 0.7 MPa for various inlet temperatures and flow velocities. The non-boiling heat transfer coefficients agreed with those by the Dittus-Boelter correlation. The heat fluxes at the inception of boiling and the departure from nucleate boiling (DNB) heat fluxes were higher for higher flow velocity and subcooling. The DNB heat fluxes were higher for larger diameter, compared with those for  = 6.0 mm. The effect of tube diameter and subcooling on the DNB heat flux was clarified.
= 6.0 mm. The effect of tube diameter and subcooling on the DNB heat flux was clarified.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Aso, Tomokazu; Otsu, Kiichi; Uehara, Toshiaki; Sakurayama, Hisashi; Kawakami, Yoshihiko; Kato, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Proceedings of International Cryogenic Engineering Conference 23 (ICEC-23) and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2010 (ICMC 2010), p.1009 - 1014, 2010/07
The cryogenic hydrogen system provides supercritical hydrogen to three hydrogen moderators and removes the nuclear heating of 3.75 kW for a 1-MW proton beam operation at the J-PARC. A pressure control system that used a heater and an accumulator was designed to mitigate a pressure fluctuation caused by the sudden heat load of kW-order. The temperature and pressure behaviors were studied for a 300-kW beam operation. It was confirmed that the pressure control system made it possible to reduce the pressure fluctuation below 13.5 kPa. A simulation model was derived and could describe the experimental results within 15% errors.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Aso, Tomokazu; Otsu, Kiichi; Uehara, Toshiaki; Sakurayama, Hisashi; Kawakami, Yoshihiko; Kato, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Yoshinaga, Seiichiro*
Proceedings of International Cryogenic Engineering Conference 23 (ICEC-23) and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2010 (ICMC 2010), p.377 - 382, 2010/07
A dynamic gas bearing centrifugal pump that circulated supercritical hydrogen with a large flow rate of more than 0.16 kg/s was developed to minimize the hydrogen density change at the moderator. The two pumps were simultaneously operated in parallel for redundancy. The performance test results indicated that the dimensionless characteristics for the single and the parallel operations existed on an identical curve. An outstanding peak adiabatic efficiency exited at the flow coefficient of 0.046, independently of the revolution. It was verified that the developed hydrogen pump satisfied the design requirement.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Aso, Tomokazu; Otsu, Kiichi; Uehara, Toshiaki; Sakurayama, Hisashi; Kawakami, Yoshihiko; Kato, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Proceedings of International Cryogenic Engineering Conference 23 (ICEC-23) and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2010 (ICMC 2010), p.601 - 606, 2010/07
At the J-PARC, the cryogenic hydrogen system provides supercritical hydrogen to three hydrogen moderators and removes the nuclear heating evolved by converting high energy neutrons into cold neutrons. As safety countermeasure, fail-safe devices such as relief valves and rupture disks are installed and a hydrogen explosion-proof structure is adopted. Additionally, the safety interlock system that is divided into 7 categories based on the trouble events is established to protect the equipments and to ensure the safety at the occurrence of a trouble. It is confirmed that the interlock system can be operated without any problems. The recovery procedures are also established.
Tanaka, Naritake*; Kimura, Hitoshi*; Faried, A.*; Sakai, Makoto*; Sano, Takaaki*; Inose, Takanori*; Soda, Makoto*; Okada, Koji*; Nakajima, Masanobu*; Miyazaki, Tatsuya*; et al.
Cancer Science, 101(6), p.1487 - 1492, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:31.77(Oncology)We examined the intracellular localization of cisplatin, a key chemotherapeutic agent, in esophageal cancer cell lines and determined their sensitivity to cisplatin using in-air micro-PIXE. Two human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell lines, TE-2 and TE-13, were examined for their response to cisplatin using MTT assay, flow cytometry and DNA fragmentation assays. Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was also used to evaluate the mRNA expression of multidrug resistance protein 2 (MRP2) in both cell lines. Platinum localizations of intracellular and intranuclear were measured using in-air micro-PIXE. TE-2 cells were more sensitive to cisplatin than TE-13 cells. The results of this study suggest that in-air micro-PIXE could be a useful quantitative method for evaluating the cisplatin sensitivity of individual cells. Finally, we speculate that MRP2 in the cell membrane may play an important role in regulating cisplatin sensitivity of ESCC cells.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Aso, Tomokazu; Otsu, Kiichi; Uehara, Toshiaki; Sakurayama, Hisashi; Kawakami, Yoshihiko; Kato, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi
AIP Conference Proceedings 1218, p.297 - 304, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.94(Thermodynamics)In JSNS, supercritical hydrogen at around 20 K and 1.5 MPa was selected as a moderator material. Three kinds of hydrogen moderators are installed to provide pulsed neutron beam with higher neutronic performance. A cryogenic hydrogen system, in which a hydrogen circulation system is cooled by a helium refrigerator system with the refrigerator capacity of 6.45 kW at 15.6 K, provides the supercritical hydrogen to the moderators and absorbs nuclear heating in the moderators. Through the off-beam commissioning, we have confirmed that the cryogenic hydrogen system can be cooled down to 18 K within 19 hours. The supercritical hydrogen with the mass flow rate of 190 g/s can be circulated at the rated condition. It is verified that the cryogenic hydrogen system is satisfied with the performance requirements. In May 2008, we have succeeded in providing the first cold neutron beam cooled by the cryogenic hydrogen system.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Aso, Tomokazu; Otsu, Kiichi; Kato, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi
AIP Conference Proceedings 1218, p.1154 - 1161, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.46(Thermodynamics)Supercritical hydrogen with a pressure of 1.5 MPa and a temperature of 20 K has been selected as a moderator material in an intense spallation neutron source (JSNS), which is one of main experimental facilities in J-PARC. The cryogenic hydrogen system, in which a hydrogen circulation system is cooled by a helium refrigerator with the refrigeration power of 6.45 kW at 15.5 K, has been designed to provide the supercritical hydrogen to the moderator and to remove the nuclear heating generated there. In this study, we have developed a simulation code that predicts temperature behaviors in the hydrogen circulation system during its cool-down process. A cool-down process analyses have been performed, and an operational method for the cool-down process has been studied. The analytical results indicate that the hydrogen circulation system would be able to be cooled down to 18 K within 19 hours.