Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C control-rods
C control-rods*; Fukumura, Nobuo*; *; *; *
PNC TN941 84-123, 108 Pages, 1984/08
Coolant void reactivities due to 0 100% change in void fraction have been measured in two-region core involving B
100% change in void fraction have been measured in two-region core involving B C control-rods fully inserted in order to evaluate the control-rods effect for the void reactivity and an accuracy of reactor calculation codes. The 28-rod PuO
C control-rods fully inserted in order to evaluate the control-rods effect for the void reactivity and an accuracy of reactor calculation codes. The 28-rod PuO -UO
-UO clusters were placed in a central region of the core and the surrounding region was occupied with 28-rod 1.2wt% enriched UO
clusters were placed in a central region of the core and the surrounding region was occupied with 28-rod 1.2wt% enriched UO clusters. Fuel clusters are arranged in a square lattice at a 25.0-cm pitch. The PuO
clusters. Fuel clusters are arranged in a square lattice at a 25.0-cm pitch. The PuO enrichments in the mixed oxides are 0.54 and 0.87wt%. The fissile content of plutonium in both mixed oxides is
enrichments in the mixed oxides are 0.54 and 0.87wt%. The fissile content of plutonium in both mixed oxides is  91%. The void reactivity was measured by changing the number and/or position of the control-rods inserted, and loading ratio of mixed-oxide clusters to UO
91%. The void reactivity was measured by changing the number and/or position of the control-rods inserted, and loading ratio of mixed-oxide clusters to UO clusters. The void reactivities were obtained by integrating a function of the level reactivity coefficient of moderator (
clusters. The void reactivities were obtained by integrating a function of the level reactivity coefficient of moderator (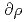 /
/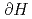 ) for the 100%-voided core between the critical levels at the non-voided and the 100%-voided cores. Values of (
) for the 100%-voided core between the critical levels at the non-voided and the 100%-voided cores. Values of (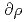 /
/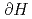 ) were measured by converting the doubling time of neutron flux change due to a small rise of moderator level (
) were measured by converting the doubling time of neutron flux change due to a small rise of moderator level ( H) to small reactivity (
H) to small reactivity (
 ). Corrections are given to the void reactivities measured for the reactivity effects of a leakage due to the difference of axial extrapolation distances between 0% and 100% void fractions and of a temperature change during the measurement. Thermal flux distributions were also measured by
). Corrections are given to the void reactivities measured for the reactivity effects of a leakage due to the difference of axial extrapolation distances between 0% and 100% void fractions and of a temperature change during the measurement. Thermal flux distributions were also measured by  -counting of irradiated copper wire or samples, in order to evaluate the change of flux distributions in the core due to coolant voiding. Experimental void reactivities were compared with calculated ones by WIMS-D4 and CITATION codes. Inserted control-rod is able to deal as a corner rod in unit cell in WIMS-D4 calculation which is applied the square boundary condition. The following are concluded from the present study. (1)Insertion ...
-counting of irradiated copper wire or samples, in order to evaluate the change of flux distributions in the core due to coolant voiding. Experimental void reactivities were compared with calculated ones by WIMS-D4 and CITATION codes. Inserted control-rod is able to deal as a corner rod in unit cell in WIMS-D4 calculation which is applied the square boundary condition. The following are concluded from the present study. (1)Insertion ...
Takemura, Morio*; *; *; *; *
PNC TN941 83-67, 96 Pages, 1983/04
Pressure tube type heavy water reactor has an advantage of load following operation compared with light water reactor. It is planned to prove the possibility of load following operation in the Fugen type demonstration reactor using stainless control-rod (SUS control-rod). Changes in local power distribution and thermal flux distribution due to a small withdrawal of SUS control-rod have been measured for the purpose of confirming the soundness of fuel pin from the viewpoint of the load following operation and fuel design. SUS control-rod (74mm ) with the same dimension as those of the demonstration reactor was inserted into the D
) with the same dimension as those of the demonstration reactor was inserted into the D O moderator of the central region of 0.54wt% plutonium mixed-oxide fuel lattice in 25-cm pitch DCA core. The lower end height of the control-rod inserted was changed from 505mm to 605mm (about 40
O moderator of the central region of 0.54wt% plutonium mixed-oxide fuel lattice in 25-cm pitch DCA core. The lower end height of the control-rod inserted was changed from 505mm to 605mm (about 40 change in reactivity). Experimental results for the local power change were compared with calculations obtained from WIMS-D and CITATION codes. The following were concluded from the present study. (1)The maximum power change in outer layer pins of fuel cluster due to a small withdrawal of the control-rod occurs in the nearest fuel pin at the middle position of the axial displacement of the control-rod. (2)Outer layer fuel pin power after 100mm withdrawal of control-rod is (1.12
change in reactivity). Experimental results for the local power change were compared with calculations obtained from WIMS-D and CITATION codes. The following were concluded from the present study. (1)The maximum power change in outer layer pins of fuel cluster due to a small withdrawal of the control-rod occurs in the nearest fuel pin at the middle position of the axial displacement of the control-rod. (2)Outer layer fuel pin power after 100mm withdrawal of control-rod is (1.12 0.03) times in maximum as large as that before withdrawal. (3)Local pin power change due to withdrawal of the control-rod occurs mainly in the fuel pins of the nearest and the second nearest fuel clusters to the control-rod. Even in the nearest fuel cluster to the control-rod, power change in the back side fuel pin to the control-rod is very small below 2%. (4)Calculated value of maximum ratio for the outer layer fuel pin power due to 100mm withdrawal of the control-rod overestimate experimental one about 4%.
0.03) times in maximum as large as that before withdrawal. (3)Local pin power change due to withdrawal of the control-rod occurs mainly in the fuel pins of the nearest and the second nearest fuel clusters to the control-rod. Even in the nearest fuel cluster to the control-rod, power change in the back side fuel pin to the control-rod is very small below 2%. (4)Calculated value of maximum ratio for the outer layer fuel pin power due to 100mm withdrawal of the control-rod overestimate experimental one about 4%.
*; Fukumura, Nobuo*; *; Takemura, Morio*; *; *
PNC TN941 83-49, 57 Pages, 1983/04
Intra-cell thermal neutron flux distributions have been measured in 36-rod and 54-rod plutonium fuel clusters by mean of dysprosium foil activation method. Enrichments of PuO in PuO
in PuO -UO
-UO fuels used are 0.54 wt% for 36-rod cluster and 0.79 wt% for 54-rod cluster. In the central region of the Deuterium Critical Assembly, nine 36-rod or 54-rod fuel clusters were loaded and the surrounding region was occupied with 1.2 wt% UO
fuels used are 0.54 wt% for 36-rod cluster and 0.79 wt% for 54-rod cluster. In the central region of the Deuterium Critical Assembly, nine 36-rod or 54-rod fuel clusters were loaded and the surrounding region was occupied with 1.2 wt% UO fuel clusters arranged in square lattice arrays of 25.0 cm pitch. The measurements were made using air or light water as coolant in the pressure tube. The measurement uncertainty in the present experiment was
fuel clusters arranged in square lattice arrays of 25.0 cm pitch. The measurements were made using air or light water as coolant in the pressure tube. The measurement uncertainty in the present experiment was  2 % which was almost the same as that in the previous experiments on plutonium lattices. The dependence of thermal neutron distributions on the number of plutonium fuel rods in the cluster were made clear by the results of present experiments. The present experimental resolts were compared with three calculation code ; the METHUSELAH-II code, the WIMS-D code and the LAMP-DCA code system. The results relevant to averaged thermal neutron flux in the fuel cluster of the METHUSELAH-II code agreed with the experimental results to within 7 %. The results calculated by the WIMS-D agreed with the experimental results within 6 %. On the other hand, the calculated values by the LAMP-DCA were in good agreement with the experimental results within 5 %.
2 % which was almost the same as that in the previous experiments on plutonium lattices. The dependence of thermal neutron distributions on the number of plutonium fuel rods in the cluster were made clear by the results of present experiments. The present experimental resolts were compared with three calculation code ; the METHUSELAH-II code, the WIMS-D code and the LAMP-DCA code system. The results relevant to averaged thermal neutron flux in the fuel cluster of the METHUSELAH-II code agreed with the experimental results to within 7 %. The results calculated by the WIMS-D agreed with the experimental results within 6 %. On the other hand, the calculated values by the LAMP-DCA were in good agreement with the experimental results within 5 %.
*; *; *; *; *
PNC TN941 82-184, 143 Pages, 1982/07
Loss-of-coolant reactivity of all channels and that of central channel have been measured in two-region core partially loaded with nine 36-rod PuO -UO
-UO clusters. Lattice pitch is 25.0-cm throughout the core, and poison content in D
clusters. Lattice pitch is 25.0-cm throughout the core, and poison content in D O moderator is O or 3.2 ppm with
O moderator is O or 3.2 ppm with  B concentration. These 36-rod PuO
B concentration. These 36-rod PuO -UO
-UO clusters were placed in a central 3
clusters were placed in a central 3 3 channels of the core and the surrounding region was occupied with eighty-eight 28-rod 1.2 wt% enriched UO
3 channels of the core and the surrounding region was occupied with eighty-eight 28-rod 1.2 wt% enriched UO clusters. Enrichment of plutonium in the 36-rod PuO
clusters. Enrichment of plutonium in the 36-rod PuO -UO
-UO fuel is 0.54 wt% or 0.87 wt%, and the fissile content in total plutonium of both PuO
fuel is 0.54 wt% or 0.87 wt%, and the fissile content in total plutonium of both PuO -UO
-UO fuels is about 91 wt% (standard grade type Plutonium). Neutron flux distributions were also measured by
fuels is about 91 wt% (standard grade type Plutonium). Neutron flux distributions were also measured by  -counting of irradiated copper wire, in order to evaluate the change of neutron flux in the core before and after loss-of-coolant. Reactivities due to loss-of-coolant were obtained by integrating the level reactivity coefficient of moderator (
-counting of irradiated copper wire, in order to evaluate the change of neutron flux in the core before and after loss-of-coolant. Reactivities due to loss-of-coolant were obtained by integrating the level reactivity coefficient of moderator ( p/
p/ H) of the perturbed core between the critical levels at the non-voided core and at the perturbed core. Values of (
H) of the perturbed core between the critical levels at the non-voided core and at the perturbed core. Values of ( p/
p/ H) were obtained by converting doubling time of neutron flux due to small rise of moderator level (
H) were obtained by converting doubling time of neutron flux due to small rise of moderator level ( H) to small reactivity(
H) to small reactivity( p). Experimental result of loss-of-coolant reactivities (
p). Experimental result of loss-of-coolant reactivities (

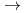 v) is tabled as below together with the ones of the core loaded with nine 28-rod PuO
v) is tabled as below together with the ones of the core loaded with nine 28-rod PuO -UO
-UO clusters and calculated values by WIMS-CITATION code. The measured
clusters and calculated values by WIMS-CITATION code. The measured 

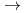 v were determined within 50 ¢ of uncertainty. If PuO
v were determined within 50 ¢ of uncertainty. If PuO -UO
-UO clusters were placed in the central 3
clusters were placed in the central 3  3 channels of the core, 36-rod PuO
3 channels of the core, 36-rod PuO -UO
-UO clusters is more effective in shifting the
clusters is more effective in shifting the 

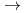 v to the negative side in comparison with 28-rod PuO
v to the negative side in comparison with 28-rod PuO -UO
-UO clusters ; the nine 36-rod PuO
clusters ; the nine 36-rod PuO -UO
-UO clusters makes the
clusters makes the 

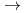 v ...
v ...
 -UO
-UO fuel clusters
fuel clustersFukumura, Nobuo*; *; *; *; *; *; Hachiya, Yuki*
PNC TN941 82-132, 54 Pages, 1982/06
Measurements and analysises of lattice parameters have been made by use of the 36-rod PuO -UO
-UO fuel clusters (0.54w/o PuO
fuel clusters (0.54w/o PuO -UO
-UO ) which are composed of the rods with the same diameters as the ones of Fugen type fuel rods. The nine 36-rod fuel clusters were loaded in the central region of the DCA eore with the square lattice of 25.0cm pitch and the surrounding region was occupied with eighty-eight 1.2w/o enriched UO
) which are composed of the rods with the same diameters as the ones of Fugen type fuel rods. The nine 36-rod fuel clusters were loaded in the central region of the DCA eore with the square lattice of 25.0cm pitch and the surrounding region was occupied with eighty-eight 1.2w/o enriched UO 28-rod fuel clusters. The experiments have been performed with (0% void)and without (100% void) H
28-rod fuel clusters. The experiments have been performed with (0% void)and without (100% void) H O coolant in the pressure tube. The lattice parameters such as
O coolant in the pressure tube. The lattice parameters such as  U resonance capture ratio (
U resonance capture ratio (
 ), the epicadmium fission ratio of
), the epicadmium fission ratio of  U or
U or  Pu (
Pu (
 or
or 
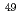 ), the fast fission ratio of
), the fast fission ratio of  U (
U (
 ) and the fission ratio of
) and the fission ratio of  Pu to
Pu to  U (
U (
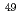
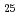 ) were obtained by the foil activation method using foils of plutonium and enriched, natural and depleted uranium. The analysises have been made by use of the sophisticated cell calculation code WIMS which is used for nuclear design of the commercial FUGEN. The results are shown in the table. Here, indices "cell" represent cell averaged values. It is concluded from these results that the code WIMS understimates the fission reaction rates of
) were obtained by the foil activation method using foils of plutonium and enriched, natural and depleted uranium. The analysises have been made by use of the sophisticated cell calculation code WIMS which is used for nuclear design of the commercial FUGEN. The results are shown in the table. Here, indices "cell" represent cell averaged values. It is concluded from these results that the code WIMS understimates the fission reaction rates of  U,
U,  U and
U and  Pu, and capture reaction rates of
Pu, and capture reaction rates of  U resonanee.
U resonanee.
*; *; *; *; Takemura, Morio*
PNC TN941 79-187, 62 Pages, 1979/11
Intra-cell thermal neutron flux distributions have been measured in plutonium fuel lattices at 20.0 cm and 28.3 cm pitch by means of dysprosium foil activation method. Enrichment of PuO in PuO
in PuO -UO
-UO fuel is 0.54 wt%. The measurements on 28.3 cm pitch lattice were made using air or H
fuel is 0.54 wt%. The measurements on 28.3 cm pitch lattice were made using air or H O as coolant. Those on 20.0 cm pitch lattice were made only using H
O as coolant. Those on 20.0 cm pitch lattice were made only using H O. The measurement uncertainty of
O. The measurement uncertainty of  2 % in the present experiment is almost the same as that in the previous experiments on plutonium lattices at 22.5 cm and 25.0 cm pitches. The dependence of thermal neutron flux distributions on lattice pitch were made clear by the results of present experiment and previously obtained 22.5 cm and 25.0 cm pitch experiment. The calculations by the code LAMP-DCA agree with the experiment better than those by the code NOAH-II.
2 % in the present experiment is almost the same as that in the previous experiments on plutonium lattices at 22.5 cm and 25.0 cm pitches. The dependence of thermal neutron flux distributions on lattice pitch were made clear by the results of present experiment and previously obtained 22.5 cm and 25.0 cm pitch experiment. The calculations by the code LAMP-DCA agree with the experiment better than those by the code NOAH-II.
*; *; *; *
PNC TN941 79-142, 41 Pages, 1979/08
Nuclear characteristics on a liquid poison tube have been studied by use of DCA. Reactivity worthes of the poison tube were measured as functions of 10B content in liquid and liquid poison level. Also, radial flux distributions around the poison tube and axial flux distribution in a fuel channel, D O moderator and poison tube were measured. The results of present experiment are summarized as follows. (1)Excess content of
O moderator and poison tube were measured. The results of present experiment are summarized as follows. (1)Excess content of  B beyond 800 ppm makes no increase in reactivity change. (2)Reactivity change in reference to poison level change in poison tube shows the S curve like the characteristics of control rod. (3)Change of liquid poison level gives a small change for the axial flux distribution in the center of fuel cluster. (4)The depression of thermal neutron flux around the poison tube with black poison remarkedly increases at about 2 cm distant from surface of poison tube. On the other hand, poison tube with gray poison makes small change in gross flux distribution at D
B beyond 800 ppm makes no increase in reactivity change. (2)Reactivity change in reference to poison level change in poison tube shows the S curve like the characteristics of control rod. (3)Change of liquid poison level gives a small change for the axial flux distribution in the center of fuel cluster. (4)The depression of thermal neutron flux around the poison tube with black poison remarkedly increases at about 2 cm distant from surface of poison tube. On the other hand, poison tube with gray poison makes small change in gross flux distribution at D O region.
O region.