Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Lee, O.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Umeda, Maki; Zollitsch, C. W.*; Elyasi, M.*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Saito, Eiji; Bauer, G. E. W.*; Kurebayashi, Hidekazu*
Physical Review Letters, 130(4), p.046703_1 - 046703_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Toyoda, Satoshi*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*
Hoshako, 35(3), p.200 - 206, 2022/05
The present status of spatiotemporal depth profiling analysis of the multilayer stacked film interface based on Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (APXPS) is presented. To begin with, depth profiles of the multilayer stacked film interfaces have been achieved by time-division Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved PhotoEmission Spectroscopy data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division angle resolved AP-XPS data including spatial resolution, which enables us to realize spatiotemporal depth profiles of the interfaces under reaction conditions such as oxidation and reduction. In addition, it is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 O
O with electrochemical Li
with electrochemical Li intercalation
intercalationMurase, Satoshi*; Yoshikawa, Yumi*; Fujiwara, Kosuke*; Fukada, Yukimasa*; Teranishi, Takashi*; Kano, Jun*; Fujii, Tatsuo*; Inada, Yasuhiro*; Katayama, Misaki*; Yoshii, Kenji; et al.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 162, p.110468_1 - 110468_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We report a trial of the valence control for mixed valence iron triangular oxide YbFe O
O in order to develop an effective technique to control the frustration of charges in strongly correlated electron systems. The electro-chemical doping of Li
in order to develop an effective technique to control the frustration of charges in strongly correlated electron systems. The electro-chemical doping of Li into YbFe
into YbFe O
O was examined on the cell type sample similar to the Li-ion secondary battery cell. Systematic change of the lattice constant, Fe-Fe and Fe-Yb distance were observed with Li doping. Maximum value of the doping was over 300 mAh/g. An EXAFS experiment indicated that Li positioned between Yb octahedron layer (U-layer) and Fe-bipyramidal layer (W-layer). However, detailed change of iron valence state of YbFe
was examined on the cell type sample similar to the Li-ion secondary battery cell. Systematic change of the lattice constant, Fe-Fe and Fe-Yb distance were observed with Li doping. Maximum value of the doping was over 300 mAh/g. An EXAFS experiment indicated that Li positioned between Yb octahedron layer (U-layer) and Fe-bipyramidal layer (W-layer). However, detailed change of iron valence state of YbFe O
O was not clearly observed because of the superimpose of the signal from iron metal nano particles in XANES observation. The results indicate that the electrochemical method might be one of the potential technique to control the frustration of charges in YbFe
was not clearly observed because of the superimpose of the signal from iron metal nano particles in XANES observation. The results indicate that the electrochemical method might be one of the potential technique to control the frustration of charges in YbFe O
O .
.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:97.1(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:262 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
 Cl in soil near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant
Cl in soil near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power PlantOta, Yuki*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Sasa, Kimikazu*; Takahashi, Tsutomu*; Matsunaka, Tetsuya*; Matsumura, Masumi*; Tosaki, Yuki*; Honda, Maki*; Hosoya, Seiji*; Takano, Kenta*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2018-002, p.99 - 102, 2019/02
no abstracts in English
Shimizu, Takeshi*; Wang, H.*; Tanifuji, Naoki*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Nakanishi, Koji*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Yoshikawa, Hirofumi*
Chemistry Letters, 47(5), p.678 - 681, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:33.47(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Yagmur, A.*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Ihara, Kazuki*; Ioka, Ikuo; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Ono, Madoka*; Endo, Junichi*; Kashiwagi, Kimiaki*; Nakashima, Tetsuya*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 109(24), p.243902_1 - 243902_4, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.8(Physics, Applied)Thermoelectric devices based on the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) were irradiated with gamma ( ) rays with the total dose of around 3
) rays with the total dose of around 3 10
10 Gy in order to investigate the
Gy in order to investigate the  -radiation resistance of the devices. To demonstrate this, Pt/Ni
-radiation resistance of the devices. To demonstrate this, Pt/Ni Zn
Zn Fe
Fe O
O /Glass and Pt/Bi
/Glass and Pt/Bi Y
Y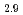 Fe
Fe O
O /Gd
/Gd Ga
Ga O
O SSE devices were used. We confirmed that the thermoelectric, magnetic, and structural properties of the SSE devices are not affected by the
SSE devices were used. We confirmed that the thermoelectric, magnetic, and structural properties of the SSE devices are not affected by the  -ray irradiation. This result demonstrates that SSE devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in high radiation environments.
-ray irradiation. This result demonstrates that SSE devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in high radiation environments.
Uchida, Kenichi*; Adachi, Hiroto; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Yorozu, Shinichi*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji*
Proceedings of the IEEE, 104(10), p.1946 - 1973, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:214 Percentile:99.2(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Saegusa, Jun; Tagawa, Akihiro; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Iijima, Kazuki; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Nakayama, Shinichi; Ishida, Junichiro
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 3(3), p.15-00609_1 - 15-00609_7, 2016/06
After the Fukushima nuclear accident, JAEA lead off demonstration tests to find out effective decontamination methods for various school facilities in Fukushima. It included (1) dose reduction measures at schoolyards, (2) purification of swimming pool water and (3) removal of surface contamination of playground equipments. Through these tests, they established practical methods suitable for each situation; (1) At school yards, dose rates were drastically reduced by removing topsoil which was then placed in trenches of 1 m deep; (2) For the purification of pool water, the flocculation-coagulation treatment was found to be effective for collecting radiocesium dissolved in the water; (3) Demonstration tests for playground equipments, such as horizontal bars and a sandbox wood frame, suggested that effectiveness of decontamination considerably varied depending on the material, paint or coating condition. This paper reviews these demonstrations.
Miyao, Tomoaki*; Miura, Akihiko; Kawane, Yusuke; Tamura, Jun; Nemoto, Yasuo; Ao, Hiroyuki*; Hayashi, Naoki; Oguri, Hidetomo; Ouchi, Nobuo; Mayama, Minoru*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1338 - 1341, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Nakashima, Yosuke*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoi, Katsuhiro*; Oki, Kensuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Hirata, Mafumi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Ikezoe, Ryuya*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 463, p.537 - 540, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:83.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Saegusa, Jun; Tagawa, Akihiro; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Iijima, Kazuki; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Nakayama, Shinichi; Ishida, Junichiro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
After the Fukushima nuclear accident, JAEA lead off demonstration tests to find out effective decontamination methods for various school facilities in Fukushima. It included (1) dose reduction measures at schoolyards, (2) purification of swimming pool water and (3) removal of surface contamination of playground equipments. Through these tests, they established practical methods suitable for each situation; (1) At school yards, dose rates were drastically reduced by removing topsoil which was then placed in trenches of 1 m deep; (2) For the purification of pool water, the flocculation-coagulation treatment was found to be effective for collecting radiocesium dissolved in the water; (3) Demonstration tests for playground equipments, such as horizontal bars and a sandbox wood frame, suggested that effectiveness of decontamination considerably varied depending on the material, paint or coating condition. This paper reviews these demonstrations.
Nakashima, Yosuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Yoshikawa, Masayuki*; Oki, Kensuke*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoi, Katsuhiro*; Hirata, Mafumi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Ikezoe, Ryuya*; et al.
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
Oshikawa, Takumi*; Funakoshi, Yoshihiko*; Imaoka, Hiroshi*; Yoshikawa, Kohei*; Maari, Yasutaka*; Iguchi, Masahide; Sakurai, Takeru; Nakahira, Masataka; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Nakajima, Hideo
Proceedings of 19th International Forgemasters Meeting (IFM 2014), p.254 - 259, 2014/09
ITER is a large-scale experiment that aims to demonstrate that it is possible to produce commercial energy from fusion. ITER Toroidal Field Coil Case (hereinafter referred to as "ITER TFCC") is one of the important components of ITER. The ITER TFCC materials are made of high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel and having various configurations. The ITER TFCC material which manufactured by JCFC has a complex configuration with heaver thickness than other materials. It is difficult to form near net shape to delivery configuration by ordinary open die forging method such as upset and stretching, because the ITER TFCC materials manufactured by JCFC have a complex configuration. Therefore ingot weight and lead time of machining increase when ITER TFCC materials are forged by ordinary open die forging method. Moreover, in order to get good attenuation at Ultrasonic examination, it is necessarily to make fine and uniform grain of the material. However, it is impossible to control grain size of austenitic stainless steel by heat treatment. The grain becomes fine and uniform by only forging process with suitable condition. Therefore, JCFC has studied suitable forging method to become near net shape to delivery configuration and also to get fine grain of center of the material. Based on these result, ITER TFCC materials were manufactured. This innovative forging process led to reduce the weight of ingot compared with general forging. And it had good Ultrasonic attenuation. It was confirmed that the results of material test and nondestructive examination satisfied the requirements of Japan domestic agency (hereinafter referred to as "JADA"). Moreover, the test coupons were taken from center of thick part of product and used for various tests. As the result of tests, it was confirmed that results of material test satisfied the requirements of JADA. It is clear that this innovative forging method is very suitable process for manufacturing of ITER TFCC materials.
Uchida, Kenichi*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; Murakami, Tomoo*; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(34), p.343202_1 - 343202_15, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:204 Percentile:84.49(Physics, Condensed Matter)Yoshikawa, Hideki; Iijima, Kazuki; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Shinichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.269 - 275, 2013/10
Following the release of radionuclides into the environment as a result of the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) had to develop an immediate and effective method of reducing the dose rate received by students in school facilities. A demonstration of a reducing method was carried out by JAEA at a junior high school ground and kindergarten yard in the center of Fukushima-city. Dose rates of the released radionuclides are largely controlled by the ground level contamination and accumulation of mainly cesium-137 ( Cs) and cesium-134 (
Cs) and cesium-134 ( Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5
Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5  Sv/h to 0.15
Sv/h to 0.15  Sv/h.
Sv/h.
Suzuki, Michitaka*; Yoshikawa, Mao*; Iimura, Kenji*; Satone, Hiroshi*; Ishii, Katsunori
Funtai Kogakkai-Shi, 50(6), p.405 - 409, 2013/06
The glass substrate is coated by the silica nanoparticle suspension using dipping or spin coat method and dried in an electric oven. The glass substrate surface is covered with nanoparticle thin layer and the transparent and tiny rugged surface can be produced on a substrate. It was experimentally confirmed to prevent dust adhesion by covering the surface of the glass substrate with nanoparticle. The adhesion force between particle and substrate is measured by the centrifugal method and the relation between the adhesion force and the surface roughness is discussed from experimental and theoretical point of view. The measured and calculated results by Van der Waals force show that adhesion force decreased with the increment of the surface roughness. From the results, nanoparticle coating is very effective to prevent the dust adhesion on the substrate and the various application of nanoparticle coating can be expected.
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Iijima, Kazuki; Zaima, Naoki; Munakata, Masahiro; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAEA-Review 2012-045, 129 Pages, 2013/01
This report shows the records of JAEA's investigation on dose rate reduction at the Fukushima University Junior High School and Kindergarten. The main outcomes are as follows. (1)  experiments were performed to investigate intrusion depth of radiocesium in the soil. Based on the experiment, we proposed a countermeasure to reduce air dose rates. (2) The action we proposed allowed dose rate reduction to about one tenth to one twentieth at playgrounds. (3) Follow-up monitoring was performed after one year, and shows no obvious evidence of recontamination at the playgrounds. (4) Decontamination of a tree was tested. Radiocesium was accumulated around the root. By removing the soil, the air dose rate at about one-meter distance from the tree was decreased.
experiments were performed to investigate intrusion depth of radiocesium in the soil. Based on the experiment, we proposed a countermeasure to reduce air dose rates. (2) The action we proposed allowed dose rate reduction to about one tenth to one twentieth at playgrounds. (3) Follow-up monitoring was performed after one year, and shows no obvious evidence of recontamination at the playgrounds. (4) Decontamination of a tree was tested. Radiocesium was accumulated around the root. By removing the soil, the air dose rate at about one-meter distance from the tree was decreased.