Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Wada, Motoi*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.392 - 395, 2023/11
Negative hydrogen (H ) ion sources which are used at high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as J-PARC or neutral beam injection system for plasma heating in the fusion devices such as ITER produce plasmas by using RF sources driving with the frequency of 1-2 MHz. We have shown that the H
) ion sources which are used at high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as J-PARC or neutral beam injection system for plasma heating in the fusion devices such as ITER produce plasmas by using RF sources driving with the frequency of 1-2 MHz. We have shown that the H beams extracted from the RF-driven H
beams extracted from the RF-driven H ion source with the frequency of several MHz have some fluctuations with the frequency of the fundamental and second harmonics. The reason is that the high plasma density is produced in the ion source with the low driving frequency. Therefore, we propose the driving RF frequency same as the RF sources with that of 324 MHz in the J-PARC linac, which is much higher than the ion plasma frequency, is used for producing the plasma to suppress the H
ion source with the frequency of several MHz have some fluctuations with the frequency of the fundamental and second harmonics. The reason is that the high plasma density is produced in the ion source with the low driving frequency. Therefore, we propose the driving RF frequency same as the RF sources with that of 324 MHz in the J-PARC linac, which is much higher than the ion plasma frequency, is used for producing the plasma to suppress the H beam fluctuations. As a first step, we performed a design of a matching circuit for the higher frequency driven H
beam fluctuations. As a first step, we performed a design of a matching circuit for the higher frequency driven H ion source. We present the background for decision of a new RF amplifier with much higher frequency and the design results.
ion source. We present the background for decision of a new RF amplifier with much higher frequency and the design results.
 Cs activity concentration in the aquatic insect
Cs activity concentration in the aquatic insect  (Tricoptera: Stenopsychidae) in the Ota River, Fukushima, Japan
(Tricoptera: Stenopsychidae) in the Ota River, Fukushima, JapanIshii, Yumiko*; Miura, Hikaru*; Jo, J.*; Tsuji, Hideki*; Saito, Rie; Koarai, Kazuma; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Urushidate, Tadayuki*; Nishikiori, Tatsuhiro*; Wada, Toshihiro*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 17(5), p.e0268629_1 - e0268629_17, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:40.21(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We investigated the variability in  Cs activity concentration in individual aquatic insects in detritivorous caddisfly (
Cs activity concentration in individual aquatic insects in detritivorous caddisfly ( ) and carnivorous dobsonfly (
) and carnivorous dobsonfly ( ) larvae from the Ota River, Fukushima. Caddisfly larvae showed sporadically higher radioactivity, whereas no such outliers were observed in dobsonfly larvae. Autoradiography and scanning electron microscopy analyses confirmed that these caddisfly larvae samples contained radiocesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs), which are insoluble Cs-bearing silicate glass particles. CsMPs were also found in potential food sources of caddisfly larvae, such as periphyton and drifting particulate organic matter, indicating that larvae may ingest CsMPs along with food particles of similar size. Although CsMPs distribution and uptake by organisms in freshwater ecosystems is relatively unknown, our study demonstrates that CsMPs can be taken up by aquatic insects.
) larvae from the Ota River, Fukushima. Caddisfly larvae showed sporadically higher radioactivity, whereas no such outliers were observed in dobsonfly larvae. Autoradiography and scanning electron microscopy analyses confirmed that these caddisfly larvae samples contained radiocesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs), which are insoluble Cs-bearing silicate glass particles. CsMPs were also found in potential food sources of caddisfly larvae, such as periphyton and drifting particulate organic matter, indicating that larvae may ingest CsMPs along with food particles of similar size. Although CsMPs distribution and uptake by organisms in freshwater ecosystems is relatively unknown, our study demonstrates that CsMPs can be taken up by aquatic insects.
 beam extracted from an RF-driven high-intensity H
beam extracted from an RF-driven high-intensity H ion source
ion sourceShinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Wada, Motoi*
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.230 - 233, 2021/10
In most proton accelerator facilities such as J-PARC, SNS, CERN, a H ion source equipped with a 2-MHz rf driver for plasma generation produces H
ion source equipped with a 2-MHz rf driver for plasma generation produces H beams. We have reported H
beams. We have reported H beam characteristics extracted from the J-PARC rf-driven high-intensity H
beam characteristics extracted from the J-PARC rf-driven high-intensity H ion source. We have been developing an emittance measurement apparatus equipped with a highly time-resolved data acquisition system in order to observe fluctuation of the beam emittance in association with the frequency of the rf driver. By using this apparatus, we found that the beam emittance is fluctuated with the frequency with the rf driver and higher harmonics. We will show some obtained results of the emittance fluctuation.
ion source. We have been developing an emittance measurement apparatus equipped with a highly time-resolved data acquisition system in order to observe fluctuation of the beam emittance in association with the frequency of the rf driver. By using this apparatus, we found that the beam emittance is fluctuated with the frequency with the rf driver and higher harmonics. We will show some obtained results of the emittance fluctuation.
Shibata, Takanori*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Wada, Motoi*; Oguri, Hidetomo; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Nammo, Kesao*
AIP Conference Proceedings 2373, p.050002_1 - 050002_9, 2021/08
Oscillation of emittance and Twiss parameters in the negative ion beam from the J-PARC 2-MHz RF ion source is measured by applications of a double-slit emittance monitor located at the RFQ (Radio Frequency Quadrupole) entrance. The emittance monitor is equipped with a newly-developed 60 MS/s data acquisition system, so that beam current oscillation in a few MHz can be observed with enough time resolution. From the measurement, it is shown that the beam phase space consists of (1) a DC component in the beam core, (2) a 2-MHz oscillating component which takes place both in the beam core and the halo and (3) a doubled RF frequency (4 MHz) oscillation which slightly exists in the beam halo. The major component is the 2-MHz component, which resultantly decides the beam emittance oscillation frequency. A typical value of the beam emittance in the present experiment is 0.34  mm-mrad, while the amplitude of the 2 MHz oscillation is around 0.04
mm-mrad, while the amplitude of the 2 MHz oscillation is around 0.04  mm-mrad. The results indicate that the high-frequency oscillation component occupying about ten-percent of the beam from the RF source travels a few meters passing through a magnetic lens focusing system.
mm-mrad. The results indicate that the high-frequency oscillation component occupying about ten-percent of the beam from the RF source travels a few meters passing through a magnetic lens focusing system.
 ion source
ion sourceWada, Motoi*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Sasao, Mamiko*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(1), p.013330_1 - 013330_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.84(Instruments & Instrumentation)The ions are extracted from an ion source through a plasma sheath where a low frequency electromagnetic induction drives transport of charged particles including the target ions. High frequency alternating current commonly excites plasmas in sources for negative hydrogen (H ) ions at a frequency in the MHz range. A high-speed beam current monitor system coupled to a narrow entrance slit enabled the investigation of the special distribution of the AC component intensity of the H
) ions at a frequency in the MHz range. A high-speed beam current monitor system coupled to a narrow entrance slit enabled the investigation of the special distribution of the AC component intensity of the H ion beam extracted from an ion source driven by a 2 MHz radio frequency (RF) power. The distribution showed a smaller oscillation of the beam at the center.
ion beam extracted from an ion source driven by a 2 MHz radio frequency (RF) power. The distribution showed a smaller oscillation of the beam at the center.
 ion source
ion sourceShinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Miura, Akihiko; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Wada, Motoi*
AIP Conference Proceedings 2011, p.080016_1 - 080016_3, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:91.55(Physics, Applied)Kobata, Masaaki; Okane, Tetsuo; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Eriko; Owada, Kenji; Kobayashi, Keisuke*; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 498, p.387 - 394, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:86.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, for the understandings of Cesium (Cs) adsorption behavior on structure materials in severe accidents at a light water nuclear reactor, the chemical state of Cs and its distribution on the surface of SUS304 stainless steel (SS) with different Si concentration were investigated by hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) and scanning electron microscope / energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM/EDX). As a result, it was found that Cs is selectively adsorbed at the site where Si distributes with high concentration. CsFeSiO is a dominant Cs products in the case of low Si content, mainly formed, while Cs
is a dominant Cs products in the case of low Si content, mainly formed, while Cs Si
Si O
O and Cs
and Cs Si
Si O
O are formed in addition to CsFeSiO
are formed in addition to CsFeSiO in the case of high Si content. The chemical forms of the Cs compounds produced in the adsorption process on the SS surface has a close correlation with the concentration and chemical states of Si originally included in SS.
in the case of high Si content. The chemical forms of the Cs compounds produced in the adsorption process on the SS surface has a close correlation with the concentration and chemical states of Si originally included in SS.
 ion source upon the extracted beam
ion source upon the extracted beamShinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Wada, Motoi*
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.648 - 650, 2017/12
In J-PARC, peak H current of several tens mA is extracted from an ion source driven by a solid-state rf amplifier with the frequency of 2 MHz for production of a cesiated hydrogen plasma. In case of the rf-driven ion source for producing the high-intensity H
current of several tens mA is extracted from an ion source driven by a solid-state rf amplifier with the frequency of 2 MHz for production of a cesiated hydrogen plasma. In case of the rf-driven ion source for producing the high-intensity H current, the plasma density in the source chamber is so high that the ion sheath around the beam extraction area can follow the rf oscillation. The H
current, the plasma density in the source chamber is so high that the ion sheath around the beam extraction area can follow the rf oscillation. The H beam current fluctuation as large as approximately 1 mA was observed at the average beam current of 44 mA measured by a Faraday cup installed downstream of the ion source. The beam exhibited some fluctuation to the transverse motion as well. To further clarify this high frequency oscillation of the beam extraction sheath, we propose a measurement system using a time-resolved and highly sensitive emittance monitor in order to observe the real-time beam fluctuation in the phase space.
beam current fluctuation as large as approximately 1 mA was observed at the average beam current of 44 mA measured by a Faraday cup installed downstream of the ion source. The beam exhibited some fluctuation to the transverse motion as well. To further clarify this high frequency oscillation of the beam extraction sheath, we propose a measurement system using a time-resolved and highly sensitive emittance monitor in order to observe the real-time beam fluctuation in the phase space.
Unno, Masayoshi*; Sugishima, Masakazu*; Wada, Kei*; Hagiwara, Yoshinori*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro; Fukuyama, Keiichi*
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 57(5), p.297 - 303, 2015/10
Bilin compounds are fundamentally important for oxygenic photosynthetic organisms, because they are utilized as pigments for photosynthesis (phycobilins) and photoreceptors (phytochromobilin). Phycocyanobilin (PCB), a phycobilin, comprises the chromophore of algal phytochromes and the core phycobiliprotein antennae of cyanobacteria and red algae. PCB is biosynthesized by a member of the ferredoxin-dependent bilin reductase family, phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA). In the present study, we determined the neutron crystal structure of PcyA in complex with its substrate biliverdin (BV). This neutron structure revealed the protonation state of BV and the surrounding residues. We found that two forms of BV, neutral BV and protonated BVH , were coupled with the two conformation/protonation states of the essential residue Asp105. Further, His88 and His74 near BV were singly protonated and were connected with an intervening hydronium ion. Neutron analysis also revealed how X-ray irradiation of the PcyA-BV crystal altered the structure of the PcyA-BV complex.
, were coupled with the two conformation/protonation states of the essential residue Asp105. Further, His88 and His74 near BV were singly protonated and were connected with an intervening hydronium ion. Neutron analysis also revealed how X-ray irradiation of the PcyA-BV crystal altered the structure of the PcyA-BV complex.
Nakajima, Kyo*; Teramoto, Takahiro*; Akagi, Hiroshi; Fujikawa, Takashi*; Majima, Takuya*; Minemoto, Shinichiro*; Ogawa, Kanade*; Sakai, Hirofumi*; Togashi, Tadashi*; Tono, Kensuke*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 5, p.14065_1 - 14065_11, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:83.96(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We report on the measurement of deep inner-shell 2p X-ray photoelectron diffraction (XPD) patterns from laser-aligned I molecules using X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) pulses. The XPD patterns of the I
molecules using X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) pulses. The XPD patterns of the I molecules, aligned parallel to the polarization vector of the XFEL, were well matched with our theoretical calculations. Further, we propose a criterion for applying our molecular-structure-determination methodology to the experimental XPD data. In turn, we have demonstrated that this approach is a significant step toward the time-resolved imaging of molecular structures.
molecules, aligned parallel to the polarization vector of the XFEL, were well matched with our theoretical calculations. Further, we propose a criterion for applying our molecular-structure-determination methodology to the experimental XPD data. In turn, we have demonstrated that this approach is a significant step toward the time-resolved imaging of molecular structures.
Unno, Masayoshi*; Ishikawa, Kumiko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro; Hagiwara, Yoshinori*; Sugishima, Masakazu*; Wada, Kei*; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137(16), p.5452 - 5460, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:64.15(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Phycocyanobilin, a light-harvesting and photoreceptor pigment in higher plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, is synthesized from biliverdin IX (BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH
(BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH , a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N
, a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H
was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H O
O . These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
. These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Wada, Motoi*; Nishida, Tomoaki*; Demura, Yasuhiro*; Sasaki, Daichi*; Tsumori, Katsuyoshi*; Nishiura, Masaki*; Kaneko, Osamu*; Kisaki, Masashi*; Sasao, Mamiko*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1390, p.675 - 683, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.19(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Shinto, Katsuhiro; Wada, Motoi*; Kaneko, Osamu*; Tsumori, Katsuyoshi*; Nishiura, Masaki*; Sasao, Mamiko*; Kisaki, Masashi*
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.999 - 1001, 2010/05
We propose a negative ion beam probe system as a new scheme to diagnose beam profile of high power positive ion beams. Two RF linacs of IFMIF have to drive the neutron source by providing continuous-wave (CW) positive deuterium ion beams with the intensity of 125 mA each at the beam energy of 40 MeV. During the CW beam operations, the extreme intensity of the beam and the severe radiation levels make the beam diagnostics with conventional techniques in the transport lines terribly difficult. A beam of negative ions liable to lose the additional electron at the occasion of impact with a high energy particle can work as a probe to measure the positive ion beam profile. On possible configuration to achieve high intensity beam profile measurement is to inject a negative ion probe beam into the target beam perpendicularly, and measure the attenuation of the negative ion beam by beam-beam interaction at each position. We have started an experimental study for the proof-of-principle of the new beam profile monitoring system. The paper presents the status quo of this beam profile monitor system development and the prospects to apply the system to the IFMIF beam line controls.

Miyazawa, Yutaka*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Negishi, Hiroshi*; Kobayashi, Akie*; Kaneyasu, Tomoko*; Oba, Atsushi*; Morohashi, Keita*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 49(4), p.373 - 379, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:63.75(Biology)We examined the role of root cap and elongation zone cells in root hydrotropism using heavy-ion and laser microbeam. Heavy-ion microbeam irradiation of the elongation zone, but not that of the columella cells, significantly and temporary suppressed the development of hydrotropic curvature. However, laser ablation confirmed that columella cells are indispensable for hydrotropism. Systemic heavy-ion broad-beam irradiation suppressed  expression of
expression of 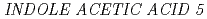 gene, but not
gene, but not 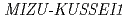 gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that
gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that 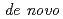 gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
 using heavy-ion microbeam
using heavy-ion microbeamMiyazawa, Yutaka*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Negishi, Hiroshi*; Kobayashi, Akie*; Kaneyasu, Tomoko*; Oba, Atsushi*; Morohashi, Keita*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 116, 2008/03
We examined the role of root cap and elongation zone cells in root hydrotropism of  using heavy ion and laser microbeam. Heavy ion microbeam irradiation of the elongation zone, but not that of the columella cells, significantly and temporarily suppressed the development of hydrotropic curvature. However, laser ablation confirmed that columella cells are indispensable for hydrotropism. Systemic heavy ion broad beam irradiation suppressed de novo expression of INDOLE ACETIC ACID 5 gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that de novo gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
using heavy ion and laser microbeam. Heavy ion microbeam irradiation of the elongation zone, but not that of the columella cells, significantly and temporarily suppressed the development of hydrotropic curvature. However, laser ablation confirmed that columella cells are indispensable for hydrotropism. Systemic heavy ion broad beam irradiation suppressed de novo expression of INDOLE ACETIC ACID 5 gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that de novo gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
 Ru
Ru O
O thin films
thin filmsTerai, Kota*; Yoshii, Kenji; Takeda, Yukiharu; Fujimori, Shinichi; Saito, Yuji; Owada, Kenji; Inami, Toshiya; Okane, Tetsuo; Arita, Masashi*; Shimada, Kenya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 77(11), p.115128_1 - 115128_6, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:54.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Suzuki, Kenji*; Wada, Kunihiko*; Matsubara, Hideaki*; Shobu, Takahisa; Kawamura, Masashi*; Tanaka, Keisuke*
Zairyo, 56(7), p.588 - 593, 2007/07
The Ni-based superalloy IN738LC was used as the substrate material, and CoNiCrAlY powder was pressureless plasma-sprayed on the substrate as the bond coating. Zirconia was coated as the top coating by the electron beam-physical vapor deposition (EV-PVD) method. In the EB-PVD process, the specimens were kept at 1223 K and rotated with 5 rpm, 10 rpm and 20 rpm. According to the microscopic observation and the result of the pole figures, the top coatings had a columnar structure, which was made by the piling up of (111) planes. The cross section of the column had a diamond shape, and its diagonal was parallel to the rotation axis. The residual stress on the surface of the top coatings was evaluated by the X-ray diffraction method. Each diffraction profile was separated into the 133 and the 331 peak, and the residual stress was measured by the sin
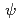 method. The measured residual stresses were -76.6 MPa for 5 rpm, -63.0 MPa for 10 rpm and -25.1 MPa for 20 rpm.
method. The measured residual stresses were -76.6 MPa for 5 rpm, -63.0 MPa for 10 rpm and -25.1 MPa for 20 rpm.
 Ru
Ru O
O thin films
thin filmsTerai, Kota; Yoshii, Kenji; Takeda, Yukiharu; Fujimori, Shinichi; Saito, Yuji; Owada, Kenji; Inami, Toshiya; Okane, Tetsuo; Arita, Masashi*; Shimada, Kenya*; et al.
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 310(2, Part2), p.1070 - 1072, 2007/03
We have studied the electronic and magnetic properties of epitaxially grown CaMn Ru
Ru O
O (x = 1.0, 0.5) thin films by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HXPES). The XMCD studies indicated that the spin moments of Mn and Ru are aligned in the opposite directions. The HXPES spectra indicated the Ru 4d states at around the Fermi edge (E
(x = 1.0, 0.5) thin films by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HXPES). The XMCD studies indicated that the spin moments of Mn and Ru are aligned in the opposite directions. The HXPES spectra indicated the Ru 4d states at around the Fermi edge (E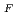 ) and the Mn 3d states below E
) and the Mn 3d states below E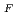 . From these results, we propose that the localized Mn 3d t
. From these results, we propose that the localized Mn 3d t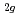 states and the itinerant Ru 4d t
states and the itinerant Ru 4d t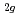 band are antiferromagnetically coupled and give rise to ferromagnetism, in analogy with the mechanism proposed for the double perovskite oxides such as Sr
band are antiferromagnetically coupled and give rise to ferromagnetism, in analogy with the mechanism proposed for the double perovskite oxides such as Sr FeMoO
FeMoO .
.
Miyazawa, Yutaka*; Negishi, Hiroshi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Akie*; Kaneyasu, Tomoko*; Oba, Atsushi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 119, 2007/02
 -phytosiderophore and as Fe
-phytosiderophore and as Fe
Ishimaru, Yasuhiro*; Suzuki, Motofumi*; Tsukamoto, Takashi*; Suzuki, Kazumasa*; Nakazono, Mikio*; Kobayashi, Takanori*; Wada, Yasuaki*; Watanabe, Satoshi; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Takahashi, Michiko*; et al.
Plant Journal, 45(3), p.335 - 346, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:549 Percentile:99.64(Plant Sciences)