Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Otani, Kyohei; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Materials Transactions, 62(6), p.763 - 769, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, the iron rust layer formed on the low alloy steel under air-solution alternating conditions was investigated by cross-sectional observation and analysis, and the mechanism of the accelerated corrosion of the steel under alternating conditions was clarified. The observations and analysis showed that the multilayered iron rust layer composed of the red rust layer (FeOOH), rust crust layer (Fe O
O ), inner crystal (Fe
), inner crystal (Fe O
O ), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multilayered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of dissolved oxygen under alternating conditions. This acceleration is the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel under alternating conditions was accelerated.
), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multilayered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of dissolved oxygen under alternating conditions. This acceleration is the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel under alternating conditions was accelerated.
Tsukada, Takashi; Soma, Yasutaka
Hozengaku, 19(4), p.37 - 44, 2021/01
Corrosion Cracking phenomena in JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor) the first Japanese Light Water Reactor is reviewed. This review describes two major cracking failure. The first was found during inspection in 1966 as the cracking failure on weld-overlay cladding at the inner wall of the top head. A series of analysis showed that some of the cracks reached the base metal across the weld boundaries and further penetrated into the vessel wall. Significant depletion of ferrite content was detected in manually welded part considered to assisted the cracking. These inspection result in improvement of the welding procedure and no similar failures have been reported in Japanese reactor. This mode of failure gave rise to a new research field studying the corrosion fatigue behavior of low alloy steel because of importance to assess pressure boundary of the reactor. The experiment of JPDR also contributed to the establishment of international cooperation for studying EAC (environmentally assisted cracking). The second failure was found in 1972 near the welded part between stainless piping and safe end. The extensive research concluded that this failure was caused by Stress Corrosion Cracking.
Ikebe, Yurie*; Oshima, Masumi*; Bamba, Shigeru*; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Toyoshima, Atsushi*; Bi, C.*; Seto, Hirofumi*; Amano, Hikaru*; et al.
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 164, p.109106_1 - 109106_7, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.28(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) is a radiotherapy for the treatment of intractable cancer. In BNCT precise determination of  B concentration in whole blood sample before neutron irradiation is crucial for control of the neutron irradiation time and the neutron dosimetry. We have applied the Charged Particle Activation Analysis (CPAA) to non-destructive and accurate determination of
B concentration in whole blood sample before neutron irradiation is crucial for control of the neutron irradiation time and the neutron dosimetry. We have applied the Charged Particle Activation Analysis (CPAA) to non-destructive and accurate determination of  B concentration in whole blood sample. The experiment was performed at JAEA Tandem Accelerator using an 8 MeV proton beam. The 478 keV
B concentration in whole blood sample. The experiment was performed at JAEA Tandem Accelerator using an 8 MeV proton beam. The 478 keV  ray of
ray of  Be produced in the
Be produced in the  B(p,
B(p, )
) Be reaction was used to quantify the
Be reaction was used to quantify the  B, and
B, and  rays of
rays of  Co originating from the reaction with Fe in blood was used to normalize the
Co originating from the reaction with Fe in blood was used to normalize the  -ray intensity. The results demonstrated that the present CPAA method can be applied to the determination of the
-ray intensity. The results demonstrated that the present CPAA method can be applied to the determination of the  B concentration in the blood sample.
B concentration in the blood sample.
Otani, Kyohei; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 69(9), p.246 - 252, 2020/09
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of artificial sea water concentration on the corrosion rate of carbon steel under air/solution alternating condition, and to clarify the corrosion mechanism of carbon steel that changes with artificial seawater concentration. Mass measurements showed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel in the alternating condition accelerates with increasing concentration in the concentration region between deionized water to 200 times diluted artificial seawater (ASW), and the corrosion rate decreases with increasing concentration in the concentration region between 20 times diluted ASW to undiluted ASW. It can be considered that the reason why the carbon steel corrosion was suppressed in highly concentrated artificial seawater would Mg ions and Ca ions in the artificial seawater precipitate and cover on the surface due to the increase in pH near the surface by oxygen reduction reaction.
 1 surfaces studied using core-level X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
1 surfaces studied using core-level X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyKakiuchi, Takuhiro*; Yamasaki, Hideki*; Tsukada, Chie*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Surface Science, 693, p.121551_1 - 121551_8, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19.68(Chemistry, Physical)We investigated the initial oxidation of ultrathin hafnium (Hf) film on Si(100)-2 1 using photoelectron spectroscopy. Metallic Hf rapidly oxidized, transforming into hafnium dioxide (HfO
1 using photoelectron spectroscopy. Metallic Hf rapidly oxidized, transforming into hafnium dioxide (HfO ) and its suboxides. The other HfSi component at the interface was nearly unreactive with O
) and its suboxides. The other HfSi component at the interface was nearly unreactive with O molecules. These facts suggest that the metallic Hf component plays a vital role in the initial oxidation of the ultrathin Hf/Si(100) film. After annealing from 873 K to 973 K, the Hf suboxides in low ionic valences progressed into fully oxidized HfO
molecules. These facts suggest that the metallic Hf component plays a vital role in the initial oxidation of the ultrathin Hf/Si(100) film. After annealing from 873 K to 973 K, the Hf suboxides in low ionic valences progressed into fully oxidized HfO . Once the annealing temperature reached c.a.1073 K, oxygen atoms were entirely removed from the ultrathin HfO
. Once the annealing temperature reached c.a.1073 K, oxygen atoms were entirely removed from the ultrathin HfO /Si(100) film containing SiO
/Si(100) film containing SiO at the interface. Simultaneously, ultrathin HfO
at the interface. Simultaneously, ultrathin HfO layers changed into islands of Hf disilicide (
layers changed into islands of Hf disilicide (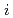 -HfSi
-HfSi ) on a bare Si(100)-2
) on a bare Si(100)-2 1 surface. The
1 surface. The 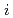 -HfSi
-HfSi component showed slight reactivity with O
component showed slight reactivity with O molecules at 298 K. In contrast to the initial oxidation of clean Si(100)-2
molecules at 298 K. In contrast to the initial oxidation of clean Si(100)-2 1 surface, the dangling bonds on bare Si(100)-2
1 surface, the dangling bonds on bare Si(100)-2 1 surface among
1 surface among 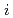 -HfSi
-HfSi oxidized preferentially.
oxidized preferentially.
Shoji, Eita*; Isogai, Shosei*; Suzuki, Rikuto*; Kubo, Masaki*; Tsukada, Takao*; Kai, Tetsuya; Shinohara, Takenao; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 175, p.29 - 32, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.21(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Oshima, Masumi*; Yamaguchi, Yurie*; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Goto, Jun*; Bamba, Shigeru*; Bi, C.*; Morimoto, Takao*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.866 - 872, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sensitivity of charged particle activation analysis with 8 MeV proton beam was studied for determination of 35 long-lived radioactive nuclides. Reaction cross sections for those nuclides were estimated with ALICE-91 code and isomer yield ratios were estimated from those of neighboring isotopes by taking into account their spins and parities. It was found that the proposed charged particle activation analysis should show high sensitivity for the determination of several hardly measurable nuclides with long half-lives such as  Cs,
Cs,  Pu,
Pu,  I,
I,  Sn,
Sn,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd,
Pd,  U,
U,  Cm, and
Cm, and  Np.
Np.
Otani, Kyohei; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(8), p.205 - 211, 2019/08
In the present study, the iron rust layer formed on the low ally steel in air-solution alternating condition was investigated by cross-sectional observation and analysis, and the mechanism of accelerated corrosion of the steel in the alternating condition was clarified. Observation and analysis showed that the multi-layered iron rust layer composed of red rust layer (FeOOH), rust crust layer (Fe O
O ), inner crystal (Fe
), inner crystal (Fe O
O ), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multi-layered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of the steel in the alternating condition. This acceleration would be the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel in the alternating condition was accelerated.
), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multi-layered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of the steel in the alternating condition. This acceleration would be the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel in the alternating condition was accelerated.
 decomposition on Si(110)
decomposition on Si(110)Yano, Masahiro; Uozumi, Yuki*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito; Tsukada, Chie*; Yoshida, Hikaru*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 16, p.370 - 374, 2018/08
 reduction reaction region at void periphery on Si(110)
reduction reaction region at void periphery on Si(110)Yano, Masahiro; Uozumi, Yuki*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Tsukada, Chie*; Yoshida, Hikaru*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Asaoka, Hidehito
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(8S1), p.08NB13_1 - 08NB13_4, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.42(Physics, Applied) and Br
and Br and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steel
and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steelHata, Kuniki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Tsukada, Takashi; Iwase, Akihiro*
Proceedings of Symposium on Water Chemistry and Corrosion in Nuclear Power Plants in Asia 2017 (AWC 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.304 - 314, 2017/09
A model simulation of  radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br
radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H
played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H O
O , was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl
, was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl +
+  OH
OH  ClOH
ClOH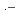 , ClOH
, ClOH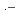
 Cl
Cl +
+  OH, and ClOH
OH, and ClOH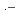 + H
+ H
 Cl
Cl + H
+ H O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl
O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl . An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H
. An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H O
O produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl
produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl and Br
and Br . However, at high pH values (
. However, at high pH values ( 12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H
12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H O
O was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
Fukui, Toshiki*; Maki, Takashi*; Miura, Nobuyuki; Tsukada, Takeshi*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(2), p.169 - 173, 2016/12
The basic research programs for the next generation vitrification technology, which are commissioned project from Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, have been implemented from 2014 until 2018 for developing the advanced vitrification technology of low level wastes and high level liquid wastes.
Hata, Kuniki; Sato, Tomonori; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Hanawa, Satoshi; Kasahara, Shigeki; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(8), p.1183 - 1191, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:49.29(Nuclear Science & Technology) radiolysis of sodium chloride solutions containing a small amount of bromide ion
radiolysis of sodium chloride solutions containing a small amount of bromide ionHata, Kuniki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Tsukada, Takashi
Nuclear Technology, 193(3), p.434 - 443, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:77.16(Nuclear Science & Technology) Nb and
Nb and  Ta for chemical studies of element 105, Db, using the GARIS gas-jet system
Ta for chemical studies of element 105, Db, using the GARIS gas-jet systemHuang, M.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Murakami, Masashi*; Asai, Masato; Kaji, Daiya*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Kikutani, Yuki*; Komori, Yukiko*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 304(2), p.845 - 849, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.85(Chemistry, Analytical)A technique to utilize radioisotopes of Nb and Ta was developed for chemical studies of element 105, Db, by coupling a gas-jet transport system to the RIKEN gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS). The short-lived  Nb and
Nb and  Ta were produced with nuclear reactions using a
Ta were produced with nuclear reactions using a  F beam whose energy was the same as that to produce
F beam whose energy was the same as that to produce  Db. Then, they were separated with GARIS and extracted to a chemistry laboratory with the gas-jet transport system. By changing only magnetic field of GARIS and inserting an energy degrader and a shutter for recoil ions, we could deliver the
Db. Then, they were separated with GARIS and extracted to a chemistry laboratory with the gas-jet transport system. By changing only magnetic field of GARIS and inserting an energy degrader and a shutter for recoil ions, we could deliver the  Nb and
Nb and  Ta to a chemistry device for
Ta to a chemistry device for  Db without changing other experimental conditions.
Db without changing other experimental conditions.
Komatsu, Atsushi; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2015/05
Effect of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide on corrosion rate of carbon steel in diluted artificial seawater was investigated by electrochemical methods. Diffusion coefficient and thickness of diffusion layer for oxygen and hydrogen peroxide were measured to estimate the diffusion limiting current density. Corrosion tests of carbon steel were also conducted in diluted artificial seawater containing oxygen and/or hydrogen peroxide at 323K. The diffusion coefficient of hydrogen peroxide was about 0.8 times lower than that of oxygen, and the thickness of diffusion layer was almost equivalent between oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Diffusion limiting current density of hydrogen peroxide was estimated to be 0.4 times lower than that of oxygen in the same concentration at 323K. Plot of corrosion rate with the addition of concentration of oxygen and 0.4 times concentration of hydrogen peroxide showed good correlation.
 radiolysis on pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater
radiolysis on pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawaterMotooka, Takafumi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Tsukada, Takashi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 18, 2015/03
The effect of changes in water by  -ray irradiation on the pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater was investigated. Surface analysis and electrochemical test were conducted. They showed that the hydrogen peroxide produced by
-ray irradiation on the pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater was investigated. Surface analysis and electrochemical test were conducted. They showed that the hydrogen peroxide produced by  irradiation forms a passive film and the passive film is resistant to the pit initiation.
irradiation forms a passive film and the passive film is resistant to the pit initiation.
Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Motooka, Takafumi; Tsukada, Takashi
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 22, 2015/03
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants experienced seawater injection into the cores and spent fuel pools as an emergent measure for a short period after the accident. The injected seawater was exposed to radiation, and radiolytic species were produced. Especially, hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) is known as an oxidant which affects corrosion of materials. In order to identify the important factor which results in the high concentration of H
) is known as an oxidant which affects corrosion of materials. In order to identify the important factor which results in the high concentration of H O
O in seawater radiolysis, the concentrations of H
in seawater radiolysis, the concentrations of H O
O in
in  -irradiated artificial seawater was measured and compared with the result of radiolysis calculation. Solutions containing some constituents of seawater were also measured to identify which ion affects H
-irradiated artificial seawater was measured and compared with the result of radiolysis calculation. Solutions containing some constituents of seawater were also measured to identify which ion affects H O
O production of seawater radiolysis. The experimental results showed that the H
production of seawater radiolysis. The experimental results showed that the H O
O production from seawater radiolysis is mainly attributed to reactions of Cl
production from seawater radiolysis is mainly attributed to reactions of Cl and Br
and Br in water radiolysis, though many kinds of ions are dissolved in seawater.
in water radiolysis, though many kinds of ions are dissolved in seawater.
Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Tsukada, Takashi; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(3), p.91 - 97, 2015/03
In the boiling water reactors (BWRs), reactor cooling water is maintained in high purity condition by controlling of a deionizing and deaerating apparatus, however H O
O contains by water radiolysis. In order to determine the corrosive condition in high-temperature pure water containing H
contains by water radiolysis. In order to determine the corrosive condition in high-temperature pure water containing H O
O , the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was performed in this study. To simulate BWR condition precisely, the measurements were performed without any electrolyte. The obtained impedance responses were changed with the H
, the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was performed in this study. To simulate BWR condition precisely, the measurements were performed without any electrolyte. The obtained impedance responses were changed with the H O
O concentration. The solution resistance and polarization resistance were determined by the equivalent circuit analyses. The conductivity was determined by the obtained solution resistance and the calculation of the current flow between the working electrode and the counter electrode by the 3-demensional finite element method. The value, 4.4
concentration. The solution resistance and polarization resistance were determined by the equivalent circuit analyses. The conductivity was determined by the obtained solution resistance and the calculation of the current flow between the working electrode and the counter electrode by the 3-demensional finite element method. The value, 4.4 10
10 S/cm, was obtained as the conductivity of the pure water at 288
S/cm, was obtained as the conductivity of the pure water at 288 C. The reciprocal of the obtained polarization resistance increased in proportion with H
C. The reciprocal of the obtained polarization resistance increased in proportion with H O
O concentration. This indicates that the corrosion current density was determined by the diffusion limiting current density of H
concentration. This indicates that the corrosion current density was determined by the diffusion limiting current density of H O
O . The diffusion coefficient of H
. The diffusion coefficient of H O
O at 288
at 288 C was determined using the relationship between the reciprocal of the polarization resistance and H
C was determined using the relationship between the reciprocal of the polarization resistance and H O
O concentration. The obtained diffusion coefficient was 1.5
concentration. The obtained diffusion coefficient was 1.5 10
10 cm
cm /s. This is about twice larger than that of the reported value of O
/s. This is about twice larger than that of the reported value of O .
.
 -ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral water
-ray irradiation on corrosion of low alloy steel in neutral waterYamamoto, Masahiro; Nakano, Junichi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Sato, Tomonori; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 19th International Corrosion Congress (19th ICC) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2014/11
Corrosion protection of RPV and PCV is an important issue for the long term maintenance until the end of the decommissioning procedures. One of the uncertain factors for the issue is an effect of radioactivity on corrosion of LAS and CS. Corrosion tests using LAS and CS were conducted in  -rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by
-rays irradiated condition. Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in the water were measured after the tests. Corrosion test results indicated that the amounts of corrosion increased by  -rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with
-rays irradiation both air and nitrogen atmosphere. And also corrosion amounts increased with  -ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H
-ray dose rates. Electrochemical analyses indicated that cathodic reaction of Hydrogen peroxide was controlled by diffusion process. The measured diffusion constant of H O
O was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in
was about 0.75 times to that of oxygen. From these results, it is estimated that corrosion of LAS and CS in  -ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.
-ray irradiated condition was evaluated by the cathodic reduction reaction of oxidant.