Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillation
Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillationOuchi, Kazuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Hirose, Kazuki*; Kurosawa, Yuika*; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shibukawa, Masami*; Saito, Shingo*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1298, p.342399_1 - 342399_7, 2024/04
Given that conventional methods of high-dose sample analysis pose substantial exposure risks and generate large amounts of secondary radioactive waste, faster procedures allowing for decreased radiation emission are highly desirable. To address this need, we developed a  Sr
Sr quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed
quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed  Sr
Sr in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify
in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify  Sr
Sr in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
Ouchi, Kazuki
Hosha Kagaku, (49), p.3 - 7, 2024/03
I introduce the elucidation of the deposition following the oxidation state of uranium and the electrochemical behavior of uranium(IV) chloride in an ionic liquid-organic mixture, as a basic study of in-solution reactions. In addition, I introduce the development of separation methods for actinides using a microchemical chip and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, as an applied study for quantitative analytical methods for small amounts of samples.
Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
KEK Proceedings 2023-2, p.132 - 137, 2023/11
New analytical method of a combination of laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) for quantification of Zr isotopes in a solid sample was investigated. Solid Zr-isotope reference was added to a simulated radioactive waste sample as a spike, then Zr isotope ratio was measured by LA-ICP-MS. As a result, we successfully quantify Zr isotopes in the simulated radioactive waste sample by new IDMS. There is a possibility that this new method can be applied for quantification of Zr-93 in difficult to dissolve radioactive wastes.
Morii, Shiori; Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 72(10.11), p.441 - 448, 2023/10
Rapid analytical method for the determination of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes has been developed. Laser ablation (LA)-ICP-MS was applied to the analysis of Zr isotopes in simulated high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Sample preparation time was dramatically reduced by using a DGA resin as the adsorbent for Zr. Direct quantification of Zr isotopes in this resin sample was carried out by LA-ICP-MS. Laser settings were optimized to obtain a reliable isotope ratio of the sample by LA-ICP-MS. Quantification of Zr isotopes in the simulated HLW solution by isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) was examined. The amount of Zr-90 in the sample obtained by IDMS corresponded to a value calculated from the given concentration of Zr in the sample within uncertainty. Thus, this method can be applied for the quantification of Zr-93 in radioactive wastes.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(24), p.16321 - 16326, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We clarified the chemical state transformation of deposits following the reduction of uranyl ion (U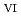 O
O
 ) from the results of electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance, impedance spectra and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. We propose the following deposition mechanism: (1) U
) from the results of electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance, impedance spectra and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. We propose the following deposition mechanism: (1) U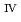 is formed by the disproportionation of U
is formed by the disproportionation of U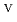 . (2) U
. (2) U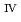 forms U
forms U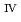 hydroxide deposits, and (3) finally, the hydroxide deposits transform into U
hydroxide deposits, and (3) finally, the hydroxide deposits transform into U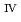 oxide, generally having a larger electrical resistance than the former.
oxide, generally having a larger electrical resistance than the former.
Yamagata, Kazuhito*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Marumo, Kazuki*; Tasaki-Handa, Yuiko*; Haraga, Tomoko; Saito, Shingo*
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(2), p.730 - 738, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.4(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The inert NpO
 complex with a fluorescein-modified phenanthroline-2,9-dicarboxylic acid was found by kinetic selection using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) from a small chemical library. The small spontaneous dissociation rate constant of 8
complex with a fluorescein-modified phenanthroline-2,9-dicarboxylic acid was found by kinetic selection using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) from a small chemical library. The small spontaneous dissociation rate constant of 8 10
10 s
s (the half-life of 23 hours) was determined. This is the singly-charged NpO
(the half-life of 23 hours) was determined. This is the singly-charged NpO
 complex exhibiting unusual kinetic inertness in aqueous solution, one million times slower than widely accepted fast kinetics of neptunyl complexes. Selective fluorescence detection of NpO
complex exhibiting unusual kinetic inertness in aqueous solution, one million times slower than widely accepted fast kinetics of neptunyl complexes. Selective fluorescence detection of NpO
 was achieved in PAGE with a detection limit of 68 pmol dm
was achieved in PAGE with a detection limit of 68 pmol dm (17 fg). This system was successfully applied to simulated spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste samples.
(17 fg). This system was successfully applied to simulated spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste samples.
 -edge to assess the U(V) electronic structure in FeUO
-edge to assess the U(V) electronic structure in FeUO
Yomogida, Takumi; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Kumagai, Yuta; Higashi, Kotaro*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kirishima, Akira*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Inorganic Chemistry, 61(50), p.20206 - 20210, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)FeUO was studied to clarify the electronic structure of U(V) in a metal monouranate compound. We obtained the peak splitting of HERFD-XANES spectra utilizing high-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy at the U L
was studied to clarify the electronic structure of U(V) in a metal monouranate compound. We obtained the peak splitting of HERFD-XANES spectra utilizing high-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy at the U L -edge, which is a novel technique in the U(V) compounds. Theoretical calculations revealed that the peak splitting was caused by splitting the 6d orbital of U(V). Such distinctive electronic states are of major interest to researchers and engineers working in various fields, from fundamental physics to the nuclear industry and environmental sciences for actinide elements.
-edge, which is a novel technique in the U(V) compounds. Theoretical calculations revealed that the peak splitting was caused by splitting the 6d orbital of U(V). Such distinctive electronic states are of major interest to researchers and engineers working in various fields, from fundamental physics to the nuclear industry and environmental sciences for actinide elements.
Yomogida, Takumi; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Koma, Yoshikazu; Konno, Katsuhiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.7191_1 - 7191_10, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.82(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Particles containing alpha ( ) nuclides were identified from sediment in stagnant water at the torus room of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station (FDiNPS)'s Unit 2 reactor. Several uranium-bearing particles were identified by SEM observation. These particles contained Zr and other elements which constituted fuel cladding and structural materials. The
) nuclides were identified from sediment in stagnant water at the torus room of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station (FDiNPS)'s Unit 2 reactor. Several uranium-bearing particles were identified by SEM observation. These particles contained Zr and other elements which constituted fuel cladding and structural materials. The  U/
U/ U isotope ratio in the solid fractions that included U particles was consistent with the nuclear fuel in the Unit 2 reactor, which indicated that the U particles had been derived from nuclear fuel. The particles with alpha-emitters detected by alpha track analysis were several tens to several hundred
U isotope ratio in the solid fractions that included U particles was consistent with the nuclear fuel in the Unit 2 reactor, which indicated that the U particles had been derived from nuclear fuel. The particles with alpha-emitters detected by alpha track analysis were several tens to several hundred  m in size. The EDX spectra showed that these particles mainly comprised iron, which indicated Pu, Am, and Cm were adsorbed on the Fe-baring particles. This study clarifies that the major morphologies of U and other
m in size. The EDX spectra showed that these particles mainly comprised iron, which indicated Pu, Am, and Cm were adsorbed on the Fe-baring particles. This study clarifies that the major morphologies of U and other  -nuclides were differed in the sediment of stagnant water in the torus room of FDiNPS's Unit 2 reactor.
-nuclides were differed in the sediment of stagnant water in the torus room of FDiNPS's Unit 2 reactor.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Tsukahara, Takehiko*; Brandt, A.*; Muto, Yuki*; Nabatame, Nozomi*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Sciences, 37(12), p.1789 - 1794, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.71(Chemistry, Analytical)We attempted to scale down a separation process of uranium (U) using the microchip column loaded with anion exchange resin to develop safety and waste-reducing separation technique. The ideal separation performance of U was obtained by the properly design of a microchannel. The concentration of U in seawater as a real-world sample could be quantified with the prepared microchip column. It indicates that the microchip column is sufficiently practical. Compared to separation of U with a general column, the column size was successfully scaled down to  1/5000.
1/5000.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Komatsu, Atsushi; Takao, Koichiro*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Watanabe, Masayuki
Chemistry Letters, 50(6), p.1169 - 1172, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The electrochemical behavior of uranium (IV) tetrachloride in ionic liquid-DMF mixture was studied for first time in order to build a redox flow battery (RFB) using U as an electrode active material. We found a quasi-reversible U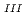 /U
/U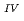 couple that could be applied to the anode reaction of the RFB.
couple that could be applied to the anode reaction of the RFB.
Haraga, Tomoko; Ouchi, Kazuki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Hoshino, Hitoshi*; Tanana, Rei*; Fujihara, Takashi*; Kurokawa, Hideki*; Shibukawa, Masami*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1032, p.188 - 196, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:45.99(Chemistry, Analytical)The development of safe, rapid and highly sensitive analytical methods for radioactive samples, especially actinide (An) ions, represents an important challenge. Here we propose a methodology for selecting appropriate emissive probes for An ions with very low consumption and emission of radioactivity by capillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence detection (CE-LIF), using a small chemical library of probes with eight different chelating moieties. It was found that the emissive probe, which possesses the tetradentate chelating moiety, was suitable for detecting uranyl ions. The detection limit for the uranyl-probe complex using CE-LIF combined with dynamic ternary complexation and on-capillary concentration techniques was determined to be 0.7 ppt. This method was successfully applied to real radioactive liquid samples collected from nuclear facilities.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Yamamoto, Masahiro
ECS Transactions, 75(27), p.51 - 57, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:38.46(Electrochemistry)We investigated the deposition of U(IV) following a valence change of U as electrodeposition using an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM). When measurements of the reduction of U(VI) in a weak acid solution were performed, deposits of U(IV) were observed on the electrode surface. From deposition rates, pH dependence of them, and oxidation potentials of deposits, we proposed the following deposition mechanism. The deposition is divided into the three phases; First, in the induction phase, U(IV) produced by the disproportionation forms U(IV) hydroxide nucleus. Next, in the growth phase, U(IV) deposits begin to grow. In this phase, the deposits catalyze the reduction of U(V) to U(IV), resulting an increase of the reduction current. Finally, in the transformation phase, U(IV) hydroxide species transform into U dioxide having more stable state.
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Nakano, Yuta*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Ito, Yuki*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Takahashi, Kuniaki; Saito, Shingo*
no journal, ,
For the development of a simple and rapid analytical method for actinides (Thorium, Uranium, Neptunium, Plutonium, Americium and Curium) in radioactive wastes, capillary electrophoresis-laser -induced fluorescence detecting method (CE-LIF) was studied. In this research, newly synthesized eight probes whose chelating group were acyclic or macrocyclic were applied to the detection of actinides using CE-LIF. As a result, Thorium and Uranium were successfully detected and separated from other actinide ions applied to octadenate acyclic probe and tetradenate planer probe, respectively. Neptunium was detected using hexadenate or heptadenate probes whose chelating groups were acyclic or macrocyclic. Plutonium was detected applied to hexadenate or octadenate acyclic probes. Americium and Curium were detected applied to seven probes except for tetradenate planer probe.
Haraga, Tomoko; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Ouchi, Kazuki*; Shibukawa, Masami*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; Saito, Shingo*
no journal, ,
Uranium is an important nuclide for the analysis of radioactive wastes from nuclear fuel cycle facilities. In order to achieve simple and rapid analysis of uranium, capillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescent detection method (CE-LIF) is one of the potential candidates. In this study, a highly emissive probe of uranyl ion suitable for CE-LIF was developed. The detection and separation of uranyl ion were examined using several new emissive complexing probes, each of which possessed a fluorophore and a different chelating moiety. Using a tetradentate probe, phenanthroline dicarboxylic acid chelating moiety, the highly sensitive fluorescent detection of uranium was successfully achieved. The detection limit of mid-ppt levels was determined, and coexisting matrix metal ions, such as Ca , Co
, Co , Cs
, Cs , Sr
, Sr , lanthanide ions and others, do not disturb the detection of uranium. This method has a great potential to be applied to analysis of radioactive waste samples.
, lanthanide ions and others, do not disturb the detection of uranium. This method has a great potential to be applied to analysis of radioactive waste samples.
Haraga, Tomoko; Nakano, Yuta*; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Ouchi, Kazuki*; Hirose, Kazuki*; Shibukawa, Masami*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; Saito, Shingo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Ouchi, Kazuki; Otobe, Haruyoshi
no journal, ,
Electrolytic reactions of Neptunium ions in a weakly acid solution were investigated by using gold electrode. It was reported previously that electrolytic reduction of Neptunium (V) ion based on mediator reaction with Np(III)/Np(IV) couple was observed in the acidic solution when bulk electrolysis was carried out at the potential around -0.2 V versus Ag/AgCl reference electrode. The reduction of Np(V), however, was not observed at the pH higher than 2. This is attributable to low reaction rate of electron exchange reaction between Np(V) and Np(III). Electrode reaction of Np(V) at more negative potential was investigated by cyclic voltammetry. The current peak due to reduction of Np(V) was observed at ca. -0.75 V, and oxidation current was appeared at +0.5 V. The reactions was determined to be reduction of Np(V) and oxidation of deposited species of reduction product of Np on the electrode. It was found that stripping current due to oxidation of deposit was saturated in spite of longer preelectrolysis time. This phenomenon is different from uranium.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
In this study, we investigated the relationship between reduction process and formation of aggregates by measuring electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM). When EQCM measurements of the reduction of U(V) to U(IV) in weakly acid solution were performed, the frequency was changed negatively. This indicates that aggregates of U(IV) were formed on the electrode. We consider that aggregates form in the three steps from the deposition rate; the induction step ( start deposition), early stage aggregation step (deposition amount
start deposition), early stage aggregation step (deposition amount  4 nmol) and secondary stage aggregation step (deposition amount
4 nmol) and secondary stage aggregation step (deposition amount  4 nmol). The pH dependence of the reduction and deposition rate was investigated. The U(IV) aggregates formed at more than pH3.1. When pH was higher, the induction time was fast, and aggregation rates at early and secondary stage were high. This suggests that a U hydroxide relates to the formation of aggregates.
4 nmol). The pH dependence of the reduction and deposition rate was investigated. The U(IV) aggregates formed at more than pH3.1. When pH was higher, the induction time was fast, and aggregation rates at early and secondary stage were high. This suggests that a U hydroxide relates to the formation of aggregates.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Ouchi, Kazuki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kihara, Sorin*
no journal, ,
Electrolytic reduction of neptunium ion in the weak acidic solution was investigated. On the cyclic voltammogram of Np(V) in the solution of pH 3.8, reduction and deposition of Np was observed. Stripping current due to oxidation of deposited Np was also appeared. Stripping voltammetry after preelectrolysis at definite potential was carried out. Stripping currents were almost constant despite variation of preelectrolysis time and concentration of Np(V). Difference of reduction-deposition behavior between U and Np was discussed.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kihara, Sorin*
no journal, ,
In this study, we investigated the relationship between reduction process and aggregation of uranium by measuring electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM). When EQCM measurements of the reduction of U(V) to U(IV) in weakly acid solution were performed, the frequency was changed negatively. This indicates that aggregates of U(IV) were formed on the electrode. We consider that aggregates form in the three steps from the deposition rate; the induction step ( start deposition), metastable stage aggregation step and stable stage aggregation step. The pH dependence of the reduction and deposition rate was investigated. The U(IV) aggregates formed at more than pH 3.1. When pH was higher, the induction time was fast, and aggregation rates at early and secondary stage were high. This suggests that a U hydroxide relates to the formation of aggregates.
start deposition), metastable stage aggregation step and stable stage aggregation step. The pH dependence of the reduction and deposition rate was investigated. The U(IV) aggregates formed at more than pH 3.1. When pH was higher, the induction time was fast, and aggregation rates at early and secondary stage were high. This suggests that a U hydroxide relates to the formation of aggregates.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
In previous study, it was found that microparticles of U(IV) formed in reduction process of U(V) enhanced the rate of the disproportionation and the electrolytic reduction of U(V). In this study, we investigated the relationship between reduction process and formation of microparticles by measuring electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM). When EQCM measurements of the reduction of U(VI) in a weakly acid solution were performed, the frequency was changed negatively. This indicates that aggregates of U(IV) were formed on the electrode surface. We consider that aggregates form in the three steps from deposition rates; the induction step ( start deposition), metastable aggregation step (temporary fast rate) and stable aggregation step (constant rate). The pH dependence of the deposition rate was investigated. When pH was higher, the deposition rates at metastability and stability step were high. This suggests that a U hydroxide relates to the formation of aggregates.
start deposition), metastable aggregation step (temporary fast rate) and stable aggregation step (constant rate). The pH dependence of the deposition rate was investigated. When pH was higher, the deposition rates at metastability and stability step were high. This suggests that a U hydroxide relates to the formation of aggregates.