Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Takumi*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Okubo, Takahiro*; Miura, Daisuke*; Kumada, Takayuki
Environmental Science & Technology, 57(26), p.9802 - 9810, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Environmental) Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculations
Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculationsOkubo, Takahiro*; Takei, Akihiro*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 127(4), p.973 - 986, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.86(Chemistry, Physical)The identification of adsorption sites of Cs on clay minerals has been studied in the fields of environmental chemistry. The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments allow direct observations of the local structures of adsorbed Cs. The NMR parameters of  Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The
Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The  Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
 Cs
Cs , and
, and  I
I in compacted Ca-montmorillonite; Experimental and modeling approaches
in compacted Ca-montmorillonite; Experimental and modeling approachesFukatsu, Yuta; Yotsuji, Kenji*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 211, p.106176_1 - 106176_10, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:75.92(Chemistry, Physical)Okubo, Takahiro*; Yamazaki, Akio*; Fukatsu, Yuta; Tachi, Yukio
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 313, p.110841_1 - 110841_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:29.65(Chemistry, Applied)Pore distributions in water-saturated Ca-montmorillonite were investigated using  H NMR measurements under various dry densities (0.8 - 1.6 g/cm
H NMR measurements under various dry densities (0.8 - 1.6 g/cm ) and porewater salinity conditions (deionized water, 0.1 and 1 M CaCl
) and porewater salinity conditions (deionized water, 0.1 and 1 M CaCl ), at the temperature range of 233 - 303 K. The volume fractions of the interlayer pore including two and three hydrated layers and the non-interlayer pore in compacted Ca-montmorillonite were quantified by NMR relaxometry including
), at the temperature range of 233 - 303 K. The volume fractions of the interlayer pore including two and three hydrated layers and the non-interlayer pore in compacted Ca-montmorillonite were quantified by NMR relaxometry including 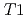 and
and 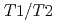 distribution analysis, and were compared with NMR cryoporometry and X-ray diffractometry. These analysis provided consistent pictures on the pore distributions in compacted Ca-montmorillonite, in contrast to Na-montmorillonite. The main factor affecting the pore distribution in compacted Ca- and Na-montmorillonite is the density, whereas the effect of porewater salinity is relatively smaller. The effect of interlayer cations is also relatively smaller at higher density, although the differences in the pore structures are significant at low density.
distribution analysis, and were compared with NMR cryoporometry and X-ray diffractometry. These analysis provided consistent pictures on the pore distributions in compacted Ca-montmorillonite, in contrast to Na-montmorillonite. The main factor affecting the pore distribution in compacted Ca- and Na-montmorillonite is the density, whereas the effect of porewater salinity is relatively smaller. The effect of interlayer cations is also relatively smaller at higher density, although the differences in the pore structures are significant at low density.
 Cs solid-state NMR and density functional theory calculations
Cs solid-state NMR and density functional theory calculationsOkubo, Takahiro*; Okamoto, Takuya*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Gu gan, R.*; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
gan, R.*; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 122(48), p.9326 - 9337, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:60.51(Chemistry, Physical)The structures of Cs adsorption on montmorillonite were investigated by the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The NMR spectra of Cs adsorbed on montmorillonite samples were measured under different Cs contents and relative humidity levels. NMR parameters were evaluated by the first principle calculations in order to identify the relationship between adsorbed Cs structures and NMR parameters. The comparisons between experimental and theoretical NMR spectra revealed that Cs is preferentially adsorbed at sites near Al for low Cs substituted montmorillonites, and that non-hydrated Cs present in partially Cs substituted samples, even after being hydrated under high relative humidity.
Yotsuji, Kenji; Tachi, Yukio; Okubo, Takahiro*
CMS Workshop Lectures, Vol.21, p.251 - 257, 2016/06
We have developed integrated sorption and diffusion model (ISD model) for assessment of diffusion parameters consistent with sorption processes in compacted bentonite. The ISD model gives consistent consideration to porewater chemistry, sorption and diffusion processes in compacted bentonite. The diffusion component based on the electric double layer theory and the homogeneous pore model in the ISD model accounts consistently for cation De overestimation and anion exclusion in narrow pores. The current ISD model can quantitatively account for diffusion of monovalent cations and anions, however, the model predictions disagree with diffusion data for multivalent cation and complex species. To improve the applicability of the model, it is necessary to consider the atomic level interactions between solute, solvent or clay mineral, and try that we apply the current ISD model to heterogeneous pore structure. In this study we try the application of the current ISD model to multiple pore structure. As results of numerical analysis of these models, the salinity dependence of effective diffusivity for the multi-pore model is comparatively smaller than that for the homogeneous pore model and the current diffusion model is improved.
Okubo, Takahiro*; Ibaraki, Moe*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
Applied Clay Science, 123, p.148 - 155, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:74.44(Chemistry, Physical)The pore distribution of water-saturated compacted clay (Na-montmorillonite at 0.8 and 1.4 g/cm saturated by three salt concentrations) was evaluated using
saturated by three salt concentrations) was evaluated using  H NMR relaxometry and freezing point depression. The populations of interlayer water with four hydrated state and non-interlayer water were calculated from the assumed thresholds. The sample with lower density exhibits higher population of non-interlayer water up to 55%. Low-temperature
H NMR relaxometry and freezing point depression. The populations of interlayer water with four hydrated state and non-interlayer water were calculated from the assumed thresholds. The sample with lower density exhibits higher population of non-interlayer water up to 55%. Low-temperature  H NMR experiments in view of freezing point depression indicated that mesopore water in approximately 4 nm space observed in the calorimetric study was considered as non-interlayer water and the threshold temperature. The result showed that population of non-interlayer water by expected from freezing point depression agreed with
H NMR experiments in view of freezing point depression indicated that mesopore water in approximately 4 nm space observed in the calorimetric study was considered as non-interlayer water and the threshold temperature. The result showed that population of non-interlayer water by expected from freezing point depression agreed with  H NMR relaxometry within 10%. Correlation experiments between longitudinal (
H NMR relaxometry within 10%. Correlation experiments between longitudinal (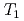 ) and transverse relation times (
) and transverse relation times (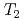 ) at -10
) at -10 C suggested that high-mobility bulk-like water molecules existed at a clay density of 1.4 g/cm
C suggested that high-mobility bulk-like water molecules existed at a clay density of 1.4 g/cm .
.
Okubo, Takahiro; Yamaguchi, Makoto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okubo, Takahiro; Yamaguchi, Makoto*
no journal, ,
The time-dependent diffusion coefficients of fluid molecules in confining geometries have been studied by NMR experiments with magnetic gradient. The characteristics of porous media such as the ratio of the surface area to pore volume, 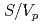 , and tortuosity,
, and tortuosity, 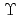 , are extracted by analyzing the diffusion coefficient of fluid molecules as a function of diffusion time,
, are extracted by analyzing the diffusion coefficient of fluid molecules as a function of diffusion time, 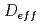 . Since
. Since 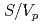 and
and 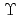 are related to permeability, it have been a very powerful technique for investigating the transport phenomena of fluids in porous media. Therefore, we attempted to apply these methods to clay saturated porous media which would be considered as barrier environment in geological disposal system of high-level radioactive waste. NMR measurements of time-dependent diffusion coefficient were performed to estimate
are related to permeability, it have been a very powerful technique for investigating the transport phenomena of fluids in porous media. Therefore, we attempted to apply these methods to clay saturated porous media which would be considered as barrier environment in geological disposal system of high-level radioactive waste. NMR measurements of time-dependent diffusion coefficient were performed to estimate 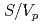 and
and 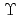 for water and clay gel saturated porous media modeled by glass beads beds. 17 interval bipolar gradient stimulated echo
for water and clay gel saturated porous media modeled by glass beads beds. 17 interval bipolar gradient stimulated echo (
(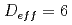 ms
ms 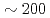 ms) and oscillating gradient spin echo sequences (
ms) and oscillating gradient spin echo sequences (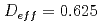 ms
ms 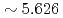 ms) were used to measure time-dependent diffusioncoefficients. Mitra equation and Pade approximation were applied to analyze time-dependent diffusion coefficient for the purpose of extracting
ms) were used to measure time-dependent diffusioncoefficients. Mitra equation and Pade approximation were applied to analyze time-dependent diffusion coefficient for the purpose of extracting 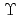 and
and 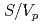 .
.
Okubo, Takahiro; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Yamaguchi, Makoto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okubo, Takahiro*; Ibaraki, Moe*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
no journal, ,
1H NMR relaxometry was applied for investigation of pore structure in compacted saturated montmorillonite with different salt concentration. The samples compacted to dry densities of 0.8 and 1.2 g/cm were saturated with pure water, 0.05, 0.10, 0.50, and 1.0 M NaCl solutions. Population of water in different hydrated layer corresponding to 1-, 2-, and 3 hydrated layer was estimated from longitudinal relaxation distributions. The population of water in 1-, 2-, and 3 hydrated layers changed as a function of NaCl concentration. The threshold to discriminate between inter- and intra-layer water is 3 hydrated layer, which is questionable from existence of 4 hydrated layer revealed by modelling of X-ray profile. The amount of water in 1- and intra-layer were negligible small for all conditions at dry density of 1.2 g/cm
were saturated with pure water, 0.05, 0.10, 0.50, and 1.0 M NaCl solutions. Population of water in different hydrated layer corresponding to 1-, 2-, and 3 hydrated layer was estimated from longitudinal relaxation distributions. The population of water in 1-, 2-, and 3 hydrated layers changed as a function of NaCl concentration. The threshold to discriminate between inter- and intra-layer water is 3 hydrated layer, which is questionable from existence of 4 hydrated layer revealed by modelling of X-ray profile. The amount of water in 1- and intra-layer were negligible small for all conditions at dry density of 1.2 g/cm . On the other hand, water in 2-hydrated layer was decreased instead of increment of water in 3-hydrated layer.
. On the other hand, water in 2-hydrated layer was decreased instead of increment of water in 3-hydrated layer.
Mitsui, Seiichiro; Oe, Toshiaki*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Kurosawa, Susumu*; Goto, Takahiro*; Inagaki, Manabu*; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko*; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Takahashi, Hirokazu*
no journal, ,
In order to develop robust performance assessment models, we have been preparing an information basis regarding glass properties and glass dissolution/alteration processes under disposal conditions as a part of NUMO-JAEA joint project. Our iterative working process for the preparation of the information basis comprises five steps: (1) integration of current knowledge; (2) development of glass dissolution scenarios based on current knowledge; (3) development of conceptual model; (4) sensitivity analyses to evaluate relative importance of relevant processes and associated uncertainties; and (5) identification of future R&D issues towards further improvement of the information basis. The current status will be presented in this talk.
 Cs solid state NMR, 1; GIPAW prediction of
Cs solid state NMR, 1; GIPAW prediction of  Cs NMR parameters
Cs NMR parametersOkubo, Takahiro*; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
The structures of Cs adsorption on montmorillonite were investigated by the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. NMR parameters were evaluated by the first principle calculations using GIPAW method in order to identify the relationship between adsorbed Cs structures and NMR parameters. It was confirmed that the chemical shift for Cs adsorbed on Al site in tetrahedral sheet was shifted to low magnetic field.
 Cs solid state NMR, 2;
Cs solid state NMR, 2;  Cs MAS and 3Q MAS NMR
Cs MAS and 3Q MAS NMROkamoto, Takuya*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Shimizu, Tadashi*; Oki, Shinobu*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
The structures of Cs adsorption on montmorillonite were investigated by the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The NMR spectra of Cs adsorbed montmorillonite samples with different Cs contents were collected by  Cs Magic Angle Spinning (MAS) NMR and
Cs Magic Angle Spinning (MAS) NMR and  Cs Triple Quantum (3Q) MAS NMR. The adsorbed Cs structures were evaluated based on the correlations between the structural characteristics and the values of the NMR parameters predicted by the first principal calculations.
Cs Triple Quantum (3Q) MAS NMR. The adsorbed Cs structures were evaluated based on the correlations between the structural characteristics and the values of the NMR parameters predicted by the first principal calculations.
Okamoto, Takuya*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Shimizu, Tadashi*; Oki, Shinobu*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
The structures of Cs adsorbed on montmorillonite were investigated by  Cs Magic Angle Spinning (MAS) NMR spectroscopy. The NMR spectra of Cs adsorbed on montmorillonite samples were measured under different relative humidity levels and were analyzed to evaluate the change in the structure of hydrated Cs sorbed on montmorillonite.
Cs Magic Angle Spinning (MAS) NMR spectroscopy. The NMR spectra of Cs adsorbed on montmorillonite samples were measured under different relative humidity levels and were analyzed to evaluate the change in the structure of hydrated Cs sorbed on montmorillonite.
Yamazaki, Akio*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
A structural analysis of water-filled pores in saturated compacted sodium montmorillonite was conducted by 1H NMR spectroscopy. The pore structure including interlayer and intraparticle pores in compacted montmorillonite was characterized by relaxation time and freezing point observed by 1H NMR and their correlations with water-filled pore sizes.
Yamazaki, Akio*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
A structural analysis of water-filled pores in saturated compacted Ca-type montmorillonite was conducted by 1H NMR spectroscopy. The pore structure including interlayer and intraparticle pores in Ca-type compacted montmorillonite was characterized by relaxation time observed by 1H NMR and their correlations with water-filled pore sizes.
Okubo, Takahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
The structures of Cs adsorption on montmorillonite were investigated by the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. NMR parameters were evaluated by the first principle calculations in order to identify the relationship between adsorbed Cs structures and NMR parameters.
Nakajima, Katsuki*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
The structures of Cs adsorption on montmorillonite were investigated by the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The NMR spectra of Cs adsorbed on montmorillonite samples were measured under different Cs contents and relative humidity levels and were analyzed to evaluate the change in the structure of hydrated Cs sorbed on montmorillonite.
Sakata, Nagisa*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*; Okubo, Takahiro*
no journal, ,
Cement-based materials will be used as a component for radioactive waste disposal facility. Understanding water paths in cement-based materials is a key to evaluate their long-term performance. It is well known that 1H transverse relaxation (T2) of water filled pores is related to their porous structure. In this study, 1H T2 distribution analyses were applied to hydration process of cement-based materials, and the relationship between porous structure and mass transport was discussed. Experimental results showed that the main path of water is the grain boundary between cement and silica sand contained in mortar. In addition, C-S-H gel layers in cement and C-S-H gel pore cannot contribute as a path of water.