Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -thrombin-bivalirubin complex at pD 5.0; Protonation states and hydration structure of the enzyme-product complex
-thrombin-bivalirubin complex at pD 5.0; Protonation states and hydration structure of the enzyme-product complexYamada, Taro*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Onishi, Yuki*; Tamada, Taro; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Masumi, Kenji*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kuroki, Ryota; Niimura, Nobuo*
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta; Proteins and Proteomics, 1834(8), p.1532 - 1538, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:48.48(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The protonation states and hydration structures of the  -thrombin-bivalirubin complex were studied by joint XN refinement of the single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data at resolutions of 1.6 and 2.8
-thrombin-bivalirubin complex were studied by joint XN refinement of the single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data at resolutions of 1.6 and 2.8  , respectively. The atomic distances were estimated by carrying out X-ray crystallographic analysis at 1.25
, respectively. The atomic distances were estimated by carrying out X-ray crystallographic analysis at 1.25  resolution. The complex represents a model of the enzyme-product (EP) complex of
resolution. The complex represents a model of the enzyme-product (EP) complex of  -thrombin. The neutron scattering length maps around the active site suggest that the side chain of H57/H was deuterated. The joint XN refinement showed that occupancies for D
-thrombin. The neutron scattering length maps around the active site suggest that the side chain of H57/H was deuterated. The joint XN refinement showed that occupancies for D 1 and D
1 and D 2 of H57/H were 1.0 and 0.7, respectively. However, no significant neutron scattering length density was observed around the hydroxyl oxygen O
2 of H57/H were 1.0 and 0.7, respectively. However, no significant neutron scattering length density was observed around the hydroxyl oxygen O of S195/H, which was close to the carboxylic carbon atom of dFPR-COOH. These observations suggest that the O
of S195/H, which was close to the carboxylic carbon atom of dFPR-COOH. These observations suggest that the O atom of S195/H is deprotonated and maintains its nucleophilicity in the EP complex. In addition to the active site, the hydration structures of the S1 subsite and the Exosite I, which are involved in the recognition of bivalirudin, are presented.
atom of S195/H is deprotonated and maintains its nucleophilicity in the EP complex. In addition to the active site, the hydration structures of the S1 subsite and the Exosite I, which are involved in the recognition of bivalirudin, are presented.
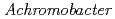 protease I at pD 8.0; Protonation states and hydration structure in the free-form
protease I at pD 8.0; Protonation states and hydration structure in the free-formOnishi, Yuki*; Yamada, Taro*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Sakiyama, Fumio*; Masaki, Takeharu*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta; Proteins and Proteomics, 1834(8), p.1642 - 1647, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:23.8(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The structure of the free-form of 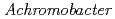 protease I (API) at pD 8.0 was refined by simultaneous use of single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data sets to investigate the protonation states of key catalytic residues of the serine protease. Occupancy refinement of the catalytic triad in the active site of API free-form showed that ca. 30% of the imidazole ring of H57 and ca. 70% of the hydroxyl group of S194 were deuterated. This observation indicates that a major fraction of S194 is protonated in the absence of a substrate. The protonation state of the catalytic triad in API was compared with the bovine
protease I (API) at pD 8.0 was refined by simultaneous use of single crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction data sets to investigate the protonation states of key catalytic residues of the serine protease. Occupancy refinement of the catalytic triad in the active site of API free-form showed that ca. 30% of the imidazole ring of H57 and ca. 70% of the hydroxyl group of S194 were deuterated. This observation indicates that a major fraction of S194 is protonated in the absence of a substrate. The protonation state of the catalytic triad in API was compared with the bovine  -trypsin-BPTI complex. The comparison led to the hypothesis that close contact of a substrate with S194 could lower the acidity of its hydroxyl group, thereby allowing H57 to extract the hydrogen from the hydroxyl group of S194. H210, which is a residue specific to API, does not form a hydrogen bond with the catalytic triad residue D113. Instead, H210 forms a hydrogen bond network with S176, H177 and a water molecule. The close proximity of the bulky, hydrophobic residue W169 may protect this hydrogen bond network, and this protection may stabilize the function of API over a wide pH range.
-trypsin-BPTI complex. The comparison led to the hypothesis that close contact of a substrate with S194 could lower the acidity of its hydroxyl group, thereby allowing H57 to extract the hydrogen from the hydroxyl group of S194. H210, which is a residue specific to API, does not form a hydrogen bond with the catalytic triad residue D113. Instead, H210 forms a hydrogen bond network with S176, H177 and a water molecule. The close proximity of the bulky, hydrophobic residue W169 may protect this hydrogen bond network, and this protection may stabilize the function of API over a wide pH range.
Onishi, Yuki*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 8th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2012/12
In the steam generator of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), self-wastage phenomena is a crack enlargement on the heat transfer tube itself caused by sodium-water reaction, a quantification of the self-wastage phenomenon is of importance from the viewpoint of safety assessment. In this study, we propose a numerical approach to evaluate the self-wastage phenomena and investigate a crack enlargement using SERAPHIM code. In the analysis, two-dimensional initial crack is assumed based on SWAT-4 experiment. The wastage rate was estimated by Arrhenius type equation, and re-meshing arrangement was performed by cut down from a part of tube in the initial model with the wastage amount. After simulated again using the re-meshing models, the resulting SWR products were distributed not only circumferential direction but also radial direction.
Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Ohara, Takashi*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Yamada, Taro*; Onishi, Yuki*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki*; Yokoyama, Takeshi*
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 66(11), p.1194 - 1197, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:94.58(Biochemical Research Methods)The IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer (iBIX), a new diffractometer for protein crystallography at the next-generation neutron source at J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex), has been constructed and has been operational since December 2008. Preliminary structure analyses of organic crystals showed that iBIX has high performance even at 120 kW operation and the first full data set is being collected from a protein crystal.
 resolution
resolutionYagi, Daichi*; Yamada, Taro*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Onishi, Yuki*; Yamashita, Masahiro*; Tamada, Taro; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kuroki, Ryota; Niimura, Nobuo*
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 65(9), p.892 - 899, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:80.35(Biochemical Research Methods)A neutron crystallographic analysis of phosphate-free bovine pancreatic RNase A has been carried out at 1.7  resolution using the BIX-4 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The high resolution structural model allowed us to determine that His12 acts mainly as a general base in the catalytic process of RNase A. Numerous other distinctive structural features such as the hydrogen positions of methyl groups, hydroxyl groups, prolines, asparagines and glutamines were also determined at 1.7
resolution using the BIX-4 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The high resolution structural model allowed us to determine that His12 acts mainly as a general base in the catalytic process of RNase A. Numerous other distinctive structural features such as the hydrogen positions of methyl groups, hydroxyl groups, prolines, asparagines and glutamines were also determined at 1.7  resolution. The protonation and deprotonation states of all of the charged amino-acid residues allowed us to provide a definitive description of the hydrogen-bonding network around the active site and the H atoms of the key His48 residue. Differences in hydrogen-bond strengths for the
resolution. The protonation and deprotonation states of all of the charged amino-acid residues allowed us to provide a definitive description of the hydrogen-bonding network around the active site and the H atoms of the key His48 residue. Differences in hydrogen-bond strengths for the  -helices and
-helices and  -sheets were inferred from determination of the hydrogen-bond lengths and the H/D-exchange ratios of the backbone amide H atoms. The correlation between the B factors and hydrogen-bond lengths of the hydration water molecules was also determined.
-sheets were inferred from determination of the hydrogen-bond lengths and the H/D-exchange ratios of the backbone amide H atoms. The correlation between the B factors and hydrogen-bond lengths of the hydration water molecules was also determined.
Ishikawa, Takuya*; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Onishi, Yuki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Kuroki, Ryota; Niimura, Nobuo*
Chemical Physics, 345(2-3), p.152 - 158, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:44.55(Chemistry, Physical) -lactoglobulin,
-lactoglobulin,  -amylase, 2Zn-insulin, cubic-insulin and RNase a for neutron diffraction experiment
-amylase, 2Zn-insulin, cubic-insulin and RNase a for neutron diffraction experimentYagi, Daichi*; Ebata, Toshinobu*; Ichige, Toshikatsu*; Kobayashi, Yoichiro*; Ishikawa, Takuya*; Yamashita, Masahiro*; Onishi, Yuki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Niimura, Nobuo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Onishi, Yuki*; Ostermann, A.*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Honjo, Eijiro; Kuroki, Ryota; Futami, Junichiro*; Yamada, Hidenori*
no journal, ,
Our goal is to develop new methods for determining macromolecular crystal structures  from neutron diffraction data and to validate these methods by making applications to several proteins. The proposed methods, which have the potential to be more powerful than X-ray ones, exploit perfectly isomorphous pairs of crystals that differ by replacement of D atoms with H atoms in selected amino-acid residues. This research involves collaboration among teams on three continents that have expertise in different aspects of neutron crystallography. The Japanese team measures high-resolution neutron diffraction data from protein crystals to answer questions about H bonding, protonation, hydration, and enzyme mechanisms. The team will focus on fundamental and simple proteins such as myoglobin, insulin, and RNase A at the first stage and then on rubredoxin, aldose reductase and other samples from the French team. In the meeting the research plan of the Japanese team will be reported.
from neutron diffraction data and to validate these methods by making applications to several proteins. The proposed methods, which have the potential to be more powerful than X-ray ones, exploit perfectly isomorphous pairs of crystals that differ by replacement of D atoms with H atoms in selected amino-acid residues. This research involves collaboration among teams on three continents that have expertise in different aspects of neutron crystallography. The Japanese team measures high-resolution neutron diffraction data from protein crystals to answer questions about H bonding, protonation, hydration, and enzyme mechanisms. The team will focus on fundamental and simple proteins such as myoglobin, insulin, and RNase A at the first stage and then on rubredoxin, aldose reductase and other samples from the French team. In the meeting the research plan of the Japanese team will be reported.
Ishikawa, Takuya*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Onishi, Yuki*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Niimura, Nobuo*
no journal, ,
It is known that the protonation status of amino acid side chains can strongly affect the biological function and stability of a protein. It is often hard to estimate it because it depends also on the local environment of the side chain. Neutron diffraction is a powerful tool to observe hydrogen atoms because of its strong interaction with hydrogen. Thus, a neutron study of cubic insulin at pD 6 has been carried out using the BIX-4 diffractometer (JRR-3, JAEA) and the result was compared with the previous neutron study at pD 9 (Maeda, et al. 2004) and by X-ray at pH 6 (Diao, 2003). A large single crystal of cubic insulin was prepared based on the crystallization phase diagram. The crystal diffracted to 2.5  resolution. It was found that only N
resolution. It was found that only N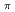 of His 5 in the B-chain is protonated whereas both N
of His 5 in the B-chain is protonated whereas both N and N
and N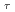 of His10 in the B-chain is protonated at pD 6 and the results at pD 9 are also the same (the pK of histidine side chains in the free form is around 6.0). These indicate that neutron diffraction study is useful to determine the protonation status of a protein.
of His10 in the B-chain is protonated at pD 6 and the results at pD 9 are also the same (the pK of histidine side chains in the free form is around 6.0). These indicate that neutron diffraction study is useful to determine the protonation status of a protein.
Ohara, Takashi; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki*; Onishi, Yuki*; Yokoyama, Takeshi*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ohara, Takashi; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki*; Yokoyama, Takeshi*; Onishi, Yuki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; et al.
no journal, ,
For a single crystal diffractometer, a data processing software which extracts a HKLF list from raw data is one of the most important components. We have developed a new data processing software, named STARGazer, for a new TOF single crystal neutron diffractometer, IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer (iBIX), which is constructed at Materials and Life-science Facility (MLF) of J-PARC. We have already collected and processed neutron diffraction dataset of ammonium bitartrate, glutamic acid and some crystals of organic molecules. The obtained cell parameters agreed with the known values and positions of hydrogen atoms are reasonable. In this presentation, we will show the feature of STARGazer and also show the results of neutron structure analyses of the organic molecules by iBIX.
Onishi, Yuki*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kurihara, Akikazu; Kikuchi, Shin; Uchibori, Akihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onishi, Yuki*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kurihara, Akikazu; Kikuchi, Shin; Uchibori, Akihiro
no journal, ,
A numerical method for self-wastage on a heat transfer tube has been developed to enable evaluation of the tube failure accident in a steam generator of sodium-cooled fast reactors. In this study, numerical analysis on discharging of water vapor from a crack was performed by using the SERAPHIM code calculating multicomponent multiphase flows with sodium-water chemical reaction. The numerical result showed that the high-temperature region appeared near the exit of the crack and the NaOH exists in the high-temperature region. We constructed a new Arrhenius-type evaluation model of a wastage rate and applied it to the numerical result. It was demonstrated that our model could reproduce expansion of the crack. The analysis mesh was reconstructed for the analysis region after expansion of the crack and the numerical analysis was performed again. The distribution of the gas-phase varied from the case of the initial crack.