Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Ono, Takuya; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Watanabe, Koji*; Abe, Hitoshi
Nuclear Technology, 208(10), p.1553 - 1561, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)To contribute to the confinement safety evaluation of the radioactive materials in the Glove box (GB) fire accident, combustion tests with the Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and the Polycarbonate (PC) as typical panel materials for the GB have been conducted with a relatively large scale apparatus. As the important data for evaluating confinement safety, the release ratio and the particle size distribution of the soot generated from the burned materials were obtained. Furthermore, the rise of the differential pressure ( P) of the high efficiency particle air (HEPA) filter by the soot loading was also investigated. As results, the release ratio of the soot from the PC was about seven times as large as the PMMA. In addition, it was found that the behavior of the rise of the
P) of the high efficiency particle air (HEPA) filter by the soot loading was also investigated. As results, the release ratio of the soot from the PC was about seven times as large as the PMMA. In addition, it was found that the behavior of the rise of the  P with soot loading could be represented uniformly regardless of kinds of combustion materials by considering effect of the loading volume of the soot particle in the relatively low loading region.
P with soot loading could be represented uniformly regardless of kinds of combustion materials by considering effect of the loading volume of the soot particle in the relatively low loading region.
Yamaguchi, Akinori*; Yokotsuka, Muneyuki*; Furuta, Masayo*; Kubota, Kazuo*; Fujine, Sachio*; Mori, Kenji*; Yoshida, Naoki; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 21(4), p.173 - 182, 2022/09
Risk information obtained from probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of measures against severe accidents in nuclear facilities. The PRA methods used for reprocessing facilities are considered immature compared to those for nuclear power plants, and to make the methods mature, reducing the uncertainty of accident scenarios becomes crucial. In this paper, we summarized the results of literature survey on the event progression of evaporation to dryness caused by boiling of high-level liquid waste (HLLW) which is a severe accident in reprocessing facilities and migration behavior of associated radioactive materials. Since one of the important characteristics of Ru is its tendency to form volatile compounds over the course of the event progression, the migration behavior of Ru is categorized into four stages based on temperature. Although no Ru has been released in the waste in the high temperature region, other volatile elements such as Cs could be released. Sufficient experimental data, however, have not been obtained yet. It is, therefore, necessary to further clarify the migration behavior of radioactive materials that predominantly depends on temperature in this region.
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Ono, Takuya; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Abe, Hitoshi
Nuclear Technology, 208(7), p.1205 - 1213, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A clogging behavior of a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter at solvent fire accidents for reprocessing facilities has been studied. In this study, the burning rates of 30% tri-butyl phosphate (TBP)/dodecane (DD) mixed solvent and DD solvent and the differential pressure ( P) of a high airflow typed HEPA filter applied in the actual facilities in Japan were measured. It was confirmed that the mainly burned was DD at the early stage of the mixed solvent burning and the TBP at the late stage. Furthermore, it was found that the
P) of a high airflow typed HEPA filter applied in the actual facilities in Japan were measured. It was confirmed that the mainly burned was DD at the early stage of the mixed solvent burning and the TBP at the late stage. Furthermore, it was found that the  P rapidly rose at the late stage of the mixed solvent burning. The increase of the release ratio of the unburned particulate composition (TBP, its degraded solvent and inorganic phosphorus (P
P rapidly rose at the late stage of the mixed solvent burning. The increase of the release ratio of the unburned particulate composition (TBP, its degraded solvent and inorganic phosphorus (P O
O )) was considered to contribute to the rapid rise. The correlating formulas with the
)) was considered to contribute to the rapid rise. The correlating formulas with the  P and the mass of the loading particulates, except for the region of the rapid rise of
P and the mass of the loading particulates, except for the region of the rapid rise of  P, could be induced.
P, could be induced.
Yoshida, Naoki; Ono, Takuya; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2021-011, 12 Pages, 2022/01
In boiling and drying accidents involving high-level liquid waste in fuel reprocessing plants, emphasis is placed on the behavior of ruthenium (Ru). Ru would form volatile species, such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ), and could be released to the environment with coexisting gases, including nitric acid, water, or nitrogen oxides. In this study, to contribute toward safety evaluations of these types of accidents, the migration behavior of gaseous Ru into the liquid phase has been experimentally measured by simulating the condensate during an accident. The gas absorption of RuO
), and could be released to the environment with coexisting gases, including nitric acid, water, or nitrogen oxides. In this study, to contribute toward safety evaluations of these types of accidents, the migration behavior of gaseous Ru into the liquid phase has been experimentally measured by simulating the condensate during an accident. The gas absorption of RuO was enhanced by increasing the nitrous acid (HNO
was enhanced by increasing the nitrous acid (HNO ) concentration in the liquid phase, indicating the occurrence of chemical absorption. In control experiments without HNO
) concentration in the liquid phase, indicating the occurrence of chemical absorption. In control experiments without HNO , the lower the temperature, the greater was the Ru recovery ratio in the liquid phase. Conversely, in experiments with HNO
, the lower the temperature, the greater was the Ru recovery ratio in the liquid phase. Conversely, in experiments with HNO , the higher the temperature, the higher the recovery ratio, suggesting that the reaction involved in chemical absorption was activated at higher temperatures.
, the higher the temperature, the higher the recovery ratio, suggesting that the reaction involved in chemical absorption was activated at higher temperatures.
Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Naoki; Abe, Hitoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(2), p.145 - 150, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the "evaporation and dryness due to the loss of cooling functions" which is one of the severe accidents at reprocessing plants in Japan, ruthenium (Ru) is possible to be released much more than other elements to the environment. This cause is considered that the volatile Ru compound can be released from high level liquid waste (HLLW) as gaseous compound in adding to the release by entrainment. It was expected that the release of the volatile Ru compound from the HLLW may be able to be restrained by coexisting nitrite ion because of its reduction power. To confirm the effect of nitrite ion on the release behavior of the volatile Ru compound, four experiments of heating the simulated HLLW (SHLLW) with setting the concentration of nitrite ion in the SHLLW as a parameter ware carried out. As a result, the release of the volatile Ru compound was seemed to be restrained by adding nitrite sodium as a source of nitrite ion under certain boiling condition. This result may contribute to improve source term analysis in the evaporation and dryness due to the loss of cooling functions.
Ono, Takuya; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Naoki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Abe, Hitoshi
PLOS ONE (Internet), 16(1), p.e0245303_1 - e0245303_16, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.76(Multidisciplinary Sciences)It is necessary to consider how a glove box's confinement function will be lost when evaluating the amount of radioactive material leaking from a nuclear facility during a fire. In this study, we build a model that consistently explains the weight loss of glove box materials because of heat input from a flame and accompanying generation of the pyrolysis gas. The weight loss suggests thinning of the glove box housing, and the generation of pyrolysis gas suggests the possibility of fire spreading. The target was polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), used as the glove box panel. Thermal gravimetric tests on PMMA determined the parameters to be substituted in the Arrhenius equation for predicting the weight loss in pyrolysis. The pyrolysis process of PMMA was divided into 3 stages with activation energies of 62 kJ/mol, 250 kJ/mol, and 265 kJ/mol. Furthermore, quantifying the gas composition revealed that the composition of the pyrolysis gas released from PMMA can be approximated as 100 percent methyl methacrylate. This result suggests that the released amount of methyl methacrylate can be estimated by the Arrhenius equation. To investigate the validity of such estimation, a sealed vessel test was performed. In this test, we observed increase of the number of gas molecules during the pyrolysis as internal pressure change of the vessel. The number of gas molecules was similar to that estimated from the Arrhenius equation, and indicated the validity of our method. Moreover, we also performed the same tests on bisphenol-A-polycarbonate (PC) for comparison. In case of PC, the number of gas molecules obtained in the vessel test was higher than the estimated value.
Yoshida, Naoki; Amano, Yuki; Ono, Takuya; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2020-014, 33 Pages, 2020/12
Considering the boiling and drying accident of high-level liquid waste in fuel reprocessing plant, Ruthenium (Ru) is an important element. It is because Ru would form volatile compounds such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric oxides (NOx) such as nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO
) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric oxides (NOx) such as nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO ). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the effect of NOx on the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO
). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the effect of NOx on the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO (RuO
(RuO (g)). As a result, the RuO
(g)). As a result, the RuO (g) decomposed over time under the atmospheric gasses with NO or NO
(g) decomposed over time under the atmospheric gasses with NO or NO , however, the decomposition rate was slower than the results of experiments without NOx. These results showed that the NOx stabilized RuO
, however, the decomposition rate was slower than the results of experiments without NOx. These results showed that the NOx stabilized RuO (g).
(g).
Yoshida, Naoki; Ono, Takuya; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(11), p.1256 - 1264, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)Emphasis has been placed on the behavior of ruthenium (Ru) in the evaporation to dryness accident due to the loss of cooling functions (EDLCF) of high-level liquid waste in fuel reprocessing plants. It is because Ru would form volatile compounds such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric acid (HNO
) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric acid (HNO ), water (H
), water (H O). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO
O). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO (RuO
(RuO (g)) under the various atmospheric conditions: temperature and composition of coexisting gasses. As a result, the behavior of the RuO
(g)) under the various atmospheric conditions: temperature and composition of coexisting gasses. As a result, the behavior of the RuO (g) was diverse depending on the atmospheric conditions. In the experiments with the dry air or H
(g) was diverse depending on the atmospheric conditions. In the experiments with the dry air or H O vapor, decomposition of RuO
O vapor, decomposition of RuO (g) was observed. In the experiment with the mixed gas which containing HNO
(g) was observed. In the experiment with the mixed gas which containing HNO , almost no decomposition of the RuO
, almost no decomposition of the RuO (g) was observed, and chemical form of the RuO
(g) was observed, and chemical form of the RuO (g) was retained.
(g) was retained.
Ono, Takuya; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Abe, Hitoshi
Nuclear Technology, 206(1), p.40 - 47, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recent Japanese nuclear regulations have focused on the hazards of in-cell solvent fires at reprocessing facilities. In this work, a mixture of tributyl phosphate and dodecane-based solvents was burned to generate an aerosol composed of soot and unburned solvent that was then loaded onto a high-efficiency particulate air filter simulating the ventilation system of reprocessing facilities. A radical increase of differential pressure occurred in the filters during these tests after the dodecane burned out from the solvent in a phenomenon we named as rapid clogging, likely caused by the burnout of dodecane. This relationship provides valuable insight into the establishment of new regulations for reprocessing facilities. This work indicates that clogging of ventilation filters during solvent fires may occur more rapidly than previously estimated.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Naoki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 18(2), p.69 - 80, 2019/06
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that nitrogen oxide affects strongly to the transport behavior of Ru. Chemical reactions of nitrogen oxide with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. An analysis method has been developed with coupling two types of computer codes to simulate not only thermo-hydraulic behavior but also chemical reactions in the flow paths of carrier gases. A simulation study has been also carried out with a typical facility building.
Yoshida, Naoki; Ono, Takuya; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(6), p.599 - 604, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:52.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the boiling and drying accident of high-level liquid waste in the fuel reprocessing plant, behavior of ruthenium (Ru) has attracted much attention because Ru could form volatile compounds such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ) and could be released into the environment. To contribute towards safety evaluation of this accident, the migration behavior and the leak path factor of the gaseous ruthenium compound has been experimentally measured in this study. The experiment was proceeded by using the Ruthenium Migration Evaluating Apparatus, which partially simulates the atmospheric condition (temperature, flow rate, and composition of water vapor and gaseous nitric acid mixture) of migration pathway in the accident. Experiments with dry air and water vapor were also performed as the control experiment to discuss the effect of nitric acid. As a result, the experiment with dry air and the experiment with water vapor demonstrated that the majority of the ruthenium deposited along the migration pathway. On the other hand, the experiment with the water vapor containing gaseous nitric acid demonstrated that almost all of the ruthenium passed through the migration pathway without deposition. These results suggested that the migration behavior of gaseous ruthenium will be affected by the gas-phase composition.
) and could be released into the environment. To contribute towards safety evaluation of this accident, the migration behavior and the leak path factor of the gaseous ruthenium compound has been experimentally measured in this study. The experiment was proceeded by using the Ruthenium Migration Evaluating Apparatus, which partially simulates the atmospheric condition (temperature, flow rate, and composition of water vapor and gaseous nitric acid mixture) of migration pathway in the accident. Experiments with dry air and water vapor were also performed as the control experiment to discuss the effect of nitric acid. As a result, the experiment with dry air and the experiment with water vapor demonstrated that the majority of the ruthenium deposited along the migration pathway. On the other hand, the experiment with the water vapor containing gaseous nitric acid demonstrated that almost all of the ruthenium passed through the migration pathway without deposition. These results suggested that the migration behavior of gaseous ruthenium will be affected by the gas-phase composition.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Naoki; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2017-015, 18 Pages, 2018/01
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing facility. It was observed at the experiments that a large amount of ruthenium (Ru) is volatilized and transfer to the vapor phase in the tank. The nitric acid and water mixed vapor released from the tank is condensed. Volatilized Ru is expected to transfer into the condensed water at the compartments in the building. Quantitative estimation of the amount of Ru transferred condensed water is key issues to evaluate the reduction the amount of Ru through leak path in the facility building. This report presents that a correlation has been developed for Ru transfer rate to condensed water with vapor condensing rate based on the experimental results and additional thermal-hydraulic simulation of the experiments. Applicability of the correlation has been also demonstrated with the accident simulation of typical facilities in full-scale.
Yoshida, Naoki; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Kazuo; Yamane, Yuichi; Abe, Hitoshi
NEA/CSNI/R(2017)12/ADD1 (Internet), p.293 - 305, 2018/01
The "Evaporation to Dryness due to the Loss of Cooling Functions" (EDLCF) of highly-active liquid waste (HALW) was newly defined as one of the severe accidents in Japan's nuclear safety standard for the reprocessing plant. Studies on accident scenarios and their source terms have led to an increased need for the development of accident management measures and the assessment of their effectiveness. Previous studies have shown that ruthenium was released at a greater rate than other elements because it formed volatile species such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ). In addition, ruthenium isotopes,
). In addition, ruthenium isotopes, 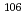 Ru and
Ru and 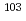 Ru, have radiotoxicity. Accordingly, the accident management measures require the experimental information on the release and transport behavior of the gaseous ruthenium (Ru(g)). This paper summarizes our experimental results on the characteristics of Ru(g) in the EDLCF. This work includes the results of the experiments carried out under the agreement among JAEA, Japan Nuclear Fuel Ltd. and Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization.
Ru, have radiotoxicity. Accordingly, the accident management measures require the experimental information on the release and transport behavior of the gaseous ruthenium (Ru(g)). This paper summarizes our experimental results on the characteristics of Ru(g) in the EDLCF. This work includes the results of the experiments carried out under the agreement among JAEA, Japan Nuclear Fuel Ltd. and Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization.
Ono, Takuya; Watanabe, Koji; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/07
After the Fukushima-Daiichi accident, countermeasures against the severe accident are newly required as regulatory items for nuclear facilities. Organic solvent fire in cell was defined as one of the accidents in the fuel reprocessing plant. When the solvent burns, aerosols including soot are released. The substances clog HEPA filters in the ventilation system and their breakthrough may happen because of differential pressure rising. Moreover, the fire can also release volatile radioactive gaseous species, which can pass through HEPA filters. These phenomena are important for evaluation of confinement capability of the facility and public exposure. We have investigated, in relating to the clogging behavior, release behavior of aerosols as well as of volatile materials from burnt solvent. In the presentation, we will report experimental data and evaluation results obtained from recent research.
Amano, Yuki; Watanabe, Koji; Masaki, Tomoo; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Technology 2016-012, 21 Pages, 2016/06
To contribute to safety evaluation of fire accident in fuel reprocessing plants, solvent extraction behavior of ruthenium, which could form volatile species, was investigated. Distribution ratios of ruthenium at fire accident conditions were obtained by extraction experiments with several solvent composition at different temperature as parameters. In order to investigate release behavior of ruthenium and europium at fire accident, release ratios of ruthenium and europium were also obtained by solvent combustion experiments.
Yamane, Yuichi; Amano, Yuki; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Abe, Hitoshi; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Yoshida, Kazuo; Ishikawa, Jun
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(6), p.783 - 789, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)The release behavior of radioactive materials from high active liquid waste (HALW) has been experimentally investigated under boiling accident conditions. In the experiments using HALW obtained through laboratory scale reprocessing, release ratio was measured for the FP nuclides such as Ru,  Tc, Cs, Sr, Nd, Y, Mo, Rh and actinides such as
Tc, Cs, Sr, Nd, Y, Mo, Rh and actinides such as  Cm,
Cm,  Am. As a result, the release ratio was 0.20 for Ru and 1
Am. As a result, the release ratio was 0.20 for Ru and 1
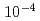 for the FP and Ac nuclides. Ru was released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas. For its released amount, weak dependency was found to the initial concentration in the test solution. The release ratio decreased with the initial concentration. For other FP nuclides and actinides as non-volatile, released into the gas phase in the form of mist, the released amount increased with the initial concentration. The release ratio of Ru and NOx concentration increased with temperature of the test solutions. They were released almost at the same temperature between 200 and 300
for the FP and Ac nuclides. Ru was released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas. For its released amount, weak dependency was found to the initial concentration in the test solution. The release ratio decreased with the initial concentration. For other FP nuclides and actinides as non-volatile, released into the gas phase in the form of mist, the released amount increased with the initial concentration. The release ratio of Ru and NOx concentration increased with temperature of the test solutions. They were released almost at the same temperature between 200 and 300 C. Size distribution of the mist and other particle was measured.
C. Size distribution of the mist and other particle was measured.
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Kazuo; Yamane, Yuichi; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(4), p.227 - 234, 2015/12
The release characteristics of Ru from highly active liquid waste (HALW) have been investigated under the condition of accidental evaporation to dryness by boiling of HALW. Using a laboratory-scale apparatus, non-radioactive simulated HALW (s-HALW) was heated with an external heater to dryness to observe the release characteristics of Ru and gaseous nitrogen oxides. As a result, Ru was significantly released between 120 and 300  C of the s-HALW. The cumulative release ratio of Ru was 0.088. It was also found that the partially released amount of Ru against the temperature of the s-HALW had two peaks with one maximal at about 140
C of the s-HALW. The cumulative release ratio of Ru was 0.088. It was also found that the partially released amount of Ru against the temperature of the s-HALW had two peaks with one maximal at about 140  C and maximum at about 240
C and maximum at about 240  C. Referring to the results of the release rate of gaseous nitrogen oxides and the volume of condensate, which was a collection of the mixed vapors of steam and nitric acid released from the s-HALW, we discussed the causes of Ru release around these peaks.
C. Referring to the results of the release rate of gaseous nitrogen oxides and the volume of condensate, which was a collection of the mixed vapors of steam and nitric acid released from the s-HALW, we discussed the causes of Ru release around these peaks.
Uchiyama, Gunzo; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi; Yamane, Yuichi; Yoshida, Kazuo; Ishikawa, Jun
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.1056 - 1063, 2015/09
The experimental study for source term data of radioactive materials has been conducted at a boiling accident of high active liquid waste (HALW) in reprocessing plants. In the study, three kinds of tests have been conducted including a cold small scale test, a cold engineering scale test and a hot small scale test. The following results were obtained: Ruthenium and Technetium were released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas under the boiling accident conditions of a simulated HALW. Non-volatile fission products (FPs) such as Nd and Cs were released into the gas phase in the form of mist. The release ratios of non-volatile FPs from a vessel of the simulated HALW were about 10 . The release ratios of actinide nuclides such as Am were almost the same as those of non-volatile FPs.
. The release ratios of actinide nuclides such as Am were almost the same as those of non-volatile FPs.
Amano, Yuki; Watanabe, Koji; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Yamane, Yuichi; Ishikawa, Jun; Yoshida, Kazuo; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(2), p.86 - 94, 2015/06
Radioactive materials could be released into air due to the accidental boiling of high active liquid waste (HALW) in reprocessing plants. Volatile radioactive nuclides, such as ruthenium, are released from the tanks into the atmosphere. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are also released due to the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates in HALW. The released NOx transport volatile ruthenium and cause redox reactions associated with the composition or decomposition of volatile ruthenium. In this study, NOx release data were obtained by heating simulated HALW up to 600 C. As a result, the release of NOx from the simulated HALW was observed from 200
C. As a result, the release of NOx from the simulated HALW was observed from 200 C to 600
C to 600 C, and the main release of NOx was observed at about 340
C, and the main release of NOx was observed at about 340 C. All the lanthanide nitrates were found to decompose in the simulated HALW, and the thermal decomposition temperature of the lanthanide nitrates decreased after the addition of ruthenium dioxide to the mixed lanthanide nitrates solution.
C. All the lanthanide nitrates were found to decompose in the simulated HALW, and the thermal decomposition temperature of the lanthanide nitrates decreased after the addition of ruthenium dioxide to the mixed lanthanide nitrates solution.
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi; Yamane, Yuichi; Yoshida, Kazuo
Nuclear Technology, 190(2), p.207 - 213, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)The release behavior of radioactive materials from high active liquid waste (HALW) has been investigated under boiling accident conditions. Results of the experiment using a nonradioactive simulated HALW found Ru to be a volatile element under the accident conditions and to be released into the gas phase in the form of both mist and gas. The Ru release rate and the apparent Ru volatilization rate constant were obtained under the boiling conditions of simulated HALW. The other fission product elements such as Cs were found to be nonvolatile and to be released into the gasphase in the form of mist. The mist size distribution near the surface of the simulated HALW in the reactor vessel was found to range from 0.05 to 20  m with a peak diameter of
m with a peak diameter of  2
2  m.
m.