Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Aoki, Katsunori; Tsurudome, Koji; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(2), p.172 - 181, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)We developed a remote continuous air monitoring (RCAM) system. The RCAM system consisted of a personal air monitor and a robot. The personal air monitor (poCAMon, SARAD, Germany) had a 400 mm ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the
ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the  Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of
Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of 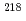 Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and
Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and  Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Torii, Tatsuo
Isotope News, (765), p.10 - 13, 2019/10
This paper reports the development of an alpha particle imaging detector to detect alpha emitters originating from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and the actual measurement of smear papers.
Morishita, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Usami, Hiroshi; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki*; Utsugi, Wataru*; Takahira, Shiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9, p.581_1 - 581_14, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:91.8(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Sato, Yuki; Tanifuji, Yuta; Terasaka, Yuta; Usami, Hiroshi; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Utsugi, Wataru*; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki*; Takahira, Shiro*; Torii, Tatsuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(9), p.965 - 970, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:96.7(Nuclear Science & Technology)Usami, Hiroshi; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Ooka, Makoto; Miura, Kuniaki*; Onizawa, Tatsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Tanifuji, Yuta; Usami, Hiroshi; Miyamura, Hiroko; Ozawa, Shingo*; Izumi, Ryo*; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Suzuki, Toshikazu*; et al.
no journal, ,
Sato, Yuki; Tanifuji, Yuta; Terasaka, Yuta; Usami, Hiroshi; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Usami, Hiroshi; Morishita, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Sugita, Takeshi*; Kobayashi, Ikuo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yuki; Tanifuji, Yuta; Terasaka, Yuta; Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Usami, Hiroshi; Morishita, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanifuji, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Usami, Hiroshi; Morishita, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
3-D radiation distribution measurements were conducted inside and outside Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station using compact Compton camera and photogrammetry technique. By using remote radiation imaging system using unmanned helicopter and Compton camera, radiation distribution was measured remotely at the outdoor environment of Fukushima prefecture. Furthermore, 3-D visualization of hotspot was demonstrated by combining the radiation distribution with the 3-D structural model created by photogrammetry. Under the high dose rate environment inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station building, 3-D radiation distribution was reconstructed using the Compton camera data measured from multiple angles. These methods may contribute to the reduction of external dose of workers because workers will be able to recognize the position of hotspots in advance.
Kaburagi, Masaaki; Sato, Yuki; Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Terasaka, Yuta; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
The 45th annual Waste Management Symposium in a forum for discussing and seeking safe and cost-effective solutions to managing and dispositioning radioactive waste and decommissioning nuclear facilities is hold, JAEA participates in it as the exhibitor. This is the introduction of the radiation imaging technology, which is one of the R&D of the acceleration of the decommissioning of the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Station.
Nanda, N.*; Usami, Hiroshi; Morishita, Yuki; Sugita, Takeshi*; Torii, Tatsuo; Yasuda, Nakahiro*
no journal, ,
Kodama, Shohei*; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Hayashi, Masateru*; Tanaka, Hiroki*; Yoshino, Masao*; Kamada, Kei*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
After Fukushima 1st Nuclear Plant accident, a large number of radioactive pollutants or nuclear debris with very high dose of more than a few Sv/h still have existed. To estimate the dose of such pollutants, a Japan Atomic Energy Agency research group has suggested a new technique to use a long optical fiber and a red-emitting scintillator, and the scintillation photons are read outside of high dose area. We tested the gamma-ray detection performance of a ruby (Cr:Al O
O ) and a newly developed Cs
) and a newly developed Cs HfI
HfI scintillators as a scintillating probe coupled with an optical fiber in this study.
scintillators as a scintillating probe coupled with an optical fiber in this study.
Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Morishita, Yuki; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Usami, Hiroshi; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Morishita, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Usami, Hiroshi; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki*; Utsugi, Wataru*; Takahira, Shiro*
no journal, ,
We measured alpha emitters obtained from a reactor building in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) by using an alpha particle imaging detector. For developing the detector, we used a very thin (0.05-mm-thick) a cerium-doped Gd (Ga,Al)
(Ga,Al)  O
O (Ce GAGG) scintillator and silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) arrays as the photodetector. The floor of the reactor building in FDNPP was wiped off by using smear papers, and the radioactivity of these papers was measured by the alpha particle imaging detector. In addition, we measured a Plutonium (Pu) sample (mainly 5.5 MeV alpha particles from
(Ce GAGG) scintillator and silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) arrays as the photodetector. The floor of the reactor building in FDNPP was wiped off by using smear papers, and the radioactivity of these papers was measured by the alpha particle imaging detector. In addition, we measured a Plutonium (Pu) sample (mainly 5.5 MeV alpha particles from  Pu) obtained from a nuclear fuel facility by using of the same detector for comparison with the smear papers. The alpha spectrum was in the energy range of 5-6 MeV, which corresponds to the alpha particle energy of
Pu) obtained from a nuclear fuel facility by using of the same detector for comparison with the smear papers. The alpha spectrum was in the energy range of 5-6 MeV, which corresponds to the alpha particle energy of  Pu (5.5 MeV). The correlation coefficient of the alpha spectra of the smear papers and the Pu sample had a strong positive linear relation. Moreover, the peak of
Pu (5.5 MeV). The correlation coefficient of the alpha spectra of the smear papers and the Pu sample had a strong positive linear relation. Moreover, the peak of  Am was identified by gamma spectrum measurement. Based on these results, it is highly likely that the alpha emitters in the reactor building of FDNPP are
Am was identified by gamma spectrum measurement. Based on these results, it is highly likely that the alpha emitters in the reactor building of FDNPP are  Pu and
Pu and  Am, which originated from the nuclear fuel. The surface contamination level of alpha emitters exceeded 4 Bq/cm
Am, which originated from the nuclear fuel. The surface contamination level of alpha emitters exceeded 4 Bq/cm .
.
Usami, Hiroshi; Morishita, Yuki; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Aoki, Katsunori; Tsurudome, Koji; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Morishita, Yuki; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*; Tamura, Ken; Usami, Hiroshi; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki*; Utsugi, Wataru*; Takahira, Shiro*; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
We have developed new alpha particle detectors for detecting the alpha contaminations accurately and instantaneously: alpha imaging detectors and alpha dust monitors. For the development of the alpha imaging detector, we used a thin cerium-doped Gd (Ga,Al)
(Ga,Al) O
O (Ce: GAGG) scintillator and silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs). The thin GAGG scintillator was optically coupled to a light-guide and the SiPMs for the detector fabrication. The detector showed a good energy resolution for 5.5 MeV alpha particles (
(Ce: GAGG) scintillator and silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs). The thin GAGG scintillator was optically coupled to a light-guide and the SiPMs for the detector fabrication. The detector showed a good energy resolution for 5.5 MeV alpha particles ( 13 % at the full width at half maximum (FWHM)). The detector is capable of capturing two-dimensional alpha images. This detector also has the advantage of its compact size, which enables to measure the alpha contaminations in narrow spaces. We demonstrated the actual measurement of smear samples obtained from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station using the developed imaging detector. Commercial alpha dust monitors with a silicon surface barrier detector (SSBD) operating at some nuclear facilities frequently produced false alarms due to environmental conditions such as humidity. For the development of the alpha dust monitor, we used a cerium-doped Gd
13 % at the full width at half maximum (FWHM)). The detector is capable of capturing two-dimensional alpha images. This detector also has the advantage of its compact size, which enables to measure the alpha contaminations in narrow spaces. We demonstrated the actual measurement of smear samples obtained from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station using the developed imaging detector. Commercial alpha dust monitors with a silicon surface barrier detector (SSBD) operating at some nuclear facilities frequently produced false alarms due to environmental conditions such as humidity. For the development of the alpha dust monitor, we used a cerium-doped Gd Si
Si O
O (GPS) scintillator plate and a photomultiplier tube (PMT). The energy resolution for 5.5-MeV alpha particles was
(GPS) scintillator plate and a photomultiplier tube (PMT). The energy resolution for 5.5-MeV alpha particles was  12% FWHM. The count-rate of the radon progeny decreased by 77% with applying energy discrimination. The alpha dust monitor was capable of conducting alpha-particle spectroscopy even though the GPS scintillator got wet. The alpha dust monitor is an ideal choice for in places lacking temperature and humidity controls. In the presentation at the IRPA 15 conference, we will present the developments and measurement results of these alpha detectors.
12% FWHM. The count-rate of the radon progeny decreased by 77% with applying energy discrimination. The alpha dust monitor was capable of conducting alpha-particle spectroscopy even though the GPS scintillator got wet. The alpha dust monitor is an ideal choice for in places lacking temperature and humidity controls. In the presentation at the IRPA 15 conference, we will present the developments and measurement results of these alpha detectors.
森下 祐樹; 鳥居 建男; 宇佐美 博士
not registered
【課題】透過力の低い放射線を高感度で検知し、これによって放射性物質を検知する。 【解決手段】試料Sにおいては、平面状のろ紙Fの一方の側の表面に測定対象物質粒子Rが転写されている。第1検出部11はこの測定対象物質粒子Rが転写された表面側に密着して使用される。一方、第2検出部12は第1検出部11とは上下関係が反転された状態で試料Sの反対側の表面側に密着されて使用される。第1検出部11によって得られた第1スペクトルから第2検出部12によって得られた第2スペクトルを減算したエネルギースペクトルを算出することができる。このエネルギースペクトルにおいては、β線の影響が低減され、α線の影響が強調される。このため、このα線を発する放射性物質を高感度で検知することができる。