Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawashima, Katsuyuki; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Okubo, Tsutomu; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles (FR 2009) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2012/00
Sodium-cooled fast reactor core design considerations are made to improve the proliferation resistance by focusing on the plutonium generated in the UO blanket in the frame of the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) project. The appropriate design and treatments of the UO
blanket in the frame of the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) project. The appropriate design and treatments of the UO blanket help to reduce the intrinsic proliferation potentials. Based on the 1500 MWe FaCT reference core, the three different cores (radial blanket-free core, the core with the low-enriched MOX fuel, and the core with MA-doped UO
blanket help to reduce the intrinsic proliferation potentials. Based on the 1500 MWe FaCT reference core, the three different cores (radial blanket-free core, the core with the low-enriched MOX fuel, and the core with MA-doped UO fuel) are configured to meet the provisional proliferation resistance criteria as well as the core performance targets.
fuel) are configured to meet the provisional proliferation resistance criteria as well as the core performance targets.
Naganuma, Masayuki; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Kotake, Shoji*
Nuclear Technology, 170(1), p.170 - 180, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)In FaCT project, sodium-cooled fast reactor with mixed-oxide fuel was selected as the primary candidate. Present study focused on effects of TRU composition on the design of JSFR. In a transitional stage from LWR to FBR, there is possibility for the JSFR fuel to have high MA content due to recycle of LWR spent fuel. That affects core and fuel designs (core reactivity, material property and so on). Thus, to evaluate the effects quantitatively, design studies for the JSFR cores with two TRU compositions were conducted, one was FBR multi-recycle composition with about 1wt% of MA and the other was LWR recycle one, for which 3wt% of MA was assumed as a typical composition. The results showed that the change from FBR multi-recycle composition to LWR recycle one leads to 10% increase of sodium void reactivity, 1-2% decrease of linear power limit and 5% extension of gas plenum length. As a result, effects of TRU composition on the core and fuel designs were indicated to be benign.
Okano, Yasushi; Kobayashi, Noboru*; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Naganuma, Masayuki; Okubo, Tsutomu; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Ogata, Takanari*; Ueda, Nobuyuki*; Nishimura, Satoshi*
JAEA-Research 2009-025, 105 Pages, 2009/10
A metal fuel core has specific features on high heavy metal density, hard neutron spectrum, and efficient neutron utilization. Enlarged applicable design envelops would improve core performances and features: higher breeding ratio, compacted reactor core, and, smaller amount of Pu-fissile inventory. A joint study on "Reactor Core and Fuel Design of Metal Fuel Core of Sodium Cooled Fast Reactor" by Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry has been conducted during Japanese fiscal years of 2007 and 2008. This report shows the results on (1) the study on applicable design ranges of metal fuel specifications, (2) the study on conceptual core designs for high breeding ratio, and (3) the safety study on metal fuel core designed in the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) Project.
Kobayashi, Noboru; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Ogata, Takanari*
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 3(1), p.126 - 135, 2009/00
Utilizing advantages of the metal fuel core to the mixed oxide fuel one, such as its higher breeding ratio and compact core size, a conceptual design for a high breeding ratio was performed without blanket fuels. The design conditions were set so a sodium void worth of less than 8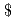 , a core height of less than 150 cm, a maximum cladding temperature of 650
, a core height of less than 150 cm, a maximum cladding temperature of 650 C, and a fuel pin bundle pressure drop of 0.4 MPa. The breeding ratio of the resultant core was 1.34 with 6wt% zirconium content fuel. Applying 3wt% zirconium content fuel enhanced the breeding ratio up to 1.40.
C, and a fuel pin bundle pressure drop of 0.4 MPa. The breeding ratio of the resultant core was 1.34 with 6wt% zirconium content fuel. Applying 3wt% zirconium content fuel enhanced the breeding ratio up to 1.40.
Oki, Shigeo; Ogawa, Takashi; Kobayashi, Noboru; Naganuma, Masayuki; Kawashima, Katsuyuki; Maruyama, Shuhei; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Tanaka, Toshihiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2008/09
Conceptual design studies of sodium-cooled fast reactor core are performed in Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development Project (FaCT Project) in Japan. The representative MOX fuel core and the metal fuel core exert excellent performances on safety and reliability, sustainability, economic competitiveness, and nuclear non-proliferation. This paper reviews their feature in terms of reactor physics, and describes recent progress in design studies. In the recent design studies, much interest has been taken in the fuel composition change in the transition stage from light water reactors to fast breeder reactors. The core flexibility is also shown to fulfil the refined objectives such as high breeding and an enhancement of non-proliferation property.
Naganuma, Masayuki; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Kubo, Shigenobu*
Proceedings of 2008 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '08) (CD-ROM), p.526 - 535, 2008/06
In FaCT project, sodium-cooled fast reactor with mixed-oxide fuel was selected as the primary candidate. Present study focused on effects of TRU composition on the design of JSFR. In a transitional stage from LWR to FBR, there is possibility for the JSFR fuel to have high MA content due to recycle of LWR spent fuel. That affects core and fuel designs (core reactivity, material property and so on). Thus, to evaluate the effects quantitatively, design studies for the JSFR cores with two TRU compositions were conducted, one was FBR multi-recycle composition with about 1wt% of MA and the other was LWR recycle one, for which 3wt% of MA was assumed as a typical composition. The results showed that the change from FBR multi-recycle composition to LWR recycle one leads to 10% increase of sodium void reactivity, 1-2% decrease of linear power limit and 5% extension of gas plenum length. As a result, effects of TRU composition on the core and fuel designs were indicated to be benign.
Kobayashi, Noboru; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Ogata, Takanari*
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2008/05
The metal fuel core is superior to the mixed oxide fuel core because of its higher breeding ratio and compact core size resulting from neutron economics, hard neutron spectrum, and high content of heavy metal nuclides. Utilizing the advantage of the metal fuel core, conceptual sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor designs have been pursued for the attractive core properties of high breeding ratio, small inventory, compact size, low sodium void reactivity, and high transmutation ratio of the minor actinides. Among attractive cores, a conceptual design for a high breeding ratio was performed without blanket fuels. The design conditions were set so a sodium void reactivity of less than 8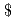 , a core height of less than 150 cm, a maximum cladding temperature of 650
, a core height of less than 150 cm, a maximum cladding temperature of 650  C, and a fuel pin bundle pressure drop of 0.4 MPa. The breeding ratio of the resultant core was 1.34 without blanket fuels.
C, and a fuel pin bundle pressure drop of 0.4 MPa. The breeding ratio of the resultant core was 1.34 without blanket fuels.
Ogawa, Takashi; Kobayashi, Noboru; Oki, Shigeo; Naganuma, Masayuki; Kubo, Shigenobu*; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
JAEA-Research 2007-084, 63 Pages, 2008/01
The sodium-cooled large-scale "high internal conversion (HIC) type" core with MOX fuel is the most promising core concept in FaCT Project in Japan. Design study on core and fuel in JFY2006 is reported. (1) Design study of the core with MOX fuel containing MA; Based on the large-scale HIC type core in FS Phase II, we have developed a core using TRU of high MA content recovered from ALWR spent fuel. MA content in the fuel heavy metal is temporarily assumed to be 3 wt%. We have confirmed the core design feasibility with the detailed evaluations of thermal hydraulic characteristics and fuel integrity. (2) Design study of the nonproliferation core by adding Pu to the blankets; As one of the measures to enhance the intrinsic nonproliferation property of fast reactors, we have developed the nonproliferation core concept that can keep the Pu in blankets to "Reactor Grade ( Pu isotope abundance ratio
Pu isotope abundance ratio  18%)" with premixing Pu (or TRU) of core fuel to blanket fuel.
18%)" with premixing Pu (or TRU) of core fuel to blanket fuel.
Oki, Shigeo; Sugino, Kazuteru; Ogawa, Takashi; Aida, Tatsuya*; Hayashi, Hideyuki
JAEA-Research 2006-077, 86 Pages, 2006/11
Core and fuel design study of 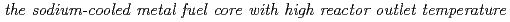 was performed. The reference specification of the large-scale (1,500 MWe) and the middle-scale (750 MWe) cores were proposed as a final result of
was performed. The reference specification of the large-scale (1,500 MWe) and the middle-scale (750 MWe) cores were proposed as a final result of  . Since the local conversion ratio of any of the core points is made close to unity with single Pu enrichment, it is possible to minimize the necessary coolant flow rate for the core region and then, accept high reactor outlet temperature of 550
. Since the local conversion ratio of any of the core points is made close to unity with single Pu enrichment, it is possible to minimize the necessary coolant flow rate for the core region and then, accept high reactor outlet temperature of 550 C. By the rationalization of hot spot factors, the coolant flow distribution design can be optimized to 5 regions for the large-scale core and 8 regions for the middle-scale core, respectively. It was also confirmed that the core specification met the criteria of fuel-assembly integrity, as well as those of shielding design. For further improvement on the reactor outlet temperature condition, the reduction of the maximum cladding inner-wall temperature was investigated with the reflection of the actual control rod insertion depth and the rationalization of the excess-reactivity uncertainty. An alternative core design was investigated by adopting the PNC-FMS steel as the cladding material instead of the ODS steel. As a result of the investigation of extending the control rod lifetime, three-cycle lifetime (which is the same as fuel assemblies) could be possible by means of the reductions in
C. By the rationalization of hot spot factors, the coolant flow distribution design can be optimized to 5 regions for the large-scale core and 8 regions for the middle-scale core, respectively. It was also confirmed that the core specification met the criteria of fuel-assembly integrity, as well as those of shielding design. For further improvement on the reactor outlet temperature condition, the reduction of the maximum cladding inner-wall temperature was investigated with the reflection of the actual control rod insertion depth and the rationalization of the excess-reactivity uncertainty. An alternative core design was investigated by adopting the PNC-FMS steel as the cladding material instead of the ODS steel. As a result of the investigation of extending the control rod lifetime, three-cycle lifetime (which is the same as fuel assemblies) could be possible by means of the reductions in  B enrichment and B
B enrichment and B C pellet diameter.
C pellet diameter.
Inaba, Yoshitomo; Fumizawa, Motoo; Hishida, Makoto; Ogawa, Masuro; Aritomi, Masanori*; Kozaki, Yasutsugu*; *; *; *; *; et al.
JAERI-Tech 96-019, 122 Pages, 1996/05
no abstracts in English
Mizoguchi, Tadanori*; *; Fujisawa, Noboru; Abe, Tetsuya; Hirayama, Toshio; Hitoki, Shigehisa*; *; Koide, Yoshihiko; *; *; et al.
JAERI-M 88-045, 126 Pages, 1988/03
no abstracts in English


 Sb
Sb; ;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 16(8), p.546 - 552, 1979/00
Times Cited Count:2no abstracts in English
;
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 14(10), p.549 - 558, 1972/00
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yoshihiko; Sato, Soichi; Inano, Masatoshi; Kimura, Arata*; Miyake, Atsumi*; Ogawa, Terushige*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Takashi; Kobayashi, Noboru; Naganuma, Masayuki; Oki, Shigeo; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Noboru; Ogawa, Takashi; Naganuma, Masayuki; Ohgama, Kazuya; Oki, Shigeo; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oki, Shigeo; Ogawa, Takashi; Kobayashi, Noboru; Naganuma, Masayuki; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Kubo, Shigenobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Noboru; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Ogata, Takanari*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oki, Shigeo; Ogawa, Takashi; Kobayashi, Noboru; Naganuma, Masayuki; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English