Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kaira, Kyoichi*; Sunose, Yutaka*; Ohshima, Yasuhiro; Ishioka, Noriko; Arakawa, Kazuhisa*; Ogawa, Tetsushi*; Sunaga, Noriaki*; Shimizu, Kimihiro*; Tominaga, Hideyuki*; Oriuchi, Noboru*; et al.
BMC Cancer, 13, p.482_1 - 482_12, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:74 Percentile:88.89(Oncology)Iguchi, Masahide; Saito, Toru; Kawano, Katsumi; Chida, Yutaka; Nakajima, Hideo; Ogawa, Tsuyoshi*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Ogata, Hiroshige*; Minemura, Toshiyuki*; Tokai, Daisuke*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(9-10), p.2520 - 2524, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:61.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)ITER TFC structures are large welding structures made of heavy thick stainless steels. JAEA plans to apply narrow gap TIG welding with FMYJJ1 which is full austenitic stainless filler material to manufacture TFC structure. FMYJJ1 is specified in "Codes for Fusion Facilities -Rules on Superconducting Magnet Structure (2008)". In order to evaluate effect of base material combinations and thickness of welded joint on tensile properties at 4 K, tensile tests were conducted at 4 K by using tensile specimens taken from 40 mm thickness weld joints of four combinations and 200 mm thickness ones of two combinations of base materials. These weld joints were manufactured by one side narrow gap TIG welding with FMYJJ1. As the results, it was confirmed that yield and tensile strengths of welded joint at 4K were decreased with decreasing of nitrogen of base material, and there were no large distribution of strengths at 4 K along the thickness of welded joints of 200 mm thickness.
Iguchi, Masahide; Chida, Yutaka; Takano, Katsutoshi; Kawano, Katsumi; Saito, Toru; Nakajima, Hideo; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Minemura, Toshiyuki*; Ogata, Hiroshige*; Ogawa, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 22(3), p.4203305_1 - 4203305_5, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:47.58(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has responsibility to procure 19 structures for ITER toroidal field (TF) coils as in-kind components. JAEA plans to use materials specified in the material section of "Codes for Fusion Facilities; Rules on Superconducting Magnet Structure (2008)" issued by the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers (JSME) in 2008. Large forged products were produced and their mechanical properties at 4K were evaluated. In addition, the following activities have been performed; (1) to optimize the design of each weld type identified in the manufacturing sequence, (2) to qualify typical welding procedure including repair, (3) to establish welding techniques other than narrow gap TIG welding with FMYJJ1, (4) to demonstrate the manufacturing procedures through manufacture of 1-m mockups and full-scale segments of TFC structure. This paper describes the results of material qualification and industrialization activities of manufacturing processes of ITER TFC structure.
Iguchi, Masahide; Chida, Yutaka; Nakajima, Hideo; Ogawa, Tsuyoshi*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Ogata, Hiroshige*; Minemura, Toshiyuki*; Miyabe, Keisuke*; Tokai, Daisuke*; Niimi, Kenichiro*
Teion Kogaku, 47(3), p.193 - 199, 2012/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted qualification and rationalization activities in Japan in order to rationalize manufacturing procedure of ITER Toroidal Field (TF) coil structures. The activities included qualification of structural materials and qualification of welding procedure according to Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers (JSME) code constituted for fusion devices, demonstration of the manufacturing method and procedures through full-scale segments of TF coil structure. From results of these activities, JAEA confirmed applicability of JSME code to actual series TF coil structures as quality control method hence the quality of structural materials and weld joints of Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) were satisfied ITER requirement. In addition, JAEA obtained knowledge of welding deformation of actual TF coil structures. This paper describes results of these qualification and development activities for TF coil structure.
 -ray spectroscopy of
-ray spectroscopy of 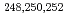 Cf by neutron-transfer reactions using a Cf target
Cf by neutron-transfer reactions using a Cf targetTakahashi, Ryuta; Ishii, Tetsuro; Asai, Masato; Nagae, Daisuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Yasuo; Matsuda, Makoto; Makishima, Akiyasu*; et al.
Physical Review C, 81(5), p.057303_1 - 057303_4, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:63.2(Physics, Nuclear)The ground-state bands of 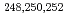 Cf have been established up to 10
Cf have been established up to 10 , 12
, 12 , and 10
, and 10 states, respectively, by in-beam
states, respectively, by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy using neutron-transfer reactions with a
-ray spectroscopy using neutron-transfer reactions with a  O beam and a highly radioactive Cf target. The deexcitation
O beam and a highly radioactive Cf target. The deexcitation  rays in
rays in 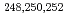 Cf were identified by taking coincidences with outgoing particles of
Cf were identified by taking coincidences with outgoing particles of  O measured with Si
O measured with Si 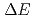 -
- detectors, and by selecting their kinetic energies. This is the first in-beam
detectors, and by selecting their kinetic energies. This is the first in-beam  -ray spectroscopy for Cf isotopes.
-ray spectroscopy for Cf isotopes.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Kinomura, Koji*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*
JAEA-Research 2009-050, 57 Pages, 2010/01
It is important to understand EDZ in assessing performance of repository and designing of plug. It is known that it remains possible that the large-scale EDZ is generated due to strain localization from boring investigations and tunnel excavation analyses and rock properties changes with increase of depth. Excavation analysis of vertical shaft in sedimentary rock taken into account strain softening, depth variation of rock properties and the actual construction procedure had been done in order to understand EDZ of Horonobe URL. The large-scale EDZ due to strain localization was generated around the border between Koetoi formation and Wakkanai formation. From result obtained from excavation analysis, scale of EDZ obtained from excavation analysis is from 60 cm to 120 cm. And it was estimated that seismic velocity changed by 20 percent, elastic modulus changed by 30 percent and hydraulic conductivity changed by 0.1 m/s order.
Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Toyota, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Takanobu*; Ogawa, Hiroyuki*; Tajima, Michio*; Hisamatsu, Tadashi*; Nakamura, Kazuyo*; Takamoto, Tatsuya*; Sato, Shinichiro; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-8), p.127 - 130, 2008/12
Results of our study of effects of high-light-intensity and high-temperature conditions (HIHT) on the output performance of an InGaP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cell are described herein. The HIHT conditions are adjusted for spacecraft environments expected for a Venus mission (Planet-C) and a Mercury mission (MMO) to be undertaken by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). Measurements of current-voltage characteristics under high light intensity for wide range of cell temperatures exhibit a kinked pattern at 0 current at +200 C. The thermal cycle test results for bare cells with a wide temperature range show no output performance degradation. Continuous operation tests of 3J cells under HIHT conditions reveal gradual current output degradation, implying that solar panel design should address decreased output specifically.
C. The thermal cycle test results for bare cells with a wide temperature range show no output performance degradation. Continuous operation tests of 3J cells under HIHT conditions reveal gradual current output degradation, implying that solar panel design should address decreased output specifically.
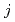 quasiparticle states in
quasiparticle states in  Cm by in-beam
Cm by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy using heavy-ion transfer reactions
-ray spectroscopy using heavy-ion transfer reactionsIshii, Tetsuro; Makii, Hiroyuki*; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Matsuda, Makoto; Makishima, Akiyasu*; Shigematsu, Soichiro*; Kaneko, Junichi*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; et al.
Physical Review C, 78(5), p.054309_1 - 054309_11, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.91(Physics, Nuclear)Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Kinomura, Koji*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya
Dai-12-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.933 - 940, 2008/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is planning to conduct researches into geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes in the Horonobe site located in Hokkaido, Japan. As part of the underground research facilities, two 500m-long vertical shafts have been constructed in tertiary sedimentary rocks since 2005. The surrounding rocks are known to exhibit strain-softening characteristics, necessitating appropriate modelling in the stability analysis. In addition the rocks physical properties often vary with depth. This study shows the results of three-dimensional numerical analysis of the ventilation shaft, taking the construction sequence and the variation of rock properties with depth into consideration.
Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Toyota, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Toru*; Ogawa, Hiroyuki*; Tajima, Michio*; Hisamatsu, Tadashi*; Nakamura, Kazuyo*; Takamoto, Tatsuya*; Sato, Shinichiro; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 8th European Space Power Conference (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/09
Results of our study of effects of high-light-intensity and high-temperature conditions (HIHT) on the output performance of an InGaP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cell are described herein. The HIHT conditions are adjusted for spacecraft environments expected for a Venus mission (Planet-C) and a Mercury mission (MMO) to be undertaken by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). Measurements of currentvoltage characteristics under high light intensity for a wide range of cell temperatures exhibit a kinked pattern at 0 current at +200 C. The thermal cycle test results for bare cells with a wide temperature range show no output performance degradation. Continuous operation tests of 3J cells under HIHT conditions reveal gradual current output degradation, implying that solar panel design should address decreased output specifically.
C. The thermal cycle test results for bare cells with a wide temperature range show no output performance degradation. Continuous operation tests of 3J cells under HIHT conditions reveal gradual current output degradation, implying that solar panel design should address decreased output specifically.
 -ray spectroscopy of neutron-rich nuclei in the uranium region through the heavy-ion transfer reaction
-ray spectroscopy of neutron-rich nuclei in the uranium region through the heavy-ion transfer reactionIshii, Tetsuro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Asai, Masato; Koura, Hiroyuki; Shigematsu, Soichiro*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Matsuda, Makoto; Makishima, Akiyasu*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 805(1-4), p.257 - 259, 2008/06
no abstracts in English
Kinomura, Koji*; Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Matsui, Hiroya; Sanada, Hiroyuki
Dai-37-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.307 - 312, 2008/01
no abstracts in English
Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Kinomura, Koji*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Matsui, Hiroya; Sanada, Hiroyuki
Dai-37-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.301 - 306, 2008/01
no abstracts in English
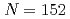 deformed shell gap; In-beam
deformed shell gap; In-beam  -ray spectroscopy of neutron-rich
-ray spectroscopy of neutron-rich 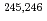 Pu
PuMakii, Hiroyuki; Ishii, Tetsuro; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Matsuda, Makoto; Makishima, Akiyasu*; Kaneko, Junichi*; Tome, Hayato*; Ichikawa, Shinichi; et al.
Physical Review C, 76(6), p.061301_1 - 061301_5, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:83.47(Physics, Nuclear)We have measured deexcitation  rays for the first time in the neutron-rich nuclei of
rays for the first time in the neutron-rich nuclei of 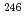 Pu
Pu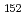 and
and 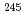 Pu
Pu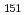 produced by the (
produced by the ( O,
O,  O) and the (
O) and the ( O,
O,  O) reactions, respectively. The ground-state band of
O) reactions, respectively. The ground-state band of 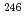 Pu was established up to 12
Pu was established up to 12 states. The systematics of the moments of inertia of
states. The systematics of the moments of inertia of 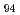 Pu isotopes suggests that the
Pu isotopes suggests that the 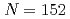 deformed subshell closure disappears in these isotopes. The measurements of deexcitation
deformed subshell closure disappears in these isotopes. The measurements of deexcitation  rays in
rays in 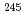 Pu shows a small energy spacing between neutron orbitals at
Pu shows a small energy spacing between neutron orbitals at 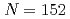 , which explans the disappearance of the subshell closure.
, which explans the disappearance of the subshell closure.
 -ray study of the neutron-rich nuclei of
-ray study of the neutron-rich nuclei of  U,
U, 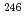 Pu, and
Pu, and 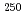 Cm produced by the (
Cm produced by the ( O,
O,  O) reaction
O) reactionIshii, Tetsuro; Shigematsu, Soichiro*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Matsuda, Makoto; Makishima, Akiyasu*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Kaneko, Junichi*; et al.
Physics of Atomic Nuclei, 70(8), p.1457 - 1461, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.38(Physics, Nuclear)We have measured deexcitation  rays in the neutron-rich nuclei of
rays in the neutron-rich nuclei of  U,
U, 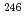 Pu and
Pu and 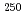 Cm. These nuclei were produced by the (
Cm. These nuclei were produced by the ( O,
O,  O) two-neutron transfer reactions with a 200, 162 and 162 MeV
O) two-neutron transfer reactions with a 200, 162 and 162 MeV  O beams and a
O beams and a  U,
U,  Pu and
Pu and  Cm targets, respectively, using the tandem accelerator at Tokai, Japan. The
Cm targets, respectively, using the tandem accelerator at Tokai, Japan. The  rays in residual nuclei were measured by taking coincidence with scattering particles using Si
rays in residual nuclei were measured by taking coincidence with scattering particles using Si 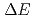 -
- detectors. We have identified
detectors. We have identified  rays in
rays in  U,
U, 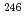 Pu and
Pu and 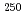 Cm by selecting the kinetic energies of
Cm by selecting the kinetic energies of  O particles which correspond to the excitation energies in these nuclei below their neutron separation energies. The ground-state bands of
O particles which correspond to the excitation energies in these nuclei below their neutron separation energies. The ground-state bands of  U,
U, 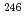 Pu and
Pu and 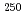 Cm were established up to 12
Cm were established up to 12 states and the
states and the 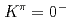 octupole band of
octupole band of  U was established up to 9
U was established up to 9 state. Because the deformations of these nuclei are well developed, the moments of inertia reflect the pairing gap, which is expected to be smaller, resulting in a larger moment of inertia, at the deformed shell closure. We have found that the moment of inertia of the ground-state band of
state. Because the deformations of these nuclei are well developed, the moments of inertia reflect the pairing gap, which is expected to be smaller, resulting in a larger moment of inertia, at the deformed shell closure. We have found that the moment of inertia of the ground-state band of  Cm
Cm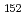 is considerably larger than that of
is considerably larger than that of 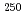 Cm
Cm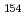 . This fact supports the existence of the deformed subshell closure at
. This fact supports the existence of the deformed subshell closure at 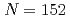 in Cm isotopes. On the other hand, the moment of inertia of
in Cm isotopes. On the other hand, the moment of inertia of 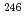 Pu
Pu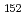 was found to be smaller than that of
was found to be smaller than that of  Pu
Pu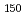 , which suggests that the deformed subshell closure at
, which suggests that the deformed subshell closure at 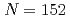 weakens or disappears in Pu isotopes. These results are consistent with the prediction by a cranking model calculation.
weakens or disappears in Pu isotopes. These results are consistent with the prediction by a cranking model calculation.
 Th and
Th and  U nuclei and implication of spherical shell closure at
U nuclei and implication of spherical shell closure at 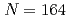
Ishii, Tetsuro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Asai, Masato; Koura, Hiroyuki; Shigematsu, Soichiro*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Matsuda, Makoto; Makishima, Akiyasu*; Kaneko, Junichi*; et al.
Physical Review C, 76(1), p.011303_1 - 011303_5, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:67.84(Physics, Nuclear)The ground-state bands of the neutron-rich  Th and
Th and  U nuclei were established up to spin 10 and 8, respectively, by in-beam
U nuclei were established up to spin 10 and 8, respectively, by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy using the (
-ray spectroscopy using the ( O,
O,  Ne) two-proton pickup reaction with a
Ne) two-proton pickup reaction with a  U and a
U and a  Pu target. Deexcitation
Pu target. Deexcitation  rays in
rays in  Th and
Th and  U were identified by selecting the kinetic energies of
U were identified by selecting the kinetic energies of  Ne using Si
Ne using Si 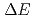 -
- detectors. The excitation energies of the first 2
detectors. The excitation energies of the first 2 states in U and Pu isotopes have local minima at
states in U and Pu isotopes have local minima at 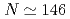 , suggesting the possibility that nuclei with
, suggesting the possibility that nuclei with 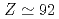 have a spherical shell closure of
have a spherical shell closure of 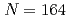 . Calculation using the Koura-Yamada single-particle potential gives an energy gap of 1.8 MeV at
. Calculation using the Koura-Yamada single-particle potential gives an energy gap of 1.8 MeV at 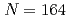 for
for  U.
U.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Jo, Mayumi*; Fujii, Yoshiaki*
Heisei-19-Nendo Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Hokkaido Shibu Sokai Oyobi Shunki Koenkai Koen Yoshishu, p.9 - 10, 2007/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting the Horonobe Underground Reseach Laboratory Project as a part of geological isolation research and development at Horonobe-town in Hokkaido, Japan. The rocks around URL have high porosity and low permeability. Therefore, the excess pore pressure caused by URL excavation is possible to affect to the stability of surrounding rock. In this point of view, the authors carried out a stress-seepage coupled analysis to understand the process of the pore pressure change due to excavation and the influence to the stability of surrounding rock and support system. As a result, the large excess pore pressure causes a part in surrounding rock on excavation in an anisotropic initial stress condition and it dissipates with time. The pore pressure change causes the complex deformation in the surrounding rock as well. However, the phenomena are not significant influence to the stability of the surrounding rock and support system.
Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Jo, Mayumi*; Matsui, Hiroya; Horii, Hideyuki*
Dai-36-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.39 - 44, 2007/01
In case rock exhibits time-dependent deformation, it is important to evaluate this effect on the tunnel stability, since the rock deforms elastically as well as inelatically even at the time of excavation. This paper introduces an engineering approach method to explain the effect of time-dependent deformation of rock at tunnel excavation stages on the stability. The mechanical parameters to describe a Burgers type rheological model are determined, based upon the drained triaxial creep test results performed on mudstone samples. With the parameters determined, plane-strain 2 dimensional numerical analyses are subsequently performed. In the analysis a couple of indices to describe the degree and timing of time-dependent deformation are introduced with reference to the instantaneous elastic deformation, and their effects on the amount of deformation and support pressure subsequent to the support erection are investigated.
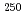 Cm
Cm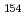
Ishii, Tetsuro; Shigematsu, Soichiro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Matsuda, Makoto; Makishima, Akiyasu*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Kaneko, Junichi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(4), p.043201_1 - 043201_4, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:68.4(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The ground-state band of the neutron-rich transuranium nucleus 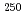 Cm was established up to spin 12 by in-beam
Cm was established up to spin 12 by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy using the two-neutron-transfer reaction with a
-ray spectroscopy using the two-neutron-transfer reaction with a  Cm target and a 162 MeV
Cm target and a 162 MeV  O beam. Deexcitation
O beam. Deexcitation  rays in
rays in 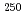 Cm were identified by selecting the kinetic energies of
Cm were identified by selecting the kinetic energies of  O particles with Si
O particles with Si 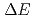 -
- detectors. The moment of inertia of
detectors. The moment of inertia of 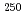 Cm
Cm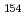 is considerably smaller than that of
is considerably smaller than that of  Cm
Cm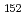 , which supports the existence of the deformed subshell closure at
, which supports the existence of the deformed subshell closure at 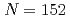 in Cm isotopes.
in Cm isotopes.
Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Matsui, Hiroya
JNC TN8400 2005-011, 157 Pages, 2005/02
Horonobe Underground Research Center has been conducting researches and developments into geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes in sedimentary rocks. In the 2003 borehole investigation programmes, 3 boreholes (HDB-6, 7, and 8) were drilled in order to acquire geoscientific information. This technical report presents the results of elastic wave velocity measurements under confining pressure, carried out on the rock cores extracted from BH HDB-6. The main observations which became clear from the laboratory tests are as follows: 1. the basic physical properties of the rock specimens are consistent with the existing measured values. Moreover, when the wet sample is dried, although P wave velocity at first shows a downward tendency, it increases gradually and approaches the dry velocity as the degree of saturation decreases. Therefore, it is felt that the sample is uniformly dried across the cross-sectional area. ; 2. It appears that the elastic wave velocities of the Horonobe sedimentary rocks are dependent upon pressure. However shear rigidity remains unchanged, even if the saturation conditions of pores change (from wet to dry conditions). In the study of anisotropy of velocities, horizontal velocity seems larger than the vertical one. Although there was no remarkable influence on elastic wave velocities when the loading and unloading of confining pressure were repeated, a certain amount of hysteresis could be observed in porosity. Continuous investigation is required. ; 3. Measured wet velocity may practically be used in evaluating in-situ velocity measurement results.