Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Uchiyama, Naoki*; Ozawa, Tatsuya*; Sato, Koji*; Kobayashi, Jun; Onojima, Takamitsu; Tanaka, Masaaki
FAPIG, (194), p.12 - 18, 2018/02
no abstracts in English
Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Ozawa, Masaki*; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Fujita, Reiko*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Okada, Ken*; Morita, Yasuji; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Procedia Chemistry, 7, p.222 - 230, 2012/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:71.08(Chemistry, Analytical)Adv.-ORIENT cycle strategy has been proposed as a basic concept for trinitarian research on separation, transmutation and utilization of nuclides and elements based on FBR fuel cycle. Validation of principal separation method and related safety research were performed from 2006 through 2011 as Phase I program. First, more than 90% of Cs could be recovered from the actual spent fuel [IXC(I) step]. The next is the adsorption of the platinum group metals (PGM), lanthanides, Am and Cm were separated by using a tertiary pyridine-type resin (TPR) as ion exchange steps [IXC(II, III, IV) steps]. The separated PGM metals will be supplied to the electrochemical extraction [CEE step]. As experiment for safety issues, Hastelloy-B at RT and Ta at 90 C were confirmed their anti-corrosive in highly concentrated HCl media. Thermo-chemical stability for TPR was verified. Issues to be solved for next phase based on the final results of phase I program.
C were confirmed their anti-corrosive in highly concentrated HCl media. Thermo-chemical stability for TPR was verified. Issues to be solved for next phase based on the final results of phase I program.
Koyama, Shinichi; Yamagishi, Isao; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Ozawa, Masaki*; Fujita, Reiko*; Okada, Ken*; Tatenuma, Katsuyoshi*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujii, Yasuhiko
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/12
Effective separation of MA and LLFP, transmutation and utilization were the main directions of Advanced OREINT Cycle project. Study for each integrant technology was concluded as first trial of the project. TPR enabled to separate MA/Ln and then Am/Cm precisely from spent fuel in HCl and HNO media. CEE method could separate the light PGM and Tc by HCl media. Recovery of Cs from simulated HLLW coul be achieved more than 90 %. In addition, the perspective for next phase was proposed.
media. CEE method could separate the light PGM and Tc by HCl media. Recovery of Cs from simulated HLLW coul be achieved more than 90 %. In addition, the perspective for next phase was proposed.
Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Reiko*; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Okada, Ken*; Ozawa, Masaki
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 53(7), p.980 - 987, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)Individual basic researches of separation step were performed in the Advanced ORIENT Cycle project. High separation selectivity for Cs and Sr by novel nano adsorbents AMP-SG (D) and D18C6-MC were confirmed, respectively. TPR well adsorbed Pd and Tc in dilute HCl condition. Formation of rare metal fission product RMFP-deposit Pt electrodes from SHLLW was verified, and it was confirmed that high catalytic reactivity on electrolytic production of hydrogen. As experiment for engineering feasibility, Hastelloy-B at RT and Ta at 90 C were confirmed their anti-corrosive in highly concentrated HCl media. Thermo-chemical stability for TPR was verified in either HCl or HNO
C were confirmed their anti-corrosive in highly concentrated HCl media. Thermo-chemical stability for TPR was verified in either HCl or HNO media toward its practical use in the separation process. Issues to be solved for optimization based on the results of lab-scale experiment have revealed in this study.
media toward its practical use in the separation process. Issues to be solved for optimization based on the results of lab-scale experiment have revealed in this study.
Ozawa, Masaki; Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*
Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Asian Nuclear Prospects 2010 (ANUP 2010) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/10
Nuclear rare metals are introduced. Advanced ORIENT cycle concept is descried toward realizing their separation, transmutation and utilization. A new hybrid separation method by IXC (Ion Exchange Chromatography) and CEE (Catalytic Electrolytic Extraction) is proposed.
Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Ozawa, Masaki
Energy Conversion and Management, 51(9), p.1799 - 1805, 2010/09
Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Ozawa, Masaki
Energy Conversion and Management, 51(9), p.1799 - 1805, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:71.46(Thermodynamics)The Ru, Rh, Pd, Tc, Mo, Cs, Sr and Lanthanides (Lns) etc. are rich in the spent fuel and are categorized as nuclear rare metal (NRM). Typical yields of Pd, Ru, Rh and Tc will reach to around 11kg, 13kg, 4kg and 3kg, respectively per metric ton of the reference fast reactor spent fuel. Especially, Mo and Lns (Dy, Er, Yb) are non-radioactive and non-exothermic elements at the separation after 5 years cooling. Stable isotopes like  Ru,
Ru,  Ru,
Ru,  Rh,
Rh,  Pd and
Pd and  Ag can be obtained without isotope separation if proper element separation of Ru/Pd, Rh/Ru, Pd/Ag, Tc/Ru will be applied. In modern utilization of the NRM, the first step is the separation from the high level liquid wastes (HLLW), and catalytic electrolytic extraction (CEE) method is applicable. The paper suggests the reality of the recycle of the NRM, with a recommendation to use light platinum group (Pt-G) and Tc after proper stockpile.
Ag can be obtained without isotope separation if proper element separation of Ru/Pd, Rh/Ru, Pd/Ag, Tc/Ru will be applied. In modern utilization of the NRM, the first step is the separation from the high level liquid wastes (HLLW), and catalytic electrolytic extraction (CEE) method is applicable. The paper suggests the reality of the recycle of the NRM, with a recommendation to use light platinum group (Pt-G) and Tc after proper stockpile.
Ozawa, Masaki; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Koyama, Shinichi; Yamagishi, Isao; Fujita, Reiko*; Okada, Ken*; Tatenuma, Katsuyoshi*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Sustainable Options & Industrial Perspectives (Global 2009) (CD-ROM), p.1117 - 1126, 2009/09
Sato, Yoshihiko*; Okada, Ken*; Akiyoshi, Miyako*; Matsunaga, Takehiro*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Koyama, Shinichi; Ozawa, Masaki
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Sustainable Options & Industrial Perspectives (Global 2009) (CD-ROM), p.962 - 969, 2009/09
The fundamental thermochemical properties of tertiary pyridine resin (TPR) and its mixtures with methanol/HCl and HNO were investigated and heating tests on gram scale with TPR/methanol/HNO
were investigated and heating tests on gram scale with TPR/methanol/HNO were carried out. It was found that TPR with HCl was thermally stable. Evident thermal decomposition peaks were identified with TPR in the presence of concentrated HNO
were carried out. It was found that TPR with HCl was thermally stable. Evident thermal decomposition peaks were identified with TPR in the presence of concentrated HNO . No specific effect was observed for methanol involving. However, it was considered that the rapidly exothermic reaction can be controlled by heating temperature.
. No specific effect was observed for methanol involving. However, it was considered that the rapidly exothermic reaction can be controlled by heating temperature.
Ozawa, Masaki; Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*
Proceedings of R'09 Twin World Congress (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2009/09
Ozawa, Masaki; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Koyama, Shinichi; Akatsuka, Hiroshi*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 50(2-6), p.476 - 482, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:90.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)For the minimization of the ecological burden originated in nuclear fuel recycling, a new R&D strategy was filed as "Adv.-ORIENT cycle". In the context, mutual precise separation of  -elements, such as minor actinide (MA)/lanthanides (Lns) and Am/Cm, are highly essential for enhancing the MA (
-elements, such as minor actinide (MA)/lanthanides (Lns) and Am/Cm, are highly essential for enhancing the MA ( Am) burning. The separation and utilization of rare metal fission products (RMFPs; Ru, Tc, etc) are a new direction in the partitioning and transmutation field. Separation of exothermic nuclides,
Am) burning. The separation and utilization of rare metal fission products (RMFPs; Ru, Tc, etc) are a new direction in the partitioning and transmutation field. Separation of exothermic nuclides,  Sr,
Sr,  Cs as well as MA, will significantly help to improve the repository tasks. A key separation media are ion exchange chromatography (IXC) by tertiary pyridine resin and a catalytic electrolytic extraction (CEE) by Pd
Cs as well as MA, will significantly help to improve the repository tasks. A key separation media are ion exchange chromatography (IXC) by tertiary pyridine resin and a catalytic electrolytic extraction (CEE) by Pd . On challenging the isotope separation of LLFP, theoretical and laboratory studies were begun for
. On challenging the isotope separation of LLFP, theoretical and laboratory studies were begun for  Cs,
Cs,  Sn in the first priority.
Sn in the first priority.
Koyama, Shinichi; Ozawa, Masaki; Okada, Ken*; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.1530 - 1536, 2007/09
Simplified separation process was proposed based on ion-exchange technique. HCl, HNO and MeOH were used as an eluent. To develop an engineering scale concept, it is indispensable to establish the condition for safety operation. Corrosion test of structural materials in the HCl was performed by using some metals. In this experiment, it was proved that the Ta, Zr, Nb and hastelloy have good endurance to HCl solution. Research of thermal hazard of pyridine-type ion-exchange resin, MeOH and HNO
and MeOH were used as an eluent. To develop an engineering scale concept, it is indispensable to establish the condition for safety operation. Corrosion test of structural materials in the HCl was performed by using some metals. In this experiment, it was proved that the Ta, Zr, Nb and hastelloy have good endurance to HCl solution. Research of thermal hazard of pyridine-type ion-exchange resin, MeOH and HNO media system was studied in the view point of fire and explosion safety. There is no hazardous reaction between IER/MeOH, HNO
media system was studied in the view point of fire and explosion safety. There is no hazardous reaction between IER/MeOH, HNO media system. In the case of more than 150
media system. In the case of more than 150 C, we should pay attention to the exothermic reaction at dried condition NO
C, we should pay attention to the exothermic reaction at dried condition NO -IER or IER/HNO
-IER or IER/HNO media system.
media system.
Ozawa, Masaki; Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujita, Reiko*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.451 - 457, 2007/09
To minimize the ecological burden originating in nuclear fuel recycling, a new R&D strategy, Adv.-ORIENT (Advanced Optimization by Recycling Instructive ElemeNTs) cycle, was set forth. A key separation tool is ion exchange chromatography (IXC) by a tertiary pyridine resin having soft donor nitrogen atoms. This method has provided individual recovery of pure Am and Cm products with a Pu/U/Np fraction from irradiated fuel in just a 3-step separation. A catalytic electrolytic extraction (CEE) method by Pd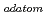 has been employed to separate, purify and fabricate RMFP catalysts. High separation efficiency of RMFP proved hydrochloric acid as a suitable media for their recovery. Different functioned ion exchangers, e.g., ammonium molybdophosphate (AMP), have been investigated for the separation of Cs
has been employed to separate, purify and fabricate RMFP catalysts. High separation efficiency of RMFP proved hydrochloric acid as a suitable media for their recovery. Different functioned ion exchangers, e.g., ammonium molybdophosphate (AMP), have been investigated for the separation of Cs . Theoretical and laboratory studies on the isotope separation of LLFPs were begun for
. Theoretical and laboratory studies on the isotope separation of LLFPs were begun for  Se,
Se,  Sn and
Sn and  Cs.
Cs.
Ozawa, Masaki; Fujita, Reiko*; Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Proceedings of 9th OECD/NEA Information Exchange Meeting on Actinide and Fission Product Partitioning and Transmutation, p.315 - 324, 2007/00
Catalytic Electrolytic extraction method has been studied as a separation tool for rare metal fission products, RMFP in the spent nuclear fuel. In an employed CEE process, Pd cation itself would not only be easily deposited from various nitric acid solutions, but enhance also the deposition of co-existing RuNO
cation itself would not only be easily deposited from various nitric acid solutions, but enhance also the deposition of co-existing RuNO , ReO
, ReO
 and
and  TcO
TcO
 by acting as a catalyst. The quaternary-, Pd-Ru-Rh-Re, deposit Pt or Ti electrode, fabricated by CEE, suggested the highest cathodic current corresponding to the hydrogen generation reaction in both alkaline solution and sea water. Advanced ORIENT Cycle, where ion exchange chromatography using tertiary pyridine resin and the CEE employ as mainstay separation technology, will enhance separation and utilization of actinide and fission product, and thus be expected to realize ultimate reducing radioactive wastes.
by acting as a catalyst. The quaternary-, Pd-Ru-Rh-Re, deposit Pt or Ti electrode, fabricated by CEE, suggested the highest cathodic current corresponding to the hydrogen generation reaction in both alkaline solution and sea water. Advanced ORIENT Cycle, where ion exchange chromatography using tertiary pyridine resin and the CEE employ as mainstay separation technology, will enhance separation and utilization of actinide and fission product, and thus be expected to realize ultimate reducing radioactive wastes.
Ozawa, Masaki; Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Czechoslovak Journal of Physics, 56(Suppl.D), p.D579 - D587, 2006/12
Radiochemical separation experiments have been performed in order to realize a novel reprocessing method based on ion-exchange technique. The newly synthesized soft-donor type tertiary pyridine resin was dedicated to the experiments, where highly irradiated mixed oxide fuel from the experimental fast reactor JOYO was used as a reference spent fuel. With a 3 step separation, pure Am and Cm were individually obtained as MA products, and  Ru group, Lns with
Ru group, Lns with  Cs (HLLW group) and Pu group were fractionated, respectively. The decontamination factor of
Cs (HLLW group) and Pu group were fractionated, respectively. The decontamination factor of  Cs and trivalent lanthanides (
Cs and trivalent lanthanides ( Eu,
Eu,  Ce) in the Am product exceeded 39,000 and 100,000, respectively. The decontamination factor for the mutual separation of
Ce) in the Am product exceeded 39,000 and 100,000, respectively. The decontamination factor for the mutual separation of  Cm and
Cm and  Am was larger than 2200 for the Am product. Moreover, the content of
Am was larger than 2200 for the Am product. Moreover, the content of  Cs, trivalent lanthanides and
Cs, trivalent lanthanides and  Cm in Am product did not exceed 2 ppm. The tertiary pyridine resin method suggests a reality as a candidate separation system for an "advanced ORIENT process", where total separation, transmutation and utilization of An, LLFP and rare metal fission product (RMFP) were oriented.
Cm in Am product did not exceed 2 ppm. The tertiary pyridine resin method suggests a reality as a candidate separation system for an "advanced ORIENT process", where total separation, transmutation and utilization of An, LLFP and rare metal fission product (RMFP) were oriented.
Ozawa, Tatsuya; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Suto, Makoto; Aoyama, Yoshio; Yamaguchi, Hiromi
JAEA-Technology 2006-050, 88 Pages, 2006/11
Melting treatment is one of the volume reduction processes for nonflammable radioactive solid wastes. Though it is applied to the volume reduction process for the low-level radioactive wastes generated at nuclear power plants, it still has technical problems to be solved. The results of our previous investigation of existing melting treatment facilities and conceptual design of the melting treatment system for transuranic waste, made these technical problems clear. To solve them, we have been carrying out the experiments of melting treatment of the simulated transuranic wastes which are nonflammable solid wastes. This report describes the progress in investigating these problems, as well as the results of recent experiments.
Koyama, Shinichi; Ozawa, Masaki; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(6), p.681 - 689, 2006/06
Multi-functional spent fuel reprocessing process was established based on ion-exchange method under collaboration between Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) and Tokyo Institute of Technology (TITEC). The tertiary pyridine-type anion exchange resin developed by TITEC was used in this experiment. The separation process was designed in hot laboratory of JNC and demonstrated by applying highly irradiated MOX fuel. As the results of experiment, we could effectively separate to some element groups. According to the results, the separation process consisting of 3 steps was proposed as follows; (1) Platinum group element separation as a pre-filtration step (STEP-I), (2) Sequential separation step of trivalent lanthanides, trivalent actinides and plutonium as for fuel matrix (STEP-II), (3) Mutual separation step of americium and curium (STEP-III)In these processes, general reagents were only used and the resin could be recycled, in addition to be salt-free CHON compounds. And we can cope with the problem of secondary waste from a new reprocessing process.
Ozawa, Tatsuya; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi; Bamba, Tsunetaka; Nakayama, Shinichi; Hotta, Katsutoshi*
JAEA-Technology 2006-001, 11 Pages, 2006/02
Melting treatment is a candidate solidification technique for nonflammable low-level radioactive wastes including metals, incineration ashes, and glasses. Simulated incineration ashes of a wide range of chemical compositions were molten at 1,600 C to produce lab-scale slag form. No visible pores and separated phases were observed in the slag specimens. It was found by optical observation that some precipitates and small voids were uniformly distributed in many of the specimens. The precipitates were identified to be iron oxides by XRD analysis. The present tests indicate that melting treatment is technically capable to produce stable slag from incineration ashes, which is one of representative TRU-cotaminated radioactive wastes.
C to produce lab-scale slag form. No visible pores and separated phases were observed in the slag specimens. It was found by optical observation that some precipitates and small voids were uniformly distributed in many of the specimens. The precipitates were identified to be iron oxides by XRD analysis. The present tests indicate that melting treatment is technically capable to produce stable slag from incineration ashes, which is one of representative TRU-cotaminated radioactive wastes.
Ozawa, Masaki; Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 6(3), p.275 - 278, 2005/12
None
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Hotta, Katsutoshi*; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi*; Ozawa, Tatsuya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 4(4), p.242 - 247, 2005/12
no abstracts in English