Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku*; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.14971_1 - 14971_8, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:78.94(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.30720_1 - 30720_7, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:63.65(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In this Letter, we report model verifications for a key physics for the L-H transition. Radial electric field excitation, using discharges having a two-step transition. Examining time derivative of Poissons equation, it is found that the sum of the loss cone loss current and neoclassical bulk viscosity current agrees the experimentally observed current in the order of magnitude at the first transition. Following second transition and an ambipolar condition in the L-mode cannot be explained by the models.
Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(7), p.073017_1 - 073017_14, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:77.37(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In the JFT-2M tokamak, limit-cycle oscillation among several variables is observed before L-to-H transition. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the LCO is analyzed in detail. Zonal fows are not seen, and modulation in edge-localized poloidal flow and density gradient is observed. Modulation is also seen in Reynolds stress, caused by that in turbulence intensity and turbulence wavenumber. However, flow acceleration is not able to be explained by the modulation in the Reynolds stress. Rapid inward propagation in density gradient and turbulence packet is also observed. Characteristics of the propagation are veried by means of turbulence spreading theory and diffusion theory.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Matsunaga, Go; Honda, Mitsuru; Miyato, Naoaki; Urano, Hajime; Kamada, Yutaka; Ida, Katsumi*; Ito, Kimitaka*; JT-60 Team
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 54(4-6), p.591 - 598, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 111(3), p.035002_1 - 035002_5, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:102 Percentile:94.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In this Letter, we report analyses of spatiotemporal dynamics of turbulence and structure in the limit cycle oscillation that precedes L-to-H transition. Zonal flows are not observed during LCO, and the oscillation is the periodic generations/decays of barrier with edge localized mean flow. Oscillatory Reynolds stress is found too small to accelerate the LCO flow. Changes of the density gradient and turbulence amplitude are found to propagate into the core in a ballistic manner, suggesting a cause of fast change of core transport after H-mode transition.
Ida, Katsumi; Kamiya, Kensaku; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 89(5), p.319 - 327, 2013/05
This paper provides and proposes a new technique to determine the location of the LCFS that is based on a characterization of the Er structure derived from CXS measurements in the LHD. We found that the spatial derivative in the Er structure had the local maximum value at the region very near, or possibly outside the vacuum LCFS location of vacuum magnetic field at the outer midplane in the low beta plasma.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Ida, Katsumi*; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; LHD Experimental Group*
Nuclear Fusion, 53(1), p.013003_1 - 013003_9, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:59.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper provides and proposes a new technique to determine the location of the LCFS that is based on a characterization of the 
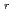 structure derived from CXS measurements in the LHD. We found that the spatial derivative in the
structure derived from CXS measurements in the LHD. We found that the spatial derivative in the 
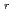 structure had the local maximum value at the region very near, or possibly outside the vacuum LCFS location of vacuum magnetic field at the outer midplane in the low
structure had the local maximum value at the region very near, or possibly outside the vacuum LCFS location of vacuum magnetic field at the outer midplane in the low  plasma.
plasma.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Honda, Mitsuru; Miyato, Naoaki; Urano, Hajime; Yoshida, Maiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Oyama, Naoyuki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 52(11), p.114010_1 - 114010_12, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:41.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Depending on the direction of the external tangential momentum input, substantial changes in not only toroidal but also poloidal flows for the carbon impurity ions are observed at around the 
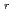 -well region. The shear in the edge
-well region. The shear in the edge 
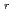 becomes wider in the co-NBI case, while the edge
becomes wider in the co-NBI case, while the edge 
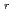 -well becomes deeper in the counter-NBI case.
-well becomes deeper in the counter-NBI case.
Ida, Katsumi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Isayama, Akihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; JT-60 Team
Physical Review Letters, 109(6), p.065001_1 - 065001_4, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:83.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The transport inside the magnetic island is investigated in the plasma during the transient phase after the back transition from  -mode to
-mode to  -mode, where a sudden drop of temperature outside the magnetic island causes a peaking of ion temperature at the
-mode, where a sudden drop of temperature outside the magnetic island causes a peaking of ion temperature at the 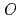 -point inside the magnetic island.
-point inside the magnetic island.
Ida, Katsumi*; Dong, J. Q.*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Kwon, J. M.*; Diamond, P. H.*
Nuclear Fusion, 52(2), p.027001_1 - 027001_10, 2012/02
This conference report summarizes the contributions to, and discussions at, the 1st Asia-Pacific Transport Working Group Meeting held in Toki, Japan, on 14-17 June 2011. The topics of the meeting were organized under four main headings: momentum transport, non-locality in transport, edge turbulence and L to H transition and 3D effects on transport physics. The events which initiated this meeting are also described in this report.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Kojima, Atsushi; Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Ida, Katsumi*; Kurki-Suonio, T.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(5), p.053009_1 - 053009_3, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:47.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We revisited to measure the edge impurity ion dynamic with new CXRS in the hot ion H-mode regime at the high magnetic field having two steps transition where a jump of Ti gradient precedes a jump of impurity Vp. Two discrete phases with different magnitude of Er in the H-phase have been observed. One is the intermediate H-phase having a large Ti gradients without significant Vp of impurity species with moderate magnitude of Er, and the other is the complete H-phase characterized by a large Er.
Wakasa, Arimitsu*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Miki, Masayuki*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Sato, Masahiko*; Toda, Shinichiro*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; Tanaka, Kenji*; Ida, Katsumi*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
 -mode edge
-mode edgeKamiya, Kensaku; Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Kojima, Atsushi; Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Kamada, Yutaka
Physical Review Letters, 105(4), p.045004_1 - 045004_4, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:78.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nagaoka, Kenichi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Osakabe, Masaki*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095024_1 - 095024_9, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:73.08(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dynamics of ion internal transport barrier (ITB) formation and impurity transport both in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and JT-60U tokamak are described. Significant differences between heliotron and tokamak plasmas are observed. The location of the ITB moves outward during the ITB formation regardless of the sign of magnetic shear in JT-60U and the ITB becomes more localized in the plasma with negative magnetic shear. In LHD, the low Te/Ti ratio ( 1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Tanaka, Kenji*; Ide, Shunsuke; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(1), p.015005_1 - 015005_7, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:48.16(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Transport analysis during the transient phase of heating (a dynamic transport study) applied to the plasma with internal transport barriers (ITBs) in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and the JT-60U tokamak is described. In the dynamic transport study the time of transition from the L-mode plasma to the ITB plasma is clearly determined by the onset of flattening of the temperature profile in the core region and a spontaneous phase transition from a zero curvature ITB (hyperbolic tangent shaped ITB) or a positive curvature ITB (concaved shaped ITB) to a negative curvature ITB (convex shaped ITB) and its back-transition are observed. The flattening of the core region of the ITB transition and the back-transition between a zero curvature ITB and a convex ITB suggest the strong interaction of turbulent transport in space.
Tanaka, Kenji*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Muraoka, Katsunori*; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Comparative studies were carried out in LHD heliotron and JT-60U tokamak plasmas to elucidate the most essential parameter(s) for control of density profiles in toroidal systems. A difference in the collisionality dependence was found between the two devices. In LHD, the density peaking factor decreased with decrease of the collisionality at the magnetic axis position (R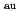 ) 3.6 m, while the density peaking factor gradually increased with a decreased of collisionality at R
) 3.6 m, while the density peaking factor gradually increased with a decreased of collisionality at R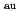 = 3.5 m. On the other hand, in JT-60U, the density peaking factor clearly increased with a decrease of the collisionality. The difference in the collisionality dependence between R
= 3.5 m. On the other hand, in JT-60U, the density peaking factor clearly increased with a decrease of the collisionality. The difference in the collisionality dependence between R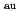 = 3.5 and R
= 3.5 and R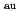 = 3.6 m is likely due to the contribution of the anomalous transport. At R
= 3.6 m is likely due to the contribution of the anomalous transport. At R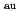 = 3.5 m, larger anomalous transport caused a similar collisionality dependence. Change of the fluctuation property was observed with different density profiles in the plasma core region on both devices. In JT-60U, the increase of the radial coherence was observed with higher density peaking profile suggesting enhanced diffusion and inward directed pinch. For a magnetic axis positions (R
= 3.5 m, larger anomalous transport caused a similar collisionality dependence. Change of the fluctuation property was observed with different density profiles in the plasma core region on both devices. In JT-60U, the increase of the radial coherence was observed with higher density peaking profile suggesting enhanced diffusion and inward directed pinch. For a magnetic axis positions (R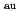 ) at 3.6 m in LHD, the increase of the fluctuation power with an increase in P
) at 3.6 m in LHD, the increase of the fluctuation power with an increase in P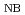 was observed for a hollow density profile suggesting an increase on diffusion due to anomalous processes. Change of density profiles from peaked to hollow indicates change in the convection direction. This is due to increase in neoclassical processes. The reduction of the density peaking factor with increase of P
was observed for a hollow density profile suggesting an increase on diffusion due to anomalous processes. Change of density profiles from peaked to hollow indicates change in the convection direction. This is due to increase in neoclassical processes. The reduction of the density peaking factor with increase of P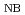 in LHD is partly due to the neoclassical effect and partly due to the anomalous effect.
in LHD is partly due to the neoclassical effect and partly due to the anomalous effect.
Ida, Katsumi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ito, Kimitaka*; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Kobuchi, Takashi*; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 101(5), p.055003_1 - 055003_4, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:79.52(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A spontaneous transition phenomena between two meta-stable states of plasmas with internal transport barrier (ITB), that are characterized by different radial profiles of second derivative of ion temperature inside the ITB region where the ion temperature gradient is large, is observed in the steady-state phase of magnetic shear in the negative magnetic shear plasma in JT-60U tokamak. The curvature asymmetry factor evaluated from the radial profile of second derivative of ion temperature profiles changes from 0.08 (symmetric curvature ITB) to -0.43 (asymmetric curvature ITB) during transition phase.
Tanaka, Kenji*; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Wakasa, Arimitsu*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Muraoka, Katsunori*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Tokuzawa, Tokihiko*; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 3, p.S1069_1 - S1069_7, 2008/08
Density profiles in LHD were measured and particle transport coefficients were estimated from density modulation experiments in LHD. The dataset of different magnetic axis, toroidal magnetic filed and heating power provided data set of widely scanned neoclassical transport. At minimized neoclassical transport configuration (
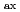 = 3.5 m,
= 3.5 m, 
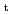 = 2.8 T) showed peaked density profile. Its peaking factor increased gradually with decrease of collisional frequency. This is a similar result observed in JT-60U. At other configuration, peaking factor reduced with decrease of collsional frequency. Data set showed that larger contribution of neoclassical transport produced hollowed density profile. Comparison between neoclassical and estimated particle diffusivity showed different minimum condition. Clear difference of spatial profile of turbulence was observed between hollowed and peaked density profiles. Major part of fluctuation existed in the unstable region of ion temperature gradient mode.
= 2.8 T) showed peaked density profile. Its peaking factor increased gradually with decrease of collisional frequency. This is a similar result observed in JT-60U. At other configuration, peaking factor reduced with decrease of collsional frequency. Data set showed that larger contribution of neoclassical transport produced hollowed density profile. Comparison between neoclassical and estimated particle diffusivity showed different minimum condition. Clear difference of spatial profile of turbulence was observed between hollowed and peaked density profiles. Major part of fluctuation existed in the unstable region of ion temperature gradient mode.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(7), p.465 - 467, 2008/07
no abstracts in English
Ida, Katsumi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Kobuchi, Takashi*; Matsunaga, Go; Koide, Yoshihiko
Review of Scientific Instruments, 79(5), p.053506_1 - 053506_6, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:62.72(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new technique to measure the first and second derivative of the ion temperature profile has been developed using a charge exchange spectroscopy system with space modulation optics. The space observed is scanned up to  3 cm with a cosine wave modulation frequency up to 30 Hz by shifting the object lens in front of the optical fiber bundle by 0.5 mm with a piezoelement. The first and second derivatives of ion temperature are derived from the modulation component of the ion temperature measured using Fourier analysis.
3 cm with a cosine wave modulation frequency up to 30 Hz by shifting the object lens in front of the optical fiber bundle by 0.5 mm with a piezoelement. The first and second derivatives of ion temperature are derived from the modulation component of the ion temperature measured using Fourier analysis.