Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kokubun, Yuji; Nakada, Akira; Seya, Natsumi; Koike, Yuko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Yamada, Ryohei*; Uchiyama, Rei; Yamashita, Daichi; Nagai, Shinji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-046, 164 Pages, 2024/03
The Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories conducts environmental radiation monitoring around the reprocessing plant in accordance with the "Safety Regulations for Reprocessing Plant of JAEA, Part IV: Environmental Monitoring". This report summarizes the results of environmental radiation monitoring conducted during the period from April 2022 to March 2023 and the results of dose calculations for the surrounding public due to the release of radioactive materials into the atmosphere and ocean. In the results of the above environmental radiation monitoring, many items were affected by radioactive materials emitted from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant of Tokyo Electric Power Company, Incorporated (changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016), which occurred in March 2011. Also included as appendices are an overview of the environmental monitoring plan, an overview of measurement methods, measurement results and their changes over time, meteorological statistics results, radioactive waste release status, and an evaluation of the data which deviated of the normal range.
Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Futagawa, Kazuo; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Yamada, Ryohei*; Uchiyama, Rei; Yamashita, Daichi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-078, 164 Pages, 2023/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2021 to March 2022. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Hikima, Ryoichi*; Hirano, Toru*; Yamashita, Masayuki*; Ishiyama, Koji*; Tanno, Takeo*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Research 2013-040, 51 Pages, 2014/03
For the research and development about high-level radioactive waste disposal, it is important to evaluate the mechanical stability of the excavation and the long-term behavior of in situ rock. However, from the limited information such as the bowling core before the excavation, it is difficult to evaluate the mechanical properties of in situ rock containing cracks. For this reason, evaluation of rock properties based on Specific Energy using mechanical data from an excavation machine is carried out. This report describes the results of the joint research carried out in FY 2010 to FY 2012.
Hikima, Ryoichi*; Hirano, Toru*; Yamashita, Masayuki*; Ishiyama, Koji*; Sato, Toshinori; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Tanno, Takeo
Heisei-25 Nendo (2013 Nen) Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Shuki Taikai Koenshu, p.247 - 248, 2013/08
no abstracts in English
Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Uzawa, Akiko*; Takase, Nobuhiro*; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Noguchi, Miho; Koda, Kana*; Ozaki, Masakuni*; Yamashita, Kei*; Li, H.*; Kase, Yuki*; et al.
Mutation Research; Genetic Toxicology And Environmental Mutagenesis, 756(1-2), p.146 - 151, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:62.77(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)Niizato, Tadafumi; Imai, Hisashi*; Maekawa, Keisuke; Yasue, Kenichi; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Shiozaki, Isao*; Yamashita, Ryo*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
A critical issue for building confidence in the long-term safety of geological disposal is to demonstrate the stability of the geosphere, taking into account its likely future evolution. This study aims to establish comprehensive techniques for characterising the overall evolution of coastal sites through studying the palaeohydrogeological evolution in the coastal system around the Horonobe area, Hokkaido, northern Japan. Information on natural events and processes related to the palaeohydrogelogical evolution of the area have been integrated into the conceptual models that indicates the temporal and spatial sequences of the events and processes, such as climatic and sea-level changes, palaeogeography, and geomorphological and geological evolution in the area. The groundwater flow simulation, which is based on the conceputualisation of the long-term geosphere evolution, shows the sensitivities of natural events and processes on groundwater flow properties in a coastal setting.
Hikima, Ryoichi; Sato, Toshinori; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Tanno, Takeo; Hirano, Toru*; Yamashita, Masayuki*; Ishiyama, Koji*
Heisei-23 Nendo (2011 Nen) Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Shuki Taikai Koenshu, p.265 - 266, 2011/09
no abstracts in English
Imai, Hisashi*; Yamashita, Ryo*; Shiozaki, Isao*; Urano, Kazuhiko*; Kasa, Hiroyoshi*; Maruyama, Yoshio*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Maekawa, Keisuke
JAEA-Research 2009-001, 116 Pages, 2009/03
Evaluation of long-term geological evolution and its impact on groundwater flow is one of the major themes within the frame of Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project. For the purpose of development of a groundwater flow modeling methodology considering the effects of long-term geological evolution, following three items were studied: (1) Upgrade of SMS (Sequential Modeling System of geo-environmental evolution impact on groundwater flow) which was developed in 2006 FY; (2) Groundwater flow simulation under more realistic conditions of geological structures and hydrogeological conditions; and (3) Sensitivity study of geo-environmental evolution impacts on groundwater flow. The studies showed following suggestive results. (1) Development of a precise time step setting enabled to narrow the gaps in simulated head between time steps in which the model configuration used to deformed. (2) Several aspects have been found from studies on impact factors such as deposition on pore pressure, recharge rate and difference in density of saline groundwater. For evaluation of pore pressure induced by deposition, it is necessary to model the porosity and permeability variation considering the exceed pore pressure change. The setting of recharge rate during the Ice Age influence the characteristics of groundwater flow in coastal and hilly areas. The density of groundwater is not so influential as topological potential factors, however it is effective for the characteristics of groundwater flow in coastal area and intrusion of recharge water from ground surface. (3) The sensitivity study on faulting characteristics indicated that the two types of fault configuration and the hydraulic conductivity setting considered are not influential on the nature of groundwater flow above the depth of 500 m.
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Yasue, Kenichi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Imai, Hisashi*; Shiozaki, Isao*; Yamashita, Ryo*
Chikasui Ryudo Kaiseki To Moderuka Ni Kansuru Shimpojium Happyo Rombunshu, p.59 - 66, 2007/01
no abstracts in English
Imai, Hisashi*; *; Yamashita, Ryo*; *; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Chijimatsu, Masakazu*
JNC TJ1400 2002-004, 357 Pages, 2002/03
Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2002-024, 53 Pages, 2002/02
no abstracts in English
Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2002-023, 147 Pages, 2002/02
In order to achieve the geological disposal of radioactive waste in safe, it is necessary to ensure the stability of the engineered barrier system (EBS). One of the most important factors for the stability of the EBS is the emplacement technology of the EBS. It is considered that the stability of the EBS is secured by the property emplacement based on the design requirement. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and over-pack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. To research the time-dependent phenomena of bentonite pellets after swelling, permeability tests were conducted with different period. Furthermore, to clarify the effect of test fluid, permeability test was conducted with synthetic seawater to compare the result with that of the test with distilled water. After emplacement of the engineered barrier system, it is expected that the near-field envilonment will be impacted by phenomena such as heat dissipation by conduction and other heat transfer mechanisms, infiltration of groundwater from the surrounding rock in to the engineered barrier system, stress imposed by the overburden pressure and generation of swelling pressure in the buffer due to water infiltration. In order to recognize and evaluate these coupled phenomena, it is necessary to make a confidence of the mathematical models and computer codes based on the information about the in-situ experiments regarding the engineered barrier system. In this research, technical investigations about the in-situ full-scale experiment (called Prototype Repository Project) in Aspo HRL facility by SKB of Sweden were performed.
Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2002-022, 70 Pages, 2002/02
no abstracts in English
Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2002-021, 258 Pages, 2002/02
After emplacement of the engineered barrier system (EBS), it is expected that the near-field environment will be impacted by phenomena such as heat dissipation by conduction and other heat transter mechanisms, infiltration of groundwater from the surrounding rock in to the engineered barrier system, stress imposed by the overburden pressure and generation of swelling pressure in the buffer due to water infiltation. In order to recognize and evaluate these coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) phenomena, it is necessary to make a confidence of the mathematical model and computer codes. Evaluating these coupled THM phenomena is important in order to clarify the initial transient behavior of the EBS within the near field. DECOVALEX project is an international co-opelative project for the DEvelopment of COupled models and their VALidation against EXperiments in nuclear waste isolation and it is significance to participate this project and to apply the code for the validation. Therefore, we tried to apply the developed numerical code against the subjects of DECOVALEX. In the above numerical code, swelling phenomenon is modeled as the function of water potential. However it does not evaluate the experiment results enough. Then, we try to apply the new model.
Imai, Hisashi*; Yamashita, Ryo*; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Shiozaki, Isao*
JNC TJ1410 2001-002, 318 Pages, 2001/08
Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2001-021, 65 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2001-020, 379 Pages, 2001/02
In order to achieve the geological disposal of radioactive waste in safe, it is necessary to ensure the stability of the engineered barrier system (EBS). One of the most important factors for the stability of the EBS is the disposal technology. It is considered that the stability of the EBS is secured by the properly emplacement based on the design requirement. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. After emplacement of the engineered barrier system, it is expected that the near-field environment will be impacted by phenomena such as heat dissipation by conduction and other heat transfer mechanisms, infiltration of groundwater from the surrounding in to the engineered barrier system, stress imposed by the overburden pressure and generation of swelling pressure in the buffer due to water infiltration. In order to recognize and evaluate these coupled phenomena, it is necessary to make a confidence of the mathematical models and computer codes based on the information about the in-situ experimats regarding the engineered barrier system. In this research, technical investigation about the in-situ full-scale experiment (called Prototype Repository Project) in Aspo HRL facility by SKB of Sweden were performed. Fathermore, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named THAMES was validated at the international project, DECOVALEX III.
Yamashita, Ryo*; Imai, Hisashi*; *; *; Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; *
JNC TJ1420 2000-008, 176 Pages, 2000/03
Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; TRAN DUC PHI OAN*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-056, 487 Pages, 2000/02
JNC presented the 2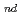 progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named TRAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named TRAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; TRAN DUC PHI OAN*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-055, 49 Pages, 2000/02
JNC presented the 2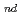 progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named THAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named THAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.