Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Uchida, Hitoshi*
Characterization of Corrosion Products on Steel Surfaces, p.199 - 222, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Proceedings of 16th International Corrosion Congress (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/09
XANES measurements of rust layers formed on Fe, Fe-Cr alloys and Fe-Ni alloys exposed to a Cl-rich atmosphere have been performed using synchrotron radiation in order to clarify the relation between the structural properties of the rust layer on weathering steel and anticorrosive alloying elements and/or chloride ions. The XANES spectra around Cl K-edge revealed that the rust layer on the Fe-based binary alloys contains unidentified chloride in addition to akagan iteite. The Fe K-edge XANES results indicated that the rust layers are composed mainly of well-known iron oxides, goethite, akagan
iteite. The Fe K-edge XANES results indicated that the rust layers are composed mainly of well-known iron oxides, goethite, akagan ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. In particular, the mole ratio of akagan
ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. In particular, the mole ratio of akagan ite in the rust layers on the Fe-Ni alloys is relatively higher than that of the Fe-Cr alloys. The Cr K-edge XANES spectra of the rust layers on the Fe-Cr alloys depends on the Cr alloy content. Therefore, the local structure of Cr in the rust layer is variable with the Cr density. In contrast, the Ni K-edge XANES results show that the local structure of Ni in the rust layer are unique in a certain Ni content range.
ite in the rust layers on the Fe-Ni alloys is relatively higher than that of the Fe-Cr alloys. The Cr K-edge XANES spectra of the rust layers on the Fe-Cr alloys depends on the Cr alloy content. Therefore, the local structure of Cr in the rust layer is variable with the Cr density. In contrast, the Ni K-edge XANES results show that the local structure of Ni in the rust layer are unique in a certain Ni content range.
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Materials Transactions, 46(2), p.329 - 336, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:80.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chloride in atmosphere considerably reduces the corrosion resistance of conventional weathering steel containing a small amount of Cr. Ni is an effective anticorrosive element for improving the corrosion resistance of steel in a Cl-rich environment. In order to clarify the structure of the protective rust layer of weathering steel, Cl and Fe K-edge X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectra of atmospheric corrosion products (rust) formed on Fe, Fe-Ni and Fe-Cr alloys exposed to Cl-rich atmosphere were measured. The Fe K-XANES measurements enable the characterization of a mixture of iron oxides such as rust. The chemical composition of the rust was determined by performing pattern fitting of the measured spectra. All the rust is composed mainly of goethite, akagan ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. Among these iron oxides, akagan
ite, lepidocrocite and magnetite. Among these iron oxides, akagan ite in particular is the major component in the rust. Additionally, the amount of akagan
ite in particular is the major component in the rust. Additionally, the amount of akagan ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is much greater than that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy. Akagan
ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is much greater than that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy. Akagan ite is generally considered to facilitate the corrosion of steel, but our results indicate that akagan
ite is generally considered to facilitate the corrosion of steel, but our results indicate that akagan ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is quantitatively different from that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy and does not facilitate the corrosion of steel. The shoulder peak observed in Cl K-XANES spectra reveals that the rust contains a chloride other than akagan
ite in the rust of Fe-Ni alloy is quantitatively different from that in rust of Fe-Cr alloy and does not facilitate the corrosion of steel. The shoulder peak observed in Cl K-XANES spectra reveals that the rust contains a chloride other than akagan ite. The energy of the shoulder peak does not correspond to that of any well-known chlorides. In the measured spectra, there is no proof that Cl, by combining with the alloying element, inhibits the alloying element from acting in corrosion resistance. The shoulder peak appears only when the content of the alloying element is lower than a certain value. This suggests that the generation of the unidentified chloride is related to the corrosion rate of steel.
ite. The energy of the shoulder peak does not correspond to that of any well-known chlorides. In the measured spectra, there is no proof that Cl, by combining with the alloying element, inhibits the alloying element from acting in corrosion resistance. The shoulder peak appears only when the content of the alloying element is lower than a certain value. This suggests that the generation of the unidentified chloride is related to the corrosion rate of steel.
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Materials Transactions, 46(2), p.337 - 341, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:57.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have performed extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis for artificial Cr-goethite to elucidate the local structure around Cr in Cr-goethite. The spectra were obtained using synchrotron radiation X-rays at the Photon Factory in Tsukuba. The first shell contributions were isolated by Fourier filtering the EXAFS data, and the inverse Fourier transformed single-shell data were analyzed using curve fitting method. The results show that Cr is coordinated with (7 1) O
1) O ions. The protective character of Cr-goethite protective rust layer on weathering steel can be interpreted in terms of the O
ions. The protective character of Cr-goethite protective rust layer on weathering steel can be interpreted in terms of the O coordination around Cr
coordination around Cr resulting in creation of negative fixed-charge in the Cr-goethite particles.
resulting in creation of negative fixed-charge in the Cr-goethite particles.
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Materials Transactions, 46(1), p.136 - 139, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The rust layer formed on weathering steel possesses a strong protective ability against corrosives in an atmosphere. This ability is related to the structure of the rust layer. The difference in the protective ability of a rust layer in a Cl-rich environment between conventional weathering steel containing Cr and advanced weathering steel containing Ni is believed to be caused by the differences in local structural and chemical properties between alloying elements, Cr and Ni, in the rust layer. In order to examine the effect of these alloying elements on the structure of the rust layer formed on steel in a Cl-rich environment, we have performed Cr and Ni K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) measurements for the rust layer of Fe-Cr and Fe-Ni binary alloys exposed to a Cl-rich atmosphere using synchrotron radiation. The results of the Cr K-edge XANES measurements for the rust layer of Fe-Cr binary alloys show that the atomic geometry around Cr depends on the concentration of Cr. Therefore, it is expected that the local structure around Cr in the rust layer is unstable. On the other hand, from the results of the Ni K-edge XANES measurements for the rust layer of Fe-Ni binary alloys, Ni is considered to be positioned at a specific site in the crystal structure of a constituent of the rust layer, such as akagan ite or magnetite. As a consequence, Ni negligibly interacts with Cl
ite or magnetite. As a consequence, Ni negligibly interacts with Cl ions in the rust layer.
ions in the rust layer.
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Materials Transactions, 45(12), p.3356 - 3359, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:50.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cl K-edge XANES measurements of atmospheric corrosion products (rust) formed on Fe, Fe-Ni and Fe-Cr alloys in chloride pollution have been performed using synchrotron radiation in order to clarify roles of anticorrosive alloying elements and of Cl in the corrosion resistance of weathering steel. The spectra of binary alloys show a shoulder structure near the absorption edge. The intensity of the shoulder peak depends on the kind and amount of the alloying element, whereas the energy position is invariant. This indicates that Cl is not combined directly with alloying elements in the rust.
 /4H-SiC(0001) interface
/4H-SiC(0001) interfaceYamashita, Kenya*; Kitabatake, Makoto*; Kusumoto, Osamu*; Takahashi, Kunimasa*; Uchida, Masao*; Miyanaga, Ryoko*; Ito, Hisayoshi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Materials Science Forum, 389-393, p.1037 - 1040, 2002/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Masato*; Konishi, Hiroyuki; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Uchida, Hitoshi*
Materials Science Research International, Special Technical Publication, 1, p.398 - 401, 2001/05
A rust layer on a weathering low-alloy steel has strong protective ability for atmospheric corrosion of the steel. In order to control the rust layer on steels, it is so important to know the detailed structure of rust and relate it to the protective ability of the rust layer. Especially, the position of atoms of the alloying elements in the rust layer directly control the structure and properties of the rust layer. We tried to find the atomic arrangement of the rust layer of Fe-Cr alloy film covered with thin film of electrolyte using synchrotron radiation. Grazing incidence X-ray diffraction and M ssbauer spectra showed that the rust layer was composed of
ssbauer spectra showed that the rust layer was composed of  -FeOOH and ultra-fine
-FeOOH and ultra-fine  -FeOOH. By examining EXAFS spectra, Cr coming from Fe-Cr alloy film would be present in the
-FeOOH. By examining EXAFS spectra, Cr coming from Fe-Cr alloy film would be present in the  -FeOOH. Some of Cr would be present between Fe-0-OH octahedron as interstitial atoms, as well as substituting Fe lattice site in the octahedron.
-FeOOH. Some of Cr would be present between Fe-0-OH octahedron as interstitial atoms, as well as substituting Fe lattice site in the octahedron.
*; *; *; *; *; *; *
PNC TN9410 89-084, 61 Pages, 1989/03
A cold trap examination for measurements of dose rate, which purpose is to grasp the distribution of Captured oxygen impurity from the surface dose rate and distribution of nuclide, was carried out in the 6th and the 7th periodic Annual Inspection. The results obtained from this examination were as follows. (1)The surface dose rate of a new modeling Cold Trap at the 7th periodic Annual Inspection was about twice rate as much as the 6th. (2) Na,
Na,  C0,
C0,  Mn, and
Mn, and 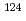 Sb were detected from C0ld Traps. (3)The distribution of
Sb were detected from C0ld Traps. (3)The distribution of  Co at a old modeling Cold Trap was same as the distribution of captured oxygen of CT4-1B which is mocked up for a old modeling Cold Trap of JOYO. Therefore the distribution at a Cold Trap will be expected that the distribution of
Co at a old modeling Cold Trap was same as the distribution of captured oxygen of CT4-1B which is mocked up for a old modeling Cold Trap of JOYO. Therefore the distribution at a Cold Trap will be expected that the distribution of  Co is same as the distribution of captured oxygen impurity. (4)The new modeling Cold Trap was designed to Capture the oxygen impurity homogeneity at mesh territory. The distribution of
Co is same as the distribution of captured oxygen impurity. (4)The new modeling Cold Trap was designed to Capture the oxygen impurity homogeneity at mesh territory. The distribution of  Co at the new modeling Cold Trap was uniformed at mesh territory. Therefore, if there are the Correlation between the distribution of
Co at the new modeling Cold Trap was uniformed at mesh territory. Therefore, if there are the Correlation between the distribution of  Co and the captured oxygen impurity, New modeling Cold Trap was displaied design function and Captured oxygen impurity homogeneity.
Co and the captured oxygen impurity, New modeling Cold Trap was displaied design function and Captured oxygen impurity homogeneity.
Shimizu, Makoto*; Kimuro, Harumi*; Ayabe, Muneo*; Kouno, Yasumasa*; Miyahara, Shuji*; Yamashita, Saburo*; Kanazawa, Kazuo*; Hayashi, Mitsuo*; Yoshizaki, Masato*
PNC TJ118 83-05VOL2, 222 Pages, 1984/03
None
Shimizu, Makoto*; Kimuro, Harumi*; Ayabe, Muneo*; Kouno, Yasumasa*; Miyahara, Shuji*; Yamashita, Saburo*; Kanazawa, Kazuo*; Hayashi, Mitsuo*; Yoshizaki, Masato*
PNC TJ118 83-05VOL1, 42 Pages, 1984/03
None
Komori, Daisuke*; Yamashita, Masato*; Konishi, Hiroyuki; Hanaki, Satoshi*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Konishi, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Masato*; Morimoto, Junichi*; Uchida, Hitoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oshikiri, Masato*; Kubo, Koji*; Ando, Masanori; Yamashita, Hayato
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oshikiri, Masato*; Kubo, Koji*; Ando, Masanori; Yamashita, Hayato
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English