Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Tamaki*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Hanamura, Kotoku*; Imao, Hiroshi*; Kamigaito, Osamu*; Kamoshida, Atsushi*; Kawachi, Toshihiko*; Koyama, Ryo*; Sakamoto, Naruhiko*; Fukunishi, Nobuhisa*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1105 - 1108, 2019/07
Upgrades for the RIKEN heavy-ion linac (RILAC) involving a new superconducting linac (SRILAC) are currently underway at the RIKEN radioactive isotope beam factory (RIBF). It is crucially important to develop nondestructive beam measurement diagnostics. We have developed a beam energy position monitor (BEPM) system which can measure not only the beam position but also the beam energy simultaneously by measuring the time of flight of the beam. We fabricated 11 BEPMs and completed the position calibration to obtain the sensitivity and offset for each BEPMs. The position accuracy has been achieved to be less than  0.1 mm by using the mapping measurement.
0.1 mm by using the mapping measurement.
Watanabe, Tamaki*; Imao, Hiroshi*; Kamigaito, Osamu*; Sakamoto, Naruhiko*; Fukunishi, Nobuhisa*; Fujimaki, Masaki*; Yamada, Kazunari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Koyama, Ryo*; Toyama, Takeshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.49 - 54, 2018/08
no abstracts in English

Nakasone, Akari*; Fujiwara, Masayuki*; Fukao, Yoichiro*; Biswas, K.; Rahman, A.*; Yamada, Maki*; Narumi, Issei; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Ono, Yutaka
Plant Physiology, 160(1), p.93 - 105, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:38.62(Plant Sciences) RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination
RecFOR proteins in homologous recombinationSato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Ishaque, A. M.*; Oba, Hirofumi*; Yamada, Mitsugu; Tejima, Kohei; Onodera, Takefumi; Narumi, Issei
DNA Repair, 11(4), p.410 - 418, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:59.83(Genetics & Heredity)In an effort to gain insights into the role of  RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination, we generated
RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination, we generated 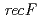 ,
, 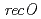 and
and 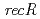 disruptant strains and characterized the disruption effects. Disruption of
disruptant strains and characterized the disruption effects. Disruption of 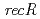 resulted in severe reduction of the transformation efficiency. On the other hand, the
resulted in severe reduction of the transformation efficiency. On the other hand, the 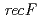 disruptant strain was the most sensitive phenotype to
disruptant strain was the most sensitive phenotype to  rays, UV irradiation and mitomycin C among the three disruptants. In the
rays, UV irradiation and mitomycin C among the three disruptants. In the 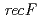 disruptant strain, the intracellular level of the LexA1 protein did not decrease following
disruptant strain, the intracellular level of the LexA1 protein did not decrease following  irradiation. These results demonstrate that the RecF protein plays a crucial role in the homologous recombination repair process by facilitating RecA activation. Thus, the RecF and RecR proteins are involved in the RecA activation and the stability of incoming DNA, respectively, during RecA-mediated homologous recombination processes that initiated the ESDSA pathway in
irradiation. These results demonstrate that the RecF protein plays a crucial role in the homologous recombination repair process by facilitating RecA activation. Thus, the RecF and RecR proteins are involved in the RecA activation and the stability of incoming DNA, respectively, during RecA-mediated homologous recombination processes that initiated the ESDSA pathway in  .
.
Arase, Sachiko*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Abe, Jun*; Kasai, Megumi*; Yamada, Tetsuya*; Kitamura, Keisuke*; Narumi, Issei; Tanaka, Atsushi; Kanazawa, Akira*
Plant Biotechnology, 28(3), p.323 - 329, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:54.28(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)
Yamada, Mitsugu; Sato, Katsuya; Narumi, Issei
Acta Crystallographica Section F, 66(12), p.1614 - 1616, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.09(Biochemical Research Methods)DNA damage response A protein (DdrA) from  has been suggested to be involved in DNA repair processes through binding to 3' ends of single-stranded DNA, thereby protecting the ends from nuclease digestion. In this study, a recombinant C-terminal truncated form of
has been suggested to be involved in DNA repair processes through binding to 3' ends of single-stranded DNA, thereby protecting the ends from nuclease digestion. In this study, a recombinant C-terminal truncated form of  DdrA (DdrA157), comprising of the first 157 residues of DdrA, was expressed in
DdrA (DdrA157), comprising of the first 157 residues of DdrA, was expressed in  , purified and crystallized. Single crystals of DdrA157 were obtained by a hanging drop method at 293 K. The crystal belonged to the monoclinic space group
, purified and crystallized. Single crystals of DdrA157 were obtained by a hanging drop method at 293 K. The crystal belonged to the monoclinic space group  2
2 , with unit-cell parameters
, with unit-cell parameters  = 46.31,
= 46.31,  = 180.26,
= 180.26,  = 114.17
= 114.17  ,
, 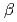 = 90.02
= 90.02 . The crystal was expected to contain fourteen molecules in the asymmetric unit. Diffraction data were collected to 2.35
. The crystal was expected to contain fourteen molecules in the asymmetric unit. Diffraction data were collected to 2.35  resolution at beamline BL-5 of the Photon Factory and initial phase determinations were attempted by a molecular-replacement method using the human Rad52 structure.
resolution at beamline BL-5 of the Photon Factory and initial phase determinations were attempted by a molecular-replacement method using the human Rad52 structure.
Asami, Itsuo*; Fukuta, Shiro*; Kuroyanagi, Satoru*; Yamada, Masato*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Yoshihara, Ryohei; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 78, 2009/12
no abstracts in English
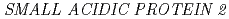 potentially mediates the response to synthetic auxin, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, in
potentially mediates the response to synthetic auxin, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, in 
Nakasone, Akari; Yamada, Maki*; Kiyosue, Tomohiro*; Narumi, Issei; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Ono, Yutaka
Journal of Plant Physiology, 166(12), p.1307 - 1313, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:13.07(Plant Sciences)Yokota, Yuichiro; Yamada, Shinya*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Shikazono, Naoya; Narumi, Issei; Tanaka, Atsushi; Inoue, Masayoshi
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 77, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Yokota, Yuichiro; Yamada, Shinya*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Shikazono, Naoya; Narumi, Issei; Tanaka, Atsushi; Inoue, Masayoshi*
Radiation Research, 167(1), p.94 - 101, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:61.29(Biology)The ability of ion beams to kill or mutate plant cells is known to depend on the linear energy transfer (LET) of the ions, although the mechanism is poorly understood. In this study, tobacco BY-2 protoplasts as a model of single plant cells were irradiated with helium, carbon and neon ions having different LETs. Following irradiation, DNA fragments were separated into sizes by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Information on DNA fragmentation was obtained by staining the gels with SYBR Green I. Initial DSB yields (Gbp Gy
Gy ) were found to depend on LET, and the highest relative biological effectiveness (about 1.6) was obtained at 124 and 241 keV/
) were found to depend on LET, and the highest relative biological effectiveness (about 1.6) was obtained at 124 and 241 keV/ m carbon ions. High-LET carbon and neon ions yielded short DNA fragments more efficiently than
m carbon ions. High-LET carbon and neon ions yielded short DNA fragments more efficiently than  rays. These results partially explain the large biological effects caused by high-LET ions in plants.
rays. These results partially explain the large biological effects caused by high-LET ions in plants.
 Al
AlOzawa, Akira*; Matsuta, Kensaku*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Mihara, Mototsugu*; Yamada, Kazunari*; Yamaguchi, Takayuki*; Otsubo, Takashi*; Momota, Sadao*; Izumikawa, Takuji*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(2), p.021301_1 - 021301_4, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:89.22(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Okonogi, Kazunari*; Nakamura, Takehiko; Yoshinaga, Makio; *
JAERI-Data/Code 99-018, 112 Pages, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
Miura, Makoto; *; *; Omori, Takuro; ; ; *
PNC TN841 79-18, 59 Pages, 1979/02
no abstracts in English
Kambara, Toyozo; Uno, Hidero; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Kohayakawa, Toru; Takayanagi, Hiroshi; Fujimura, Tsutomu; Morita, Morito; Ichihara, Masahiro; et al.
JAERI 1045, 11 Pages, 1963/03
no abstracts in English
Yokota, Yuichiro; Yamada, Shinya*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Shikazono, Naoya; Narumi, Issei; Tanaka, Atsushi; Inoue, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokota, Yuichiro; Yamada, Shinya*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Shikazono, Naoya; Narumi, Issei; Tanaka, Atsushi; Inoue, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
The ability of ion beams to kill or mutate plant cells is known to depend on LET of the ions, although the mechanism of damage is poorly understood. In this study, tobacco BY-2 protoplasts, as a model of single plant cells, were irradiated by helium, carbon and neon ions with different LETs at ice temperature. Resulting DNA fragments were separated into sizes by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Initial DSB yields and intervals between neighboring DSBs were evaluated from the DNA fragmentation patterns. Initial DSB yields (Gbp DNA Gy
Gy ) were found to depend on LET, and the highest value was obtained at 124 and 241 keV/
) were found to depend on LET, and the highest value was obtained at 124 and 241 keV/ m carbon ions in the investigated range. High-LET carbon and neon ions induced DSBs at closer sites than
m carbon ions in the investigated range. High-LET carbon and neon ions induced DSBs at closer sites than  rays did. These results partially explained the large biological effects caused by high-LET heavy ions in plants.
rays did. These results partially explained the large biological effects caused by high-LET heavy ions in plants.
Yamada, Mitsugu; Adachi, Motoyasu; Sato, Katsuya; Tamada, Taro; Yura, Kei*; Kuroki, Ryota; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Asami, Itsuo*; Fukuta, Shiro*; Kuroyanagi, Satoru*; Yamada, Masato*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Oba, Hirofumi*; Yamada, Mitsugu; Tejima, Kohei; Onodera, Takefumi; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
In an effort to gain an insight into the role of the RecFOR in DNA repair through homologous recombination in  , we generated a RecFOR disruptant strains and characterized the disruption effects. The RecF disruptant strain exhibited sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents, suggesting that RecF has a crucial role in DNA repair. This result indicates that RecF takes an important role in the RecA activation in the homologous recombination process with DNA damage. While, the recombination assay revealed that RecR is essential for the process of homologous intermolecular recombination, suggesting that RecR is important factor in the homologous recombination process without DNA damage. The importance of RecF and RecR in the homologous recombination processes is reversed due to the existence of DNA damage. Therefore,
, we generated a RecFOR disruptant strains and characterized the disruption effects. The RecF disruptant strain exhibited sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents, suggesting that RecF has a crucial role in DNA repair. This result indicates that RecF takes an important role in the RecA activation in the homologous recombination process with DNA damage. While, the recombination assay revealed that RecR is essential for the process of homologous intermolecular recombination, suggesting that RecR is important factor in the homologous recombination process without DNA damage. The importance of RecF and RecR in the homologous recombination processes is reversed due to the existence of DNA damage. Therefore,  will use the different homologous recombination processes through the RecFOR or RecOR, respectively.
will use the different homologous recombination processes through the RecFOR or RecOR, respectively.