Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154799_1 - 154799_20, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of near-stoichiometric (U,Pu,Am)O doped with Nd
doped with Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT)
, which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT) . The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C
. The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C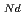 and C
and C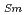 , respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70
, respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70  10
10 + 0.93C
+ 0.93C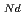 + 1.20C
+ 1.20C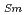 , B(m/W)=2.39
, B(m/W)=2.39  10
10 .
.
Hirooka, Shun; Horii, Yuta; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Vauchy, R.; Hayashizaki, Kohei; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1313 - 1323, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:95.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Additive MOX pellets are fabricated by a conventional dry powder metallurgy method. Nd O
O and Sm
and Sm O
O are chosen as the additive materials to simulate the corresponding soluble fission products dispersed in MOX. Shrinkage curves of the MOX pellets are obtained by dilatometry, which reveal that the sintering temperature is shifted toward a value higher than that of the respective regular MOX. The additives, however, promote grain growth and densification, which can be explained by the effect of oxidized uranium cations covering to a pentavalent state. Ceramography reveals large agglomerates after sintering, and Electron Probe Micro-Analysis confirms that inhomogeneous elemental distribution, whereas XRD reveals a single face-centered cubic phase. Finally, by grinding and re-sintering the specimens, the cation distribution homogeneity is significantly improved, which can simulate spent nuclear fuels with soluble fission products.
are chosen as the additive materials to simulate the corresponding soluble fission products dispersed in MOX. Shrinkage curves of the MOX pellets are obtained by dilatometry, which reveal that the sintering temperature is shifted toward a value higher than that of the respective regular MOX. The additives, however, promote grain growth and densification, which can be explained by the effect of oxidized uranium cations covering to a pentavalent state. Ceramography reveals large agglomerates after sintering, and Electron Probe Micro-Analysis confirms that inhomogeneous elemental distribution, whereas XRD reveals a single face-centered cubic phase. Finally, by grinding and re-sintering the specimens, the cation distribution homogeneity is significantly improved, which can simulate spent nuclear fuels with soluble fission products.
 ceramics
ceramicsVauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Ceramics International, 49(2), p.3058 - 3065, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:75.06(Materials Science, Ceramics)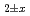 and (U,Pu,Am,Np)O
and (U,Pu,Am,Np)O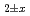
Hirooka, Shun; Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Yamada, Tadahisa*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 542, p.152424_1 - 152424_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:60.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The measurement of oxygen potential was conducted at 1,673, 1,773, and 1,873 K for (U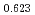 Pu
Pu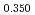 Am
Am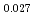 )O
)O and at 1,873 and 1,923 K for (U
and at 1,873 and 1,923 K for (U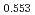 Pu
Pu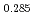 Am
Am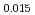 Np
Np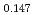 )O
)O by using a thermo-gravimeter and an oxygen sensor. Am inclusion in terms of substituting the U significantly increased the oxygen potential. Similarly, the inclusion of Np as a substitute for U increased the oxygen potential; however, the effect was not as large as that with the Pu or Am addition at the same rate. The results were analyzed via defect chemistry and certain defect formations were suggested in the reducing region and the near-stoichiometric region by plotting the relationship between PO
by using a thermo-gravimeter and an oxygen sensor. Am inclusion in terms of substituting the U significantly increased the oxygen potential. Similarly, the inclusion of Np as a substitute for U increased the oxygen potential; however, the effect was not as large as that with the Pu or Am addition at the same rate. The results were analyzed via defect chemistry and certain defect formations were suggested in the reducing region and the near-stoichiometric region by plotting the relationship between PO and the deviation from the stoichiometry. The equilibrium constants of the defect reactions were arranged to reproduce the experiment such that Am/Np contents were included in the entropy with coefficients fitting the experimental data.
and the deviation from the stoichiometry. The equilibrium constants of the defect reactions were arranged to reproduce the experiment such that Am/Np contents were included in the entropy with coefficients fitting the experimental data.
 O
O powder in MOX fuel production
powder in MOX fuel productionTsuchimochi, Ryota; Hirooka, Shun; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Yamada, Tadahisa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Okumura, Kazuyuki
no journal, ,
As part of studies on physical properties of low-decontaminated fuel pellets, simulated FPs (Sm O
O and Nd
and Nd O
O ) and impurities included at such as fuel fabrication process (Al
) and impurities included at such as fuel fabrication process (Al O
O and SiO
and SiO ) were added to MOX, and their effects on thermal conductivity were evaluated. Addition of Sm
) were added to MOX, and their effects on thermal conductivity were evaluated. Addition of Sm O
O and Nd
and Nd O
O in MOX, that can be solutionized, decreased thermal conductivity whereas addition of Al
in MOX, that can be solutionized, decreased thermal conductivity whereas addition of Al O
O and SiO
and SiO , that don't make a solid solution with MOX, increased thermal conductivity.
, that don't make a solid solution with MOX, increased thermal conductivity.
Nakamichi, Shinya; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Okumura, Kazuyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*
no journal, ,
The low-decontaminated fuel which contains significant amount of fission products (FPs) has been investigated as a fuel for the advanced fast reactor cycle. In this cycle, it is expected to reduce reprocessing cost and strengthen nuclear proliferation resistance of recovered plutonium accompanying high radiation dose FPs. However, FPs could affect on thermal properties of MOX. In particular, thermal conductivity is one of the most important properties for fuel design. Many studies have been reported on the thermal conductivity of MOX that evaluated the effect of plutonium and minor actinide (Am, Np) contents. However, the number of studies on the thermal conductivity of MOX containing FPs are limited; only Nd, Eu and Zr. In this study, thermal conductivity of MOX including Nd O
O and Sm
and Sm O
O , which are expected to be the main FPs remaining as solid solutions in low-decontaminated fuel, was evaluated by measuring thermal diffusivity of sintered pellet. Nd
, which are expected to be the main FPs remaining as solid solutions in low-decontaminated fuel, was evaluated by measuring thermal diffusivity of sintered pellet. Nd O
O powder and Sm
powder and Sm O
O powder was added into raw MOX powder of 20% plutonium content and they were milled by ball-mill. Sintered pellets were obtained by pressing and sintering this powder. The thermal diffusivities were measured by a laser flash method from 973 K to 1673 K at every 100 K. The thermal conductivities up to 1400K are expressed by classical phonon transport model as
powder was added into raw MOX powder of 20% plutonium content and they were milled by ball-mill. Sintered pellets were obtained by pressing and sintering this powder. The thermal diffusivities were measured by a laser flash method from 973 K to 1673 K at every 100 K. The thermal conductivities up to 1400K are expressed by classical phonon transport model as  =(A+BT)
=(A+BT) where A(mK/W)=2.0
where A(mK/W)=2.0 10
10 +4.8
+4.8 10
10 C
C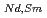 and B(m/W)=2.5
and B(m/W)=2.5 10
10 . This means the thermal conductivity decreased with enhancement of phonon scattering by adding Nd
. This means the thermal conductivity decreased with enhancement of phonon scattering by adding Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , similar to the previous studies.
, similar to the previous studies.
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
The low-decontaminated fuel which contains significant amount of fission products (FPs) has been investigated as a fuel for the advanced fast reactor cycle. In this cycle, it is expected to reduce reprocessing cost and strengthen nuclear proliferation resistance of recovered plutonium accompanying high radiation dose FPs. As part of studies on physical properties of low-decontaminated fuel pellets, Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O powders were added to the MOX raw powder as simulated fission products (FPs). The effects of simulated FPs on thermal conductivity were evaluated focusing on the microstructural homogeneities of simulated FPs. From the results of thermal diffusivity measurement and the EPMA mapping, the homogeneous simulated FPs decreased the thermal conductivity of the MOX.
powders were added to the MOX raw powder as simulated fission products (FPs). The effects of simulated FPs on thermal conductivity were evaluated focusing on the microstructural homogeneities of simulated FPs. From the results of thermal diffusivity measurement and the EPMA mapping, the homogeneous simulated FPs decreased the thermal conductivity of the MOX.
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Hayashizaki, Kohei; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Ohwada, Hideaki*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
no journal, ,
Fission products (FPs), which are generated and stored in fuel matrix by irradiating nuclear fuels, affect thermo-physical fuel properties. To improve accuracy of computer simulation of irradiation behaviors, studies on the fuel properties containing FPs are needed. However, only a limited number of studies on the irradiated fuel properties, especially MOX fuels, have been reported in the world due to difficulties in handling of the irradiated fuels. Moreover, the effect of individual FP cannot be evaluated because many kinds of FPs are stored in the irradiated fuels. Thus, an alternative method should be suggested to easily study the effects of FPs on the fuel properties. In this study, fuel properties were measured to evaluate the effects of FPs by using simulated FP-doped MOX specimens instead of a real irradiated fuel. For the measurement, the homogeneity of FP in a specimen is also important, as well as uranium and plutonium. To obtain homogeneous specimens, re-grinding and re-sintering processes were repeated and the improvement was confirmed by EPMA and XRD at each set of the process. A specimen with suitable homogeneity for measurement was prepared by repeating the series of processes three times. Sm O
O , Gd
, Gd O
O and ZrO
and ZrO , which are major and soluble FPs in irradiated MOX fuels, were selected as simulated FPs. The effect of individual FP on the properties, such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, was evaluated on the specimens. In addition, Nd
, which are major and soluble FPs in irradiated MOX fuels, were selected as simulated FPs. The effect of individual FP on the properties, such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, was evaluated on the specimens. In addition, Nd O
O , Sm
, Sm O
O and Gd
and Gd O
O co-doped MOX was also prepared to compare the influence of containing multiple lanthanides.
co-doped MOX was also prepared to compare the influence of containing multiple lanthanides.
 O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O /Gd
/Gd O
O /ZrO
/ZrO )-doped MOX for studies on MOX fuel properties
)-doped MOX for studies on MOX fuel propertiesHorii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Hayashizaki, Kohei; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Ohwada, Hideaki*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
no journal, ,
Fission products (FPs), which are generated and stored in the fuel matrix by irradiating MOX fuels, affect the fuel properties. In previous studies, many properties of unirradiated MOX were reported. On the other hand, the number of studies on irradiated MOX properties are limited. Studying properties of irradiated materials has difficulties in handling, therefore, using simulated FP-doped (U,Pu)O is an alternative method in studying irradiated fuel properties. In order to evaluate the effect of simulated FPs, the homogeneity is one of the important factors. In this study, two dry-processing methods, namely melting and grinding-mixing methods, respectively, are employed and evaluated the aptitude as methods to prepare the homogeneous simulated FP-doped (U,Pu)O
is an alternative method in studying irradiated fuel properties. In order to evaluate the effect of simulated FPs, the homogeneity is one of the important factors. In this study, two dry-processing methods, namely melting and grinding-mixing methods, respectively, are employed and evaluated the aptitude as methods to prepare the homogeneous simulated FP-doped (U,Pu)O .
.
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -x with y = 0.30, 0.45, and 1.00
-x with y = 0.30, 0.45, and 1.00Vauchy, R.; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
no journal, ,
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English