Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C powder and B
C powder and B C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steel
C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steelHong, Z.*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Erkan, N.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 171, p.105160_1 - 105160_13, 2024/06
In this study, it is found that the eutectic reaction between B C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B
C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B
C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
 C-SS and its relocation behavior
C-SS and its relocation behaviorAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of Saudi International Conference On Nuclear Power Engineering (SCOPE2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/11
In this study, the eutectic behavior and subsequent melt structure of boron migration are observed by a quantitative and high-resolution visualization method using radiative heating. Experiments were conducted using B4C pellet and powder within SS tubes, replicating the actual control rod design in the temperature range of 1150 C to 1372
C to 1372 C to study long-duration melting and relocation behavior. The visualization technique accurately identified the time of eutectic melting onset and the related temperature, pointing out different values for the pellet and the powder cases.
C to study long-duration melting and relocation behavior. The visualization technique accurately identified the time of eutectic melting onset and the related temperature, pointing out different values for the pellet and the powder cases.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 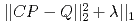 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, K.*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Takata, Takashi*; Okamoto, Koji*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 13(13), p.7705_1 - 7705_29, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nanjo, Kotaro; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Maruyama, Yu; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.816 - 823, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Okita, Shoichiro; Mizuta, Naoki; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Goto, Minoru; Yoshida, Katsumi*; Nishimura, Yosuke*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/02
Machida, Masahiko; Shi, W.*; Yamada, Susumu; Miyamura, Hiroko; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji; Aoki, Yuto; Ito, Rintaro; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
Hong, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Liao, H.*; Yang, H.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 180, p.109462_1 - 109462_9, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A series of experiments were conducted using B C material and SUS304 tubes as a simulant of the real control rods. Reaction rate constant data in the 1450K-1500K range were obtained, and are consistent with the reference values. The reaction layer microstructure observation and the associated chemical composition analysis were also carried onto the experiment samples.
C material and SUS304 tubes as a simulant of the real control rods. Reaction rate constant data in the 1450K-1500K range were obtained, and are consistent with the reference values. The reaction layer microstructure observation and the associated chemical composition analysis were also carried onto the experiment samples.
Nanjo, Kotaro; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Pellegrini, M.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1407 - 1416, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:88.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
ACS Omega (Internet), 7(33), p.29326 - 29336, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.84(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Li, C.-Y.; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Dai-25-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/07
The capability of stable cooling and avoiding re-criticality on the debris bed are the main issues for achieving IVR (In-Vessel Retention). In the actual situation, the debris bed is composed of mixed-density debris particles. Hence, when these mixed-density debris particles were launched to re-distribute, the debris bed would possibly form a density-stratified distribution. For the proper evaluation of this scenario, the multi-physics model of CFD-DEM-Monte-Carlo based neutronics is established to investigate the coolability and re-criticality on the heterogeneous density-stratified debris bed with considering the particle relocation. The CFD-DEM model has been verified by utilizing water injection experiments on the mixed-density particle bed in the first portion of this research. In the second portion, the coupled system of the CFD-DEM-Monte-Carlo based neutronics model is applied to reactor cases. Afterward, the debris particles' movement, debris particles' and coolant's temperature, and the k-eff eigenvalue are successfully tracked. Ultimately, the relocation and stratification effects on debris bed's coolability and re-criticality had been quantitatively confirmed.
Aihara, Jun; Ueta, Shohei; Honda, Masaki*; Mizuta, Naoki; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(1), p.107 - 116, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The concept of a Pu-burner high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) has been proposed for purpose of more safely reducing amount of recovered Pu. This concept employs coated fuel particles (CFPs) with ZrC coated PuO -YSZ kernel and with tristructural (TRISO) coating for very high Pu burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. In this report, we investigate the microstructure of the region that includes the surface of an as-fabricated CeO
-YSZ kernel and with tristructural (TRISO) coating for very high Pu burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. In this report, we investigate the microstructure of the region that includes the surface of an as-fabricated CeO -YSZ kernel simulating PuO
-YSZ kernel simulating PuO -YSZ kernel. We found both Zr-rich grains and Ce-rich grains to be densely distributed in that region including surface of CeO
-YSZ kernel. We found both Zr-rich grains and Ce-rich grains to be densely distributed in that region including surface of CeO -YSZ kernel. On the other hand, it has been reported that there was a porous region near surface of the CeO
-YSZ kernel. On the other hand, it has been reported that there was a porous region near surface of the CeO -YSZ kernel of Batch I. This finding confirms that Ce-rich grains near surface of CeO
-YSZ kernel of Batch I. This finding confirms that Ce-rich grains near surface of CeO -YSZ kernels coated with ZrC layers have been corroded during the deposition of the ZrC layer, whereas the Zr-rich grains were hardly affected.
-YSZ kernels coated with ZrC layers have been corroded during the deposition of the ZrC layer, whereas the Zr-rich grains were hardly affected.
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(9), p.1062 - 1073, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)The interaction of cesium hydroxide and a calcium silicate insulation material was experimentally investigated at high temperature conditions. A thermogravimetry equipped with differential thermal analysis was used to analyze thermal events in the samples of mixed calcium silicate and cesium hydroxide under Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 with maximum temperature of 1100
0 with maximum temperature of 1100 C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca
C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca Si
Si 0
0 (0H)
(0H) ), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730
), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730 C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0
C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0 ), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100
), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100 C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H
C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0
0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0 was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
Rizaal, M.; Saito, Takumi*; Okamoto, Koji*; Erkan, N.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00563_1 - 19-00563_10, 2020/06
The adsorption of cesium (Cs) on calcium silicate insulation of primary piping system is postulated to contribute in high dose rate of surrounding pedestal area in Fukushima Daiichi NPP unit 2. In this study, room-temperature experiment of Cs adsorption on calcium silicate has been studied as an initial approach of Cs adsorption behavior toward higher temperature condition. As the result of analyzing of Cs adsorption kinetics, it was expected that the underlying adsorption mechanism is chemisorption. Furthermore, analysis of adsorption isotherm suggested unrestricted monolayer formation followed by multilayer formation.
Ueta, Shohei; Mizuta, Naoki; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; Honda, Masaki*; Saiki, Yohei*; Takahashi, Masashi*; Ohira, Koichi*; Nakano, Masaaki*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 357, p.110419_1 - 110419_10, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The concept of a plutonium (Pu) burner HTGR is proposed to incarnate highly-effective Pu utilization by its inherent safety features. The security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) employs the coated fuel particle with a fuel kernel made of plutonium dioxide (PuO ) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
Chai, P.; Wu, Y.*; Okamoto, Koji
Mechanical Engineering Letters (Internet), 6, p.20-00204_1 - 20-00204_7, 2020/00
In a High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR), radiation is the dominant form of heat transfer due to the high temperature environment. Therefore, the emissivity of the core materials (mainly nuclear grade graphite) is important for reactor safety assessment. In this paper, the emissivity of nuclear grade graphite IG-110 was measured in the temperature range from 500 C to 1000
C to 1000 C by using an infrared thermometer. Besides, the impact of the graphite oxidation, which may take place in a postulated air ingress accident, was also evaluated. As a result, it was found that the emissivity of IG-110 grade graphite decreases slightly as the temperature increase. Moreover, a relatively high emissivity was detected in the pre-oxidized specimen. Based on the measurement data, two experimental correlations were suggested for the engineering applications. It could also be concluded that the commonly used value of the graphite emissivity (0.8), is conservative for engineering judgment.
C by using an infrared thermometer. Besides, the impact of the graphite oxidation, which may take place in a postulated air ingress accident, was also evaluated. As a result, it was found that the emissivity of IG-110 grade graphite decreases slightly as the temperature increase. Moreover, a relatively high emissivity was detected in the pre-oxidized specimen. Based on the measurement data, two experimental correlations were suggested for the engineering applications. It could also be concluded that the commonly used value of the graphite emissivity (0.8), is conservative for engineering judgment.
Aihara, Jun; Ueta, Shohei; Honda, Masaki*; Mizuta, Naoki; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 522, p.32 - 40, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to realize Pu-burner high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR), coated fuel particles (CFPs) with PuO -yittria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) fuel kernel coated with ZrC is employed for high nuclear proliferation resistance and very high burn-up. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have carried out ZrC coatings of particles which simulated PuO
-yittria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) fuel kernel coated with ZrC is employed for high nuclear proliferation resistance and very high burn-up. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have carried out ZrC coatings of particles which simulated PuO -YSZ kernels (CeO
-YSZ kernels (CeO -YSZ particles or commercially available YSZ particles). Ce was used as simulating element of Pu. In this manuscript, microstructures of ZrC coated CeO
-YSZ particles or commercially available YSZ particles). Ce was used as simulating element of Pu. In this manuscript, microstructures of ZrC coated CeO -YSZ or YSZ particles were reported.
-YSZ or YSZ particles were reported.