Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.37(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Oka, Toshitaka; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*
JJAP Conference Proceedings (Internet), 9, p.011003_1 - 011003_7, 2023/00
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In the
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In the  CF reaction, muon transfer from deuteron to triton and muonic molecular formation are rate-limiting processes. In this work, we have investigated the role of resonance states of muonic molecule in the
CF reaction, muon transfer from deuteron to triton and muonic molecular formation are rate-limiting processes. In this work, we have investigated the role of resonance states of muonic molecule in the  CF which affects the muonic deuterium atom population. Solving simultaneous rate equations numerically by the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method, we determined the muonic molecular formation rate so that the number of fusion events reproduces a latest experimental result. It is revealed that the resonance states play a role to enhance the fusion rate by accelerating the de-excitation of the muonic atoms.
CF which affects the muonic deuterium atom population. Solving simultaneous rate equations numerically by the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method, we determined the muonic molecular formation rate so that the number of fusion events reproduces a latest experimental result. It is revealed that the resonance states play a role to enhance the fusion rate by accelerating the de-excitation of the muonic atoms.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 170, p.112712_1 - 112712_4, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) and a muon decays immediately via nuclear fusion and the muon will be released as a recycling muon, and start to find another hydrogen isotope nucleus. The reaction cycle continues until the muon ends up its lifetime of 2.2  s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion (
s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after
CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 169, p.112580_1 - 112580_5, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by  and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt
and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt . Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt
. Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt , the nuclear fusion, d +t
, the nuclear fusion, d +t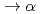 + n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion (
+ n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). Recently, the interest on
CF). Recently, the interest on  CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of
CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of  CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:80.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion (
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion ( CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed
CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed  CF cycles in the two layers (H
CF cycles in the two layers (H /D
/D and D
and D /T
/T ). The T
). The T concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
 CF experiment at J-PARC MLF
CF experiment at J-PARC MLFNatori, Hiroaki*; Doiuchi, Shogo*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Miyashita, Konan*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Nagatani, Yukinori*; Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Oka, Toshitaka; et al.
no journal, ,
A muonic molecule which consists of muon and two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) decays immediately via nuclear fusion (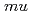 CF) and the muon will be released as a recycling muon. We attempted to use these muons to develop the scanning muon microscope. In this work, we will report the detection of neutron which emits during the
CF) and the muon will be released as a recycling muon. We attempted to use these muons to develop the scanning muon microscope. In this work, we will report the detection of neutron which emits during the  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalized fusion ( CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we attemped to observe a released muon after intermolecular nuclear reaction using muonic X-ray.
CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we attemped to observe a released muon after intermolecular nuclear reaction using muonic X-ray.
 CF experiment at J-PARC MLF
CF experiment at J-PARC MLFOkutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalized fusion ( CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we discussed how to observe a kinetic energy distribution of a recycling muon emitted after
CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we discussed how to observe a kinetic energy distribution of a recycling muon emitted after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Miyashita, Konan*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
To observe a kinetic energy distribution of a recycling muon emitted after  CF reaction, it is necessary to guide the recycling muons to a detector. In this work, we simulated the muon transportation using PHITS code and designed an experimental system.
CF reaction, it is necessary to guide the recycling muons to a detector. In this work, we simulated the muon transportation using PHITS code and designed an experimental system.
Nakashima, Ryota*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
The recycling muon emitted after the muon catalized fusion ( CF) has a kinetic energy between a few keV to 10 keV. To observed the kinetic energy distribution of the recycling muon, we have to guide and inject muons to Ti foil, and measure the muonic X-ray. In this work, we utilized SIMION code to calculate the electric field and the trajectory of muons from deuteron target to Ti foil.
CF) has a kinetic energy between a few keV to 10 keV. To observed the kinetic energy distribution of the recycling muon, we have to guide and inject muons to Ti foil, and measure the muonic X-ray. In this work, we utilized SIMION code to calculate the electric field and the trajectory of muons from deuteron target to Ti foil.
Miyashita, Konan*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
To measure the kinetic energy of a recycling muon, we discussed how to reduce the background radiation and the trajectory of the transported recycling muons by simulation code.
Nakashima, Ryota*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
To detect a recycling muon emitted after muon catalyzed fusion reaction, it is necessary to guide the recycling muons from the target to a detector in a low background area. In this work, we simulated the muon transportation using SIMONS and PHITS codes and designed an experimental system.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A muon is one of elementary particles which is known to weight 207 times more than an electron. A nuclear fusion reaction occurs in a muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei and a muon because the muon binds more tightly than electron. Since the muon does not directly participate in the fusion reaction, the reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The muon released after the reaction is called a "recycling muon", and maintains the molecular orbital information when the muonic molecule formed. Therefore, information of the muon wavefunction can be investigated by observing the energy distribution of the recycling muon. We will report the experimental setup for measuring the energy distribution of the recycling muons after the nuclear reaction.
CF). The muon released after the reaction is called a "recycling muon", and maintains the molecular orbital information when the muonic molecule formed. Therefore, information of the muon wavefunction can be investigated by observing the energy distribution of the recycling muon. We will report the experimental setup for measuring the energy distribution of the recycling muons after the nuclear reaction.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes, such as
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes, such as 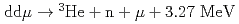 or
or 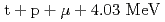 . In this work, we have investigated the shape and characteristic of solid hydrogen isotope target.
. In this work, we have investigated the shape and characteristic of solid hydrogen isotope target.
Miyashita, Konan*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we have designed the shape of the thermal shield to reduce the background noise.
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we have designed the shape of the thermal shield to reduce the background noise.
Nakashima, Ryota*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We are developing an experimental system to measure the kinetic energy distribution of regenerated muons emitted after muon catalytic nuclear reactions. The trajectory of the regenerated muon emitted from a solid hydrogen target, and the transport efficiency of the regenerated muon and its dependence on the emitted position are calculated/discussed using SIMION code.
Yomogida, Takumi; Yamada, Shinya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Sato, Toshiki*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Toyama, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Noda, Hirofumi*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Biotite is known as a host phase that retains uranium (U) in uranium deposits at Ningyo-Toge and Tono, and it is expected that the distribution of U in biotite will provide insight into the concentration and long-term immobilization of U. However, biotite contains rubidium (Rb), which interferes with X-ray fluorescence analysis, making it difficult to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite by measurement using a conventional solid state detector (SSD). In this study, we developed a method to use a transition edge sensor (TES) as a detector in microbeam X-ray fluorescence analysis, which enables us to detect X-ray fluorescence with an energy resolution of about 20 eV and to obtain a Rb K line at 13.373 keV and a U L
line at 13.373 keV and a U L line at 13.612 keV can be completely separated. Therefore,the developed method enables us to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite.
line at 13.612 keV can be completely separated. Therefore,the developed method enables us to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite.
Konishi, Ren*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sasaki, Kyosuke*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we used PHITS code to simulate the behavior of the low-energy muon in a thin layer of the solid hydrogen.
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we used PHITS code to simulate the behavior of the low-energy muon in a thin layer of the solid hydrogen.