Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sonoda, Tetsu*; Wada, Michiharu*; Tomita, Hideki*; Sakamoto, Chika*; Takatsuka, Takaaki*; Furukawa, Takeshi*; Iimura, Hideki; Ito, Yuta*; Kubo, Toshiyuki*; Matsuo, Yukari*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 295, p.1 - 10, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:83.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Sano, Asami; Yagi, Takehiko*; Okada, Taku*; Goto, Hirotada*; Kikegawa, Takumi*
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 39(5), p.375 - 383, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:55.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)X-ray diffraction measurements of distorted rutile-type oxyhydroxides  -GaOOH, InOOH,
-GaOOH, InOOH,  -CrOOH, and
-CrOOH, and  -CrOOD were taken at a maximum pressure of up to 35 GPa under quasi-hydrostatic conditions, at ambient temperature. Anomalies in the evolution of the relative lattice constants and the axial ratios of
-CrOOD were taken at a maximum pressure of up to 35 GPa under quasi-hydrostatic conditions, at ambient temperature. Anomalies in the evolution of the relative lattice constants and the axial ratios of  -GaOOH, InOOH, and
-GaOOH, InOOH, and  -CrOOD suggest anisotropic stiffening along the a- and/or b-axes where the hydrogen bond is formed. The changes were observed at 15 GPa in
-CrOOD suggest anisotropic stiffening along the a- and/or b-axes where the hydrogen bond is formed. The changes were observed at 15 GPa in  -GaOOH and InOOH and at 4 GPa in
-GaOOH and InOOH and at 4 GPa in  -CrOOD. The pressures were higher in oxyhydroxides that have longer O...O distances of the hydrogen bond at ambient pressure. In contrast, such stiffening behavior was not observed in CrOOH, which has a significant short O...O distance and strong hydrogen bond. The stiffening behaviors observed in the present study can be attributed to the symmetrization of the hydrogen bonds in oxyhydroxides, as was previously found in
-CrOOD. The pressures were higher in oxyhydroxides that have longer O...O distances of the hydrogen bond at ambient pressure. In contrast, such stiffening behavior was not observed in CrOOH, which has a significant short O...O distance and strong hydrogen bond. The stiffening behaviors observed in the present study can be attributed to the symmetrization of the hydrogen bonds in oxyhydroxides, as was previously found in  -AlOOH(D).
-AlOOH(D).
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
Yogo, Akifumi; Sato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Mori, Michiaki; Teshima, Teruki*; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Murakami, Masao*; Demizu, Yusuke*; Akagi, Takashi*; Nagayama, Shinichi*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 94(18), p.181502_1 - 181502_3, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:110 Percentile:94.75(Physics, Applied)
Fuchizaki, Kazuhiro*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*; Oishi, Yasuo*; Omura, Ayako*; Hamaya, Nozomu*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Okada, Taku
Journal of Chemical Physics, 120(23), p.11196 - 11199, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:58.21(Chemistry, Physical)The location of the liquidus in the low-pressure crystalline phase of SnI was determined utilizing
was determined utilizing  X-ray diffraction measurements under pressures up to approximately
X-ray diffraction measurements under pressures up to approximately 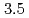 GPa. The liquidus is not well fitted to a monotonically increasing curve such as Simon's equation, but breaks near
GPa. The liquidus is not well fitted to a monotonically increasing curve such as Simon's equation, but breaks near  GPa and then becomes almost flat. The results are compared to those from molecular dynamics simulations. Ways to improve the model potential adopted in the simulations are discussed.
GPa and then becomes almost flat. The results are compared to those from molecular dynamics simulations. Ways to improve the model potential adopted in the simulations are discussed.
Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru; Kaneko, Hiroshi*; Turkevich, V.*; Hamaya, Nozomu; Shimomura, Osamu*
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 31(4), p.261 - 268, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:41.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The graphite-diamond transformation was investigated by in situ time-resolved X-ray diffraction experiments using aqueous fluid containing dissolved MgO as the diamond forming catalyst under conditions of 6.6-8.9 GPa and 1400-1835  C. The transformed volume fractions of diamond as a function of time under various pressure-temperature conditions were obtained and analyzed using the JMAK rate equation. Variations in the nucleation and growth processes during diamond formation as a function of pressure and temperature were clarified.
C. The transformed volume fractions of diamond as a function of time under various pressure-temperature conditions were obtained and analyzed using the JMAK rate equation. Variations in the nucleation and growth processes during diamond formation as a function of pressure and temperature were clarified.
 X-ray diffraction of graphite-diamond transformation using various catalysts under high pressures and high temperatures
X-ray diffraction of graphite-diamond transformation using various catalysts under high pressures and high temperaturesUtsumi, Wataru; Okada, Taku; Taniguchi, Takashi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kikegawa, Takumi*; Hamaya, Nozomu; Shimomura, Osamu
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 16(14), p.S1017 - S1026, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54(Physics, Condensed Matter)The graphite-diamond transformation was investigated using in-situ time-resolved X-ray diffraction experiments with a MgO dissolved aqueous fluid as the diamond forming catalyst under conditions of 6.6-8.8 GPa and 1400-1835 C. Experiments were conducted using a 180-ton DIA-type cubic-anvil apparatus installed on the beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8, a third-generation synchrotron radiation facility in Japan. By analyzing the kinetic data using the JMAK rate equation, it was clarified that altering the pressure-temperature conditions drastically changes the nucleation and growth process of diamond.
C. Experiments were conducted using a 180-ton DIA-type cubic-anvil apparatus installed on the beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8, a third-generation synchrotron radiation facility in Japan. By analyzing the kinetic data using the JMAK rate equation, it was clarified that altering the pressure-temperature conditions drastically changes the nucleation and growth process of diamond.
Utsumi, Wataru; Katayama, Yoshinori; Saito, Hiroyuki; Kaneko, Hiroshi*; Okada, Taku*; Otaka, Osamu*
Mirai O Hiraku Koatsuryoku Kagaku Gijutsu Semina Shirizu, 28, p.14 - 20, 2004/01
no abstracts in English
 X-ray diffraction
X-ray diffractionWang, W. H.*; Wen, P.*; Zhao, D. Q.*; Pan, M. X.*; Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru
Applied Physics Letters, 83(25), p.5202 - 5204, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:61.65(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 Al
Al Fe
Fe Co
Co bulk metallic glass under high pressure
bulk metallic glass under high pressureZhao, D. Q.*; Pan, M. X.*; Wang, W. H.*; Wei, B. C.*; Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(50), p.L749 - L753, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:31.91(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Wang, W. H.*; Okada, Taku; Wen, P.*; Wang, X. L.*; Pan, M. X.*; Zhao, D. Q.*; Utsumi, Wataru
Physical Review B, 68(18), p.184105_1 - 184105_6, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:79.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Wang, Z. X.*; Zhao, D. Q.*; Pan, M. X.*; Wang, W. H.*; Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(35), p.5923 - 5932, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:73.73(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 X-ray observations of the diamond formation process in the C-H
X-ray observations of the diamond formation process in the C-H O-MgO system
O-MgO systemOkada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru; Shimomura, Osamu
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 14(44), p.11331 - 11335, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.6(Physics, Condensed Matter)In order to clarify the mechanism of diamond formation in the Earth's mantle, we studied the diamond formation in the H O-fluid by in situ X-ray observation with the simple C-H
O-fluid by in situ X-ray observation with the simple C-H O-MgO system. The results suggest that the solubility of MgO component increases greatly as a function of pressure. However, the generation of fluid is not a sufficient condition for diamond formation, because the carbon quantity in fluid is not increased drastically until just before the diamond formation temperature. This is the first report of the kinetics study in fluid using synchrotron radiation.
O-MgO system. The results suggest that the solubility of MgO component increases greatly as a function of pressure. However, the generation of fluid is not a sufficient condition for diamond formation, because the carbon quantity in fluid is not increased drastically until just before the diamond formation temperature. This is the first report of the kinetics study in fluid using synchrotron radiation.
Turkevich, V.*; Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru; Garan, A.*
Diamond and Related Materials, 11(10), p.1769 - 1773, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:62.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru; Kaneko, Hiroshi*; Yamakata, Masaaki*; Shimomura, Osamu
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 29(7), p.439 - 445, 2002/08
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:53.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)An experimental technique to make real-time observations at high pressure and temperature of the diamond forming process in candidate material of mantle fluids as a catalyst has been established for the first time. In situ X-ray diffraction experiments using synchrotron radiation have been performed upon a mixture of brucite (Mg(OH) ) and graphite as starting material. Brucite decomposes into periclase (MgO) and H
) and graphite as starting material. Brucite decomposes into periclase (MgO) and H O at 3.6 GPa and 1050
O at 3.6 GPa and 1050 C while no periclase is formed after the decomposition of brucite at 6.2 GPa and 1150
C while no periclase is formed after the decomposition of brucite at 6.2 GPa and 1150 C, indicating that the solubility of the MgO component in H
C, indicating that the solubility of the MgO component in H O greatly increases with increasing pressure. The conversion of graphite to diamond in aqueous fluid has been observed at 7.7 GPa and 1835
O greatly increases with increasing pressure. The conversion of graphite to diamond in aqueous fluid has been observed at 7.7 GPa and 1835 C. Time-dependent X-ray diffraction profiles for this transformation have been successfully obtained.
C. Time-dependent X-ray diffraction profiles for this transformation have been successfully obtained.
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Kiminori*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku
Geophysical Research Letters, 29(8), p.68_1 - 68_3, 2002/05
The in situ viscosity measurements of the pure molten Fe under high pressures were made by falling sphere X-ray radiography method. Viscosity coefficients at about 2000 K were 15-24 mPa s at 2.7-5.0 GPa, and 4-9 mPa s at 5.0-7.0 GPa. Drastic decrease was found at around 5 GPa, at which stable solid phase below the melting temperatures change from delta (bcc) to gamma (fcc) phases. The observation indicates the possibility that the structural change in the molten Fe occurs in a narrow pressure interval (1 GPa) at the similar condition with the phase transformation in the solid.
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku; Maeda, Makoto*; Sato, Jin*; Kubo, Tomoaki*; Kasai, Shizu*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 190(1-2), p.93 - 101, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:68.57(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The Fe-FeS melt is thought to be the major candidate of the outer core material. Its viscosity is one of the most important physical properties to study the dynamics of the convection in the outer core. We performed the in situ viscosity measurement of the Fe-FeS melt under high pressure using X-ray radiography falling sphere method with a novel sample assembly. Viscosity was measures in the temperature, pressure, and compositional conditions of 1233-1923 K, 1.5-6.9 GPa, and Fe-Fe 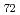 S
S 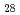 (wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm
(wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm  /mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe
/mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe 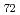 S
S 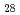 melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
 X-ray observation of cubic BC
X-ray observation of cubic BC N formation under high pressures and temperatures
N formation under high pressures and temperaturesUtsumi, Wataru; Okada, Taku; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Shimomura, Osamu
Proceeding of the 8th NIRIM International Symposium on Advanced Materials (ISAM 2001), p.39 - 40, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
;
PNC TN9410 93-086, 81 Pages, 1992/11
Since vessels of fast breeder reactors (FBRs) are relatively thin wallcd, the prevention of buckling against seismic loading is one of the key issues in their structural design. This paper is the first report on buckling analysis by use of FEM to rationalize a design method for FBR components. In this paper, we conducted FEM analyses with the FINAS computer code modelling the test conditions precisely, especially the initial shape imperfections and material nonlinearity of the test specimens. Further, the effect of the initial shape imperfections on buckling strength was evaluated quantitatively, and the applicability of FEM to the present problem was studied. The following results were obtained. (1)It was confirmed that the initial shapes of test specimens could be modeled precisely by use of SAXON and the measured data by CIMD. (2)By modelling precisely the initial shape imperfections and material nonlinearity of the test specimens, FEM results agreed well with the test data in terms of the buckling strength, regardless of the buckling mode. The deferences of buckling strength between FEM and experiment results were within -2.5%  4.5% of experimental results. (3)Concerning the case in which the ratio of length to radius is 2.0, we confirmed that the buckling mode was changed by the existence of initial shape imperfections.
4.5% of experimental results. (3)Concerning the case in which the ratio of length to radius is 2.0, we confirmed that the buckling mode was changed by the existence of initial shape imperfections.