Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mori, Kazuhiro*; Okumura, Ryo*; Yoshino, Hirofumi*; Kanayama, Masaya*; Sato, Setsuo*; Oba, Yojiro; Iwase, Kenji*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Hino, Masahiro*; Sano, Tadafumi*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011093_1 - 011093_6, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
 S)
S) (SiS
(SiS )
)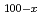 superionic glasses
superionic glassesMori, Kazuhiro*; Iwase, Kenji*; Oba, Yojiro; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Fukunaga, Toshiharu*
Solid State Ionics, 344, p.115141_1 - 115141_10, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.81(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Tsai, P.-E.; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(6), p.684 - 690, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:775 Percentile:100(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have upgraded many features of the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) and released the new version as PHITS3.02. The accuracy and the applicable energy ranges of the code were greatly improved and extended, respectively, owing to the revisions to the nuclear reaction models and the incorporation of new atomic interaction models. In addition, several user-supportive functions were developed, such as new tallies to efficiently obtain statistically better results, radioisotope source-generation function, and software tools useful for applying PHITS to medical physics. In this paper, we summarize the basic features of PHITS3.02, especially those of the physics models and the functions implemented after the release of PHITS2.52 in 2013.
Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 60(5), p.294 - 298, 2018/05
, 60(5), p.294 - 298, 2018/05
For calculations of neutron productions and radiation damages in nuclear design of Accelerator Driven System (ADS) and exposure doses in radiation cancer therapy, radiation transport simulations with the high-energy nuclear data library evaluated with experimental data play an important role. Experimental data are needed for validation of nuclear reaction models in calculation codes. In this paper, we explain examples of nuclear data measurements in high energy region and the progress of the Particle and Heavy-Ion Transport code System (PHITS) developed in Japan.
Sanami, Toshiya*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Nakamura, Shoji
JAEA-Conf 2017-001, 222 Pages, 2018/01
The 2016 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Kobayashi Hall of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, on November 17 and 18, 2016. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan in cooperation with Radiation Science Center, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency and North Kanto Branch of Atomic Energy Society of Japan. In the symposium, there were one tutorial, "Historical Evolution of Accelerators" and four oral sessions, "Overview of the ImPACT Program - Reduction and Resource Recycling of High Level Wastes through Nuclear Transmutation", "Facilities and experiments for nuclear data in Japan", "Nuclear data from measurement to application", and "Progress of neutron nuclear data measurement and research for its basics and application". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, evaluation, benchmark and application was presented in the poster session. Among 65 participants, all presentations and following discussions were very active and fruitful. This report consists of total 31 papers including 10 oral and 21 poster presentations.
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kowatari, Munehiko; Nishino, Sho; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwase, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1188 - 1195, 2017/11
The equivalent doses to the lens of the eye and extremities for radiation workers should be assessed properly to ensure that the dose limits are not exceeded. Recently, the following two issues has pressed demand on more appropriate evaluation of the equivalent doses of the lens of the eye and extremity. One is the new occupational dose limit for the lens of the eye the ICRP recommended. The other is growing demand on handling of highly activated materials in the maintenance works of an accelerator and contaminated materials during the decommissioning works of nuclear facility, which increases the potential exposure risk to the extremities to a wider variety of radio-nuclides. Since the points to be assessed for the exposures to the lens of the eye and the extremities are apart from the trunk, the homogeneity of the radiation fields would be significantly impact on the assessment of these equivalent doses. However, there has been no sufficient and available method to identify the nonhomogeneous situations systematically in terms of the eye lens or extremity monitoring. The goal of this study is to provide the framework to identify the nonhomogeneous exposure situations. In order to fulfil this purpose, newly proposed indices to represent the homogeneity were calculated by Monte Carlo simulation incorporated with mathematical phantom, verifying the benchmark measurements. Important parameters that significantly impact on these indices were also shown from the various trials of calculations of homogeneity indices.
 -ray energy spectra of 80-400 MeV
-ray energy spectra of 80-400 MeV  Li(p,n) reactions under the quasi-monoenergetic neutron field at RCNP, Osaka University
Li(p,n) reactions under the quasi-monoenergetic neutron field at RCNP, Osaka UniversityIwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Nakamura, Takashi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08019_1 - 08019_3, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)To develop 100-400 MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutron field, we measured neutron and unexpected  -ray energy spectra of the
-ray energy spectra of the  Li(p,n) reaction with 80-389 MeV protons in the 100-m time-of-flight (TOF) tunnel at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP). Neutron energy spectra with energies above 3 MeV were measured by the TOF method and
Li(p,n) reaction with 80-389 MeV protons in the 100-m time-of-flight (TOF) tunnel at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP). Neutron energy spectra with energies above 3 MeV were measured by the TOF method and  energy spectra with energies above 0.1 MeV were measured by the automatic unfolding function of the radiation dose monitor DARWIN. For neutron spectra, the contribution of peak intensity to the total intensity integrated with energies above 3 MeV varied between 0.38 and 0.48. For
energy spectra with energies above 0.1 MeV were measured by the automatic unfolding function of the radiation dose monitor DARWIN. For neutron spectra, the contribution of peak intensity to the total intensity integrated with energies above 3 MeV varied between 0.38 and 0.48. For  -ray spectra, high-energetic
-ray spectra, high-energetic  -rays at around 70 MeV originated from the decay of
-rays at around 70 MeV originated from the decay of 
 were observed over 200 MeV. For the 246-MeV proton incident reaction, the contribution of
were observed over 200 MeV. For the 246-MeV proton incident reaction, the contribution of  -ray dose to neutron dose is negligible because the ratio of
-ray dose to neutron dose is negligible because the ratio of  -ray to neutron is 0.014.
-ray to neutron is 0.014.
Theis, C.*; Carbonez, P.*; Feldbaumer, E.*; Forkel-Wirth, D.*; Jaegerhofer, L.*; Pangallo, M.*; Perrin, D.*; Urscheler, C.*; Roesler, S.*; Vincke, H.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08018_1 - 08018_5, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)At CERN, gas-filled ionization chambers PTW-34031 (PMI) are commonly used in radiation fields including neutrons, protons and  -rays. A response function for each particle is calculated by the radiation transport code FLUKA. To validate a response function to high energy neutrons, benchmark experiments with quasi mono-energetic neutrons have been carried out at RCNP, Osaka University. For neutron irradiation with energies below 200 MeV, very good agreement was found comparing the FLUKA simulations and the measurements. In addition it was found that at proton energies of 250 and 392 MeV, results calculated with neutron sources underestimate the experimental data due to a non-negligible gamma component originating from the target
-rays. A response function for each particle is calculated by the radiation transport code FLUKA. To validate a response function to high energy neutrons, benchmark experiments with quasi mono-energetic neutrons have been carried out at RCNP, Osaka University. For neutron irradiation with energies below 200 MeV, very good agreement was found comparing the FLUKA simulations and the measurements. In addition it was found that at proton energies of 250 and 392 MeV, results calculated with neutron sources underestimate the experimental data due to a non-negligible gamma component originating from the target  Li(p,n)Be reaction.
Li(p,n)Be reaction.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.06008_1 - 06008_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:95.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, has been developed under the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. It can deal with the transport of nearly all particles up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ion) using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. More than 2,500 researchers and technicians have used the code for a variety of applications such as accelerator design, radiation shielding and protection, medical physics, and space and geosciences. This paper briefly summarizes physics models and functions newly implemented in PHITS between versions 2.52 and 2.82.
Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08016_1 - 08016_3, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron energy spectra behind concrete and iron shields were measured for quasi-monoenergetic neutrons above 200 MeV using a Bonner sphere spectrometer (BSS). Quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were produced by the  Li(p,xn) reaction with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons. The response function of BSS was also measured at neutron energies from 100 MeV to 387 MeV. In data analysis, the measured response function was used and the multiple neutron scattering effect between the BSS and the shielding material was considered. The neutron energy spectra behind the concrete and iron shields were obtained by the unfolding method using the MAXED code. Ambient dose equivalents were obtained as a function of a shield thickness successfully. For the case of the 244 MeV neutron incidence, the multiple neutron scattering effect on the effective dose is large under 50 cm thickness of the concrete shield.
Li(p,xn) reaction with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons. The response function of BSS was also measured at neutron energies from 100 MeV to 387 MeV. In data analysis, the measured response function was used and the multiple neutron scattering effect between the BSS and the shielding material was considered. The neutron energy spectra behind the concrete and iron shields were obtained by the unfolding method using the MAXED code. Ambient dose equivalents were obtained as a function of a shield thickness successfully. For the case of the 244 MeV neutron incidence, the multiple neutron scattering effect on the effective dose is large under 50 cm thickness of the concrete shield.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Niita, Koji*
Hoshasen, 43(2), p.55 - 58, 2017/05
Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, has been developed under the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. It can deal with the transport of nearly all particles up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ion) using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. More than 2,500 registered researchers and technicians have used this system for various applications such as accelerator design, radiation shielding and protection, medical physics, and space- and geo-sciences. This paper summarizes the physics models and functions recently implemented in PHITS, between versions 2.52 and 2.88.
Masuda, Akihiko*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nishiyama, Jun*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 849, p.94 - 101, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Instruments & Instrumentation)Quasi-monoenergetic high-energy neutron fields induced by  Li(p,n) reactions are used for the response evaluation of neutron-sensitive devices. The quasi-monoenergetic high-energy field consists of high-energy monoenergetic peak neutrons and unwanted continuum neutrons down to the low-energy region. A two-angle differential method has been developed to compensate for the effect of the continuum neutrons in the response measurements. In this study, the two-angle differential method was demonstrated for Bonner sphere detectors, which are typical examples of moderator-based neutron-sensitive detectors, to investigate the method's applicability and its dependence on detector characteristics. Through this study, the adequacy of the two-angle differential method was experimentally verified, and practical suggestions were made pertaining to this method.
Li(p,n) reactions are used for the response evaluation of neutron-sensitive devices. The quasi-monoenergetic high-energy field consists of high-energy monoenergetic peak neutrons and unwanted continuum neutrons down to the low-energy region. A two-angle differential method has been developed to compensate for the effect of the continuum neutrons in the response measurements. In this study, the two-angle differential method was demonstrated for Bonner sphere detectors, which are typical examples of moderator-based neutron-sensitive detectors, to investigate the method's applicability and its dependence on detector characteristics. Through this study, the adequacy of the two-angle differential method was experimentally verified, and practical suggestions were made pertaining to this method.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.63 - 69, 2016/09
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. PHITS users apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some new models such as muon-induced nuclear reaction model and a  de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
 Li(p,n) reactions using a time-of-flight method
Li(p,n) reactions using a time-of-flight methodIwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Araki, Shohei*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Masuda, Akihiko*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Nakao, Noriaki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 804, p.50 - 58, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:87.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have measured neutron energy spectra for the 80, 100 and 296 MeV proton incident reactions at the RCNP cyclotron facility using time-of-flight method. The neutron energy spectrum consisted of the peak and continuum parts and the peak intensity was 0.9-1.1  10
10 neutrons/sr/
neutrons/sr/ C. The ratio of peak intensity of the spectrum to the total intensity was between 0.38 and 0.48. To consider the correction required to derive a response in the peak region from the measured total response for neutron monitors, we proposed the subtraction method using energy spectra between 0
C. The ratio of peak intensity of the spectrum to the total intensity was between 0.38 and 0.48. To consider the correction required to derive a response in the peak region from the measured total response for neutron monitors, we proposed the subtraction method using energy spectra between 0 and 25
and 25 . The normalizing factor k against the 25
. The normalizing factor k against the 25 neutron fluence that equalizes the 0
neutron fluence that equalizes the 0 neutron fluence in the continuum region was from 0.74 to 1.02. With our previous results, we have obtained data for characterization of monoenergetic neutron field for the
neutron fluence in the continuum region was from 0.74 to 1.02. With our previous results, we have obtained data for characterization of monoenergetic neutron field for the  Li(p,n) reaction with 80
Li(p,n) reaction with 80 389 MeV protons at the RCNP cyclotron facility.
389 MeV protons at the RCNP cyclotron facility.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 82, p.110 - 115, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:93.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)The general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through a collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is responsible for managing the entire project. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. This paper briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions useful for particular purposes, such as an event generator mode and beam transport functions.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.69 - 74, 2015/02
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. All components of PHITS such as its source, executable and data-library files are assembled in one package and then distributed to many countries. More than 1,000 researchers apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions for specific applications, such as an event generator mode and a radiation damage calculation function.
Sihver, L.*; Kohama, Akihisa*; Iida, Kei*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Niita, Koji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 334, p.34 - 39, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:85.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)Accurate calculations of the nucleon + nucleus and nucleus + nucleus total reaction cross sections are of great importance for designing accelerator facilities and estimating dose in particle therapy with particle and heavy ion transport calculations, because the probability of nuclear reactions in the calculations depends on the cross sections. The Kurotama model assumes a target nucleus to be Black Sphere (BS), and gives the total reaction cross sections systematically using its radius determined from proton-nucleus elastic scattering data. However, the BS model breaks down below around 100 MeV/u. In this study, we developed the "hybrid Kurotama" model by connecting the BS model to the semi-empirical model of Tripathi et al. at low energies. The model has been tested against available p + He, p + nucleus, and nucleus + nucleus data and an overall better agreement has been found than for earlier published models. This model is suitable to be used in particle transport calculations.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Tamii, Atsushi*; Hatanaka, Kichiji*
IAEA-TECDOC-1743, Annex (CD-ROM), p.177 - 188, 2014/07
A quasi-monoenergetic neutron field using  Li(p,n) reaction for the higher energy range of 100 to 400 MeV has been developed at the RCNP cyclotron facility of Osaka University. The neutron energy spectra at angles from 0
Li(p,n) reaction for the higher energy range of 100 to 400 MeV has been developed at the RCNP cyclotron facility of Osaka University. The neutron energy spectra at angles from 0 to 30
to 30 have been investigated for the proton beams with the energies of 140, 250, 350 and 392 MeV. The highest neutron fluence reaches 1.0
have been investigated for the proton beams with the energies of 140, 250, 350 and 392 MeV. The highest neutron fluence reaches 1.0  10
10 n/sr/
n/sr/ C, and the contribution of peak intensity to the total intensity varied between 0.4 and 0.5. Using the quasi-monoenergetic neutron beam, measurement of neutron induced activation cross sections, elastic scattering cross sections for neutron and a shielding benchmark experiment have been performed, successfully. Thus quasi-monoenergetic neutron field at RCNP are suitable for measurement of nuclear data, shielding experiments and the calibration of monitors in the energy region from 100 to 400 MeV.
C, and the contribution of peak intensity to the total intensity varied between 0.4 and 0.5. Using the quasi-monoenergetic neutron beam, measurement of neutron induced activation cross sections, elastic scattering cross sections for neutron and a shielding benchmark experiment have been performed, successfully. Thus quasi-monoenergetic neutron field at RCNP are suitable for measurement of nuclear data, shielding experiments and the calibration of monitors in the energy region from 100 to 400 MeV.
 Li(p,n) reactions
Li(p,n) reactionsIwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Satoh, Daiki; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Pioch, C.*; Mares, V.*; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.657 - 660, 2014/04
The authors measured the neutron energy spectra of the proton incident reaction on the lithium target with 137, 200, 246 and 389 MeV protons at several angles (0 , 2.5
, 2.5 , 5
, 5 , 10
, 10 , 15
, 15 , 20
, 20 , 25
, 25 and 30
and 30 ), using a time-of-flight (TOF) method employing organic scintillators NE213 at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of Osaka University. For the neutron energy spectrum at 0
), using a time-of-flight (TOF) method employing organic scintillators NE213 at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of Osaka University. For the neutron energy spectrum at 0 , the ratio of the peak neutron intensity to the total one varied between 0.4 and 0.5 depending on the incident energy. In order to consider the correction required to derive the response in the peak region from the measured total response for high-energy neutron detectors, the authors showed the subtractions of H*(10) obtained at larger angles from the 0
, the ratio of the peak neutron intensity to the total one varied between 0.4 and 0.5 depending on the incident energy. In order to consider the correction required to derive the response in the peak region from the measured total response for high-energy neutron detectors, the authors showed the subtractions of H*(10) obtained at larger angles from the 0 data in the continuum part. It was found that subtracting the dose equivalent at about 22
data in the continuum part. It was found that subtracting the dose equivalent at about 22 from the 0
from the 0 data reduces the continuum component most efficiency.
data reduces the continuum component most efficiency.
Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Harano, Hideki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.332 - 336, 2014/04
Recently, many high-energy accelerators are used for various fields. Shielding data for high-energy neutrons are therefore very important from the point of view of radiation protection in high energy accelerator facilities. However, the shielding experimental data for high energy neutrons above 100 MeV are very poor both in quality and in quantity. In this study, neutron penetration spectral fluence and ambient dose through iron and concrete shields were measured with a Bonner sphere spectrometer (BSS). Quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were produced by the  Li(p,xn) reaction by bombarding a 1-cm thick Li target with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of the Osaka University. Shielding materials are iron blocks with a thickness from 10 cm to 100 cm and concrete blocks with a thickness from 25 cm to 300 cm.
Li(p,xn) reaction by bombarding a 1-cm thick Li target with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of the Osaka University. Shielding materials are iron blocks with a thickness from 10 cm to 100 cm and concrete blocks with a thickness from 25 cm to 300 cm.