Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 275, p.107882_1 - 107882_9, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:38.03(Optics)Following the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, an isotope-selective analysis method using laser resonance ionization has been developed for strontium-90. In this study, the isotope shifts and hyperfine structure constants of stable isotopes were measured for two schemes expected to have high isotopic selectivity, and the isotope shifts of strontium-90 were evaluated using the King plot analysis. The measured strontium-90 optical isotopic selectivities ranged from 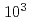 to
to 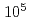 , which are sufficient for analysis of real samples.
, which are sufficient for analysis of real samples.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 265, p.107549_1 - 107549_7, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.84(Optics)Following the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, an isotope-selective analysis method using laser resonance ionization has been developed for strontium-90. In this study, we focused on ionization via autoionization states in terms of high isotopic selectivity and ionization efficiency, and the DC Stark shifts caused by the external electric field were measured for these states. It was found that the external electric field in the ionization region has to be of the order of 0.1 V/cm or less to suppress its effect on the observed spectra.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Sekiya, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 797, p.64 - 69, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)An ultrasensitive resonance ionization mass spectrometer that can be applied to evaluate krypton (Kr) contamination in xenon (Xe) dark matter detectors has been developed for measuring Kr at the parts-per-trillion (ppt) or sub-ppt level in Xe. The gas sample is introduced without any condensation into a time-of-flight mass spectrometer through a pulsed supersonic valve. Using a nanosecond pulsed laser at 212.6 nm,  Kr atoms in the sample are resonantly ionized along with other Kr isotopes.
Kr atoms in the sample are resonantly ionized along with other Kr isotopes.  Kr ions are then mass separated and detected by the mass spectrometer in order to measure the Kr impurity concentration. With our current setup, approximately 0.4 ppt of Kr impurities contained in pure argon (Ar) gas are detectable with a measurement time of 1,000 s. Although Kr detection sensitivity in Xe is expected to be approximately half of that in Ar, our spectrometer can evaluate Kr contamination in Xe to the sub-ppt level.
Kr ions are then mass separated and detected by the mass spectrometer in order to measure the Kr impurity concentration. With our current setup, approximately 0.4 ppt of Kr impurities contained in pure argon (Ar) gas are detectable with a measurement time of 1,000 s. Although Kr detection sensitivity in Xe is expected to be approximately half of that in Ar, our spectrometer can evaluate Kr contamination in Xe to the sub-ppt level.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Ito, Chikara; Harano, Hideki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(4), p.465 - 475, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)To prevent a fuel failure event from becoming a serious radiation accident, sodium-cooled fast reactors are equipped with a system for failed fuel detection and location (FFDL). The FFDL instrument employed in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju is based on the gas tagging method, in which precise and accurate measurements of krypton and xenon isotope ratios (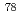 Kr/
Kr/ Kr,
Kr, 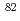 Kr/
Kr/ Kr and
Kr and  Xe/
Xe/ Xe) must be performed in a short time. Burnup measurements also contribute to accurate determination of
Xe) must be performed in a short time. Burnup measurements also contribute to accurate determination of 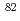 Kr/
Kr/ Kr. We have developed a highly sensitive resonance ionization mass spectrometer for the isotopic analyses, which uses resonance ionization of Kr and Xe atoms by a pulsed laser at wavelengths of 216.7 nm and 249.6 nm, respectively. In evaluating the performance of our spectrometer, we find that systematic errors caused by isotope shifts can be reduced to negligible levels, and that statistical errors of 3% at a nuclide concentration of 7 ppt can be achieved with a single measurement time of about 40 minutes for each Kr and Xe isotope ratio. This means that, within one hour, about 200 fuel assemblies can be individually identified with a probability of 99%, verifying the applicability of our spectrometer to the FFDL system of fast reactors.
Kr. We have developed a highly sensitive resonance ionization mass spectrometer for the isotopic analyses, which uses resonance ionization of Kr and Xe atoms by a pulsed laser at wavelengths of 216.7 nm and 249.6 nm, respectively. In evaluating the performance of our spectrometer, we find that systematic errors caused by isotope shifts can be reduced to negligible levels, and that statistical errors of 3% at a nuclide concentration of 7 ppt can be achieved with a single measurement time of about 40 minutes for each Kr and Xe isotope ratio. This means that, within one hour, about 200 fuel assemblies can be individually identified with a probability of 99%, verifying the applicability of our spectrometer to the FFDL system of fast reactors.
Aoyama, Takafumi; Ishikawa, Takashi; Ito, Chikara; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Harano, Hideki*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 106(1), p.611 - 613, 2012/06
We studied the failed fuel detection and location (FFDL) system by means of laser resonance ionization mass spectrometry (RIMS). The applicability of the RIMS system for Monju and its installation were investigated in this study. It was found that the RIMS is able to identify the neighboring tag gas which is used for Monju with the 68% reliability. The newly designed RIMS system can be accommodated in the present facility and can be connected to primary cover gas lines without affects to the current FFDL function of the conventional system.
Ito, Chikara; Araki, Yoshio; Naito, Hiroyuki; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Aoyama, Takafumi
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles (FR 2009) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2012/00
no abstracts in English
Ito, Chikara; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Harano, Hideki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Aoyama, Takafumi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 102(1), p.416 - 417, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Ito, Chikara; Aoyama, Takafumi*
KEK Proceedings 2010-10, p.52 - 62, 2010/02
For the fast reactors, rapid and accurate detection of fuel failures as well as subsequent identification of failed fuel location, if occurred, are essential to protect workers from radiation exposure and to reduce radiation contamination. A new type of failed fuel detection and location (FFDL) technique focused on the gas tagging method has been proposed by using resonance ionization mass spectrometry (RIMS) for the isotope analysis of the cover gas. Precise isotope analysis of ppt level Kr and Xe in Ar needed involves the two problems, which are the saturation of the output voltage by Ar ions and the Ar
ions and the Ar interference mainly with
interference mainly with  Kr. We proposed two methods, Brewster window and electrode with a slit-type hole, to decrease the adverse effect of Ar
Kr. We proposed two methods, Brewster window and electrode with a slit-type hole, to decrease the adverse effect of Ar and Ar
and Ar
 ions without any loss of Kr
ions without any loss of Kr and Xe
and Xe ion signals. The obtained measurement results using 100 ppt of Kr containing Ar standard gas show that we could successfully decrease the Ar
ion signals. The obtained measurement results using 100 ppt of Kr containing Ar standard gas show that we could successfully decrease the Ar ion yield by one to two orders of magnitude or more and that the mass peak of
ion yield by one to two orders of magnitude or more and that the mass peak of  Kr corresponding to its nuclide concentration of
Kr corresponding to its nuclide concentration of  2 ppt was clearly observed without any obvious Ar
2 ppt was clearly observed without any obvious Ar
 peak. The precision of the isotope analysis seems to be about 10% for ppt level detection of Kr and slightly better for Xe, and is dominated by statistical errors. The next step is to increase the detection efficiency of our RIMS system to reduce statistical errors for further reliability improvement of RIMS in the FFDL system.
peak. The precision of the isotope analysis seems to be about 10% for ppt level detection of Kr and slightly better for Xe, and is dominated by statistical errors. The next step is to increase the detection efficiency of our RIMS system to reduce statistical errors for further reliability improvement of RIMS in the FFDL system.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Ito, Chikara; Harano, Hideki*; Aoyama, Takafumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aoyama, Takafumi; Ito, Chikara; Araki, Yoshio; Naito, Hiroyuki; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Okazaki, Koki*; Harano, Hideki*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Takegawa, Nobuyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Ito, Chikara; Aoyama, Takafumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Ito, Chikara; Aoyama, Takafumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Chikara; Maeda, Shigetaka; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Aoyama, Takafumi; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Araki, Yoshio; Naito, Hiroyuki; Ito, Chikara; Aoyama, Takafumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Chikara; Araki, Yoshio; Naito, Hiroyuki; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Aoyama, Takafumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Ito, Chikara; Aoyama, Takafumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Ito, Chikara; Harano, Hideki*; Aoyama, Takafumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aoyama, Takafumi; Ito, Chikara; Naito, Hiroyuki; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Harano, Hideki*; Okazaki, Koki*; Araki, Yoshio*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Takegawa, Nobuyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Harano, Hideki*; Ito, Chikara; Aoyama, Takafumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Ito, Chikara; Harano, Hideki*; Aoyama, Takafumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English