Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsubara, Ryuta*; Ueno, Fuga*; Iwata, Hajime; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*
NUMO-TR-24-03, p.55 - 61, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Koike, Ayaka*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Iwata, Hajime; Fukatsu, Yuta; Taneichi, Yayoi
NUMO-TR-24-03, p.85 - 86, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Kimuro, Shingo; Taneichi, Yayoi; Iwata, Hajime; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kitamura, Akira; Tachi, Yukio; Tanaka, Takeru*; Hirano, Kana*; Hieda, Manami*; Miyabe, Shunsuke*; et al.
Journal of Solution Chemistry, 53(6), p.854 - 868, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Miyazaki, Kanako*; Takehara, Masato*; Minomo, Kenta*; Horie, Kenji*; Takehara, Mami*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Saito, Takumi*; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Takano, Masahide; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 470(15), p.134104_1 - 134104_11, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:36.75(Engineering, Environmental)Matsubara, Ryuta*; Takubo, Yusaku*; Iwata, Hajime; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*
NUMO-TR-24-01, p.104 - 108, 2024/05
no abstracts in English
Kaneko, Makoto*; Iwata, Hajime; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Masaki, Shota*; Kawamoto, Yuji*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Nakamatsu, Yuki*; Imoto, Jumpei*; Furuki, Genki*; Ochiai, Asumi*; et al.
Frontiers in Energy Research (Internet), 3, p.37_1 - 37_10, 2015/09
The mobility of the aggregates of submicron-sized sheet aluminosilicate in the surface environment is a key factor controlling the current Cs migration in Fukushima.
Doi, Reisuke; Iwata, Hajime; Kitamura, Akira
JAEA-Review 2014-014, 27 Pages, 2014/05
The solubility method is one of the most powerful tools to obtain reliable thermodynamic data for (1) solubility products of discrete solids and double salts, (2) complexation constants for various ligands, (3) development of data in a wide range of pH values, (4) evaluation of data for metals that form very insoluble solids (e.g. tetravalent actinides), (5) determining solubility-controlling solids in different types of wastes and (6) elevated temperatures for redox sensitive systems. This document is focused on describing various aspects of obtaining thermodynamic data using the solubility method. This manuscript deals with various aspects of conducting solubility studies, including selecting the study topic, modeling to define important variables, selecting the range of variables and experimental parameters, anticipating results, general equipment requirements, conducting experiments, and interpreting experimental data.
Iwata, Hajime; Kitamura, Akira
no journal, ,
The solubility of Nb was measured using oversaturation and undersaturation method. Compared with the values evaluated using JAEA-TDB, in the OS method a similar solubility was observed, and the measured values in the US method were around three orders magnitude below the evaluated values. It suggests that the solubility limiting solid differ between OS and US method.
Iwata, Hajime*; Sakamaki, Keiko*; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Onuki, Toshihiko; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
The aim of this study is to understand the fate of plutonium derived from atomic bomb, which has been preserved in the bottom sediment for 60 years, based on the investigation of the speciation and size distribution of plutonium. Approximately 60 % of plutonium is present as bound to organic matters and 30 % is present as insoluble species such as Pu oxides. Our results also suggest that the fast transformation of plutonium to the species bound to the organic matter for the period of 60 years, evidencing the important role of the natural organic matters on the plutonium speciation in the environment.
Matsubara, Ryuta*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Iwata, Hajime
no journal, ,
In order to improve reliability of performance assessment of vitrified waste for geological disposal, we have been developing a model to predict the long-term glass dissolution under disposal conditions. This presentation provides our R&D plan and the recent progress.
Matsubara, Ryuta*; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Iwata, Hajime
no journal, ,
Iwata, Hajime; Sekine, Nobuyuki*; Mitsui, Seiichiro
no journal, ,
Static leaching tests of simulated nuclear waste glass were carried out at 90 C in an air atmosphere using a MgCl
C in an air atmosphere using a MgCl solution and deionized water. As a result, in the MgCl
solution and deionized water. As a result, in the MgCl solution, temporal plateau and following resumption of glass dissolution were observed, while an ordinary dissolution behavior, which shows rate decrease with time, was observed in the deionized water. It is considered that these unique dissolution behavior in MgCl
solution, temporal plateau and following resumption of glass dissolution were observed, while an ordinary dissolution behavior, which shows rate decrease with time, was observed in the deionized water. It is considered that these unique dissolution behavior in MgCl solution may be related to the evolution of the Mg-containing mineral species deposited on the glass surface.
solution may be related to the evolution of the Mg-containing mineral species deposited on the glass surface.
 -isosaccharinic acid, 2
-isosaccharinic acid, 2Iwata, Hajime; Kimuro, Shingo; Kitamura, Akira; Miyabe, Shunsuke*; Maeno, Mamiko*; Tanaka, Takeru*; Hieda, Manami*
no journal, ,
The effect of  -isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility of palladium (Pd) in alkaline aqueous solution (pH 8.5, 10.0) was investigated by solubility experiments. The Pd concentration increased with the increase of ISA concentration. The equilibrium constant was calculated from the solubility data obtained in this study.
-isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility of palladium (Pd) in alkaline aqueous solution (pH 8.5, 10.0) was investigated by solubility experiments. The Pd concentration increased with the increase of ISA concentration. The equilibrium constant was calculated from the solubility data obtained in this study.
Iwata, Hajime
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsubara, Ryuta*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Iwata, Hajime; Sekine, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
Restriction of radionuclide release by low dissolution rate is expected for the vitrified waste as a one of safety functions of the geological disposal system. In order to assess the performance of vitrified waste, it is important to understand how its safety function works under the environmental condition of a deep geological repository. This presentation provides the recent progress on the R&D to improve the current understanding of the key processes affecting glass dissolution rate and the predictive modeling of long-term behavior of the vitrified waste.
Matsubara, Ryuta*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Iwata, Hajime; Sekine, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
Since the performance of vitrified High-level Radioactive Waste depends on thermal, hydraulic, mechanical, and chemical (THMC) conditions, NUMO, as the implementer of geological disposal, has been promoting R&D of operational model the long-term performance of vitrified High-level Radioactive Waste in consideration of THMC conditions. NUMO has identified R&D issues regarding the glass dissolution and planed the R&D program through FEP (Features, Events, and Processes) analysis and parametric study with numerical model to evaluate relative importance of relevant processes. At present, three R&D programs are ongoing as joint researches with JAEA and two universities: long term glass dissolution experiment to understand evolution of glass dissolution kinetics, glass dissolution experiment at various environmental conditions to assess the performance under several potential repository conditions with the time evolution, and molecular dynamics simulation to understand elemental migration at the interface between glass surface and groundwater. The current status of R&D programs will be introduced in this presentation.
Iwata, Hajime; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Sekine, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
In order to measure Fe-silicates precipitated under geological disposal conditions, a static leaching test has been conducted of simulated vitrified waste in 0.01 M FeCl solution with a surface area to volume ratio = 10 m
solution with a surface area to volume ratio = 10 m at 90
at 90 C under a N
C under a N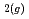 atmosphere. Obtained results indicate that Fe bearing minerals change from green rust to Fe-rich serpentine over time. Such mineral transitions are important as they may have an effect on the alteration behavior of glasses used for geological disposal of HLW.
atmosphere. Obtained results indicate that Fe bearing minerals change from green rust to Fe-rich serpentine over time. Such mineral transitions are important as they may have an effect on the alteration behavior of glasses used for geological disposal of HLW.
Iwata, Hajime; Kitamura, Akira
no journal, ,
The solubility of Nb was measured using oversaturation and undersaturation method. Compared with the values evaluated using JAEA-TDB, in the OS method a similar solubility was observed, and the measured values in the US method were around three orders magnitude below the evaluated values. It suggests that the solubility limiting solid differ between OS and US method.
Kimuro, Shingo; Iwata, Hajime; Eguchi, Ayano; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Hajime
no journal, ,
Prediction of the long-term behavior of vitrified waste is very important in the safety assessment of geological disposal. In this study, static leaching tests of international standard glass in FeCl solution (Fe condition) and deionized water (DIW condition) were conducted in a nitrogen atmosphere for up to about 400 days to investigate the effect of the coexistence of Fe ions on the glass dissolution behavior. The results showed that glass dissolution was suppressed under the Fe condition compared to the DIW condition. This may be due to the protective effect of the dense alteration layer generated in the Fe condition.
solution (Fe condition) and deionized water (DIW condition) were conducted in a nitrogen atmosphere for up to about 400 days to investigate the effect of the coexistence of Fe ions on the glass dissolution behavior. The results showed that glass dissolution was suppressed under the Fe condition compared to the DIW condition. This may be due to the protective effect of the dense alteration layer generated in the Fe condition.