Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,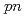 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.2(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
 C targets on Au backings
C targets on Au backingsSugai, Isao*; Takeda, Yasuhiro*; Kawakami, Hirokane*; Ota, Naoto*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Miyatake, Hiroari*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 655(1), p.24 - 33, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.67(Instruments & Instrumentation)Tochigi, Yoshikatsu; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Yui, Mikazu; Asano, Takahiro*; Honjo, Hideko*; Haginuma, Masashi*; Kawakami, Yasushi*; Suzuki, Kazunori*
JAEA-Research 2008-025, 55 Pages, 2008/03
Results of joint research on fiscal year 2006 between Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Institute of Research and Innovative (IRI) titled as "Study on investigation of microbial effects for geological disposal" are described in this report. The objective of this study is to develop a method for estimating microbial effects for barrier performance of geological disposal site. The modeling was performed to examine the effect on the change in groundwater chemistry (mainly by electron acceptors) by microbial metabolism as well as microbial activities. In order to use the data (chemical composition, biomass, etc.) in the MINT code, groundwater was collected from the drilled well prepared for chemical and microbial analyses of groundwater. The well was prepared in observation field near Horonobe Underground Research Center of JAEA in fiscal year 2006. Then, numerical modeling using collected data of groundwater with numerical modeling program code "MINT" considering microbial effects was carried out. The modeling was carried out to evaluate the microbial effect for stability of chemical and microbial composition of groundwater. As the result of the modeling, relatively low microbial effect for groundwater composition was observed in particular for the concentration of dissolved methane, methanogen, sulfur reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfur ion. The result shows that low redox potential is stable in the well in spite of shallow depth.
Tochigi, Yoshikatsu; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Yui, Mikazu; Honjo, Hideko*; Haginuma, Masashi*; Kawakami, Yasushi*; Suzuki, Kazunori*
JAEA-Research 2007-010, 51 Pages, 2007/03
Results of joint research on Fiscal 2005 between Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Institute of Research and Innovative (IRI) titled as "Study for investigation of microbial effects on geological disposal" are described in this report. The objective of this study is constructing advanced method for examining microbial effect for barrier performance of geological disposal site. In fiscal 2005, groundwater and rock core sample have been collected from drilled well on observation field near Horonobe Underground Research Center of JAEA and chemical analysis for collected ground water have been carried out and sensitivity analysis for existing observed data of groundwater with numerical analysis program code "MINT" considering microbial effect have been carried out.
Suzuki, Hideaki*; Ito, Akira; Yoshida, Yasushi*; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Kawakami, Susumu; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 2003-033, 235 Pages, 2004/02
The research for numerical experiments on the coupled Thermo -Hydro -Mechanical and Chemical (THMC) processes in the near-field of a high-level radioactive waste repository has been initiated, in order to increase reality in the near-field environmental condition adopted in the evaluation of engineered barrier design and performance assessment.As a part of this research, experimental studies on the coupled THMC processes by COUPLE equipment have been carried out. The COUPLE equipment simulates the coupled processes in the near-field after emplacement of the engineered barrier. The specimen of COUPLE equipment is composed of heater, buffer material and mortar block. In this experiment, temperature at heater and side surface of mortar block was kept at 100 and 70 C, respectively. And high-pH water reacted with mortar infiltrates into the buffer material.This report presents the results of measured data by embedded sensor (thermocouple, psychrometer, pressure transducer and pH meter etc.) during the experiment, and direct measurement of pH and water content of buffer material after the experiment.This report also presents the preliminary simulations, of coupled T-H processes, and of chemical process in mortar block and buffer material in the experiment.
C, respectively. And high-pH water reacted with mortar infiltrates into the buffer material.This report presents the results of measured data by embedded sensor (thermocouple, psychrometer, pressure transducer and pH meter etc.) during the experiment, and direct measurement of pH and water content of buffer material after the experiment.This report also presents the preliminary simulations, of coupled T-H processes, and of chemical process in mortar block and buffer material in the experiment.
Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro; ; *; *
JNC TN8430 2000-003, 33 Pages, 2000/04
On the geological disposal system of the radioactive wastes, the activities of the microorganisms that could degrade the asphalt might be significant for the assessment of the system performance. As the main effects of the biodegradation of the asphalt, the fluctuation of leaching behavior of the nuclides included in asphalt waste has been indicated. In this study, the asphalt biodegradation test was carried out. The microorganism of which asphalt degradation ability was comparatively higher under aerobic condition and anaerobic condition was used. The asphalt biodegradation rate was calculated and it was evaluated whether the asphalt biodegradation in this system could occur. The results show that the asphalt biodegradation rate under anaerobic and high alkali condition will be 300 times lower than under aerobic and neutral pH.
; *
JNC TN9450 2000-002, 335 Pages, 1999/10
This report summarizes the material test dala of SUS304 welded joints. Numbers of the data are as follows: [Tensile tests 71 (Post-irradiation: 39, others: 32) [Creep tests 77 (Post-irradiation: 20, others: 57) [Fatigue tests 50 (Post-irradiation: 0) [Creep-fatigue tests 14 (Post-irradiation: 0) This report consists of the printouts from "the structural material data processing system".
; *
JNC TN9450 2000-001, 1370 Pages, 1999/10
This report summarizes the material test data of SUS304. Numbers of the data are as follows. (1)Tensile tests 738 (Post-irradiation: 250, others: 488) (2)Creep tests 434 (Post-irradiation: 89, others: 345) (3)Fatigue tests 612 (Post-irradiation: 60, others: 552) (4)Creep-fatigue tests 200 (Post-irradiation: 40, others: 160) This report consists of the printouts from "the structural material data processing system".
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 40(9), p.684 - 696, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sazarashi, Masami*; *; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Kumagai, Mikio*; *; *
PNC TJ1564 97-002, 20 Pages, 1997/03
None
Sazarashi, Masami*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Kumagai, Mikio*; *; *
PNC TJ1564 96-002, 19 Pages, 1996/03
None
Fujiki, Kazuo;
EUR-15691, 0, p.397 - 403, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
; ;
NGK Genshiryoku Giho, 0(3), p.4 - 13, 1991/03
no abstracts in English
Udagawa, Akira; Sasuga, Tsuneo; Seguchi, Tadao; *; *; *; *; *; Sonoda, Katsumi*; *
JAERI-M 89-203, 20 Pages, 1989/12
no abstracts in English
Udagawa, Akira; Egusa, Shigenori; Sasuga, Tsuneo; Seguchi, Tadao; Ono, Toshio*; *; *; *; Hashimoto, Osamu*; Sonoda, Katsumi*; et al.
JAERI-M 88-047, 27 Pages, 1988/03
no abstracts in English
 U(n,f)
U(n,f) Mo Reaction,I (Method for Treating High Radioactive Organic Liquid Waste)
Mo Reaction,I (Method for Treating High Radioactive Organic Liquid Waste); Motoki, Ryozo; ; Motoishi, Shoji; ; ; ; ; *
JAERI-M 84-024, 27 Pages, 1984/02
no abstracts in English