Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Takahiro, Katsumi*
Thin Solid Films, 562, p.648 - 652, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Liquid organic-hydrides such as cyclohexane which can release-absorbing hydrogen in reversible have been proposed approvable carriers to store and transport hydrogen. However, organic-hydrides are known as highly flammable in air. To realize practical use of this hydrogen production process, the monitoring of leakage of organic-hydride gas is strongly required. In the present work, we have examined the plasmonic sensing ability of Au nanoparticle (NP) arrays for dilute cyclohexane. Au NP arrays were prepared on SiO by a sputter deposition technique. The change in an extinction spectrum of Au NP arrays before and after exposure of cyclohexane vapor enabled us to detect it. The Au NP array prepared with 4.4
by a sputter deposition technique. The change in an extinction spectrum of Au NP arrays before and after exposure of cyclohexane vapor enabled us to detect it. The Au NP array prepared with 4.4  10
10 Au atoms/cm
Au atoms/cm deposited at 300
deposited at 300 C was and demonstrated a high sensitivity for cyclohexane at RT. The experimentally detectable concentration of cyclohexane was as low as 0.5 vol%, much lower than its explosion limit (1.3 vol%).
C was and demonstrated a high sensitivity for cyclohexane at RT. The experimentally detectable concentration of cyclohexane was as low as 0.5 vol%, much lower than its explosion limit (1.3 vol%).
Kato, Sho; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 314, p.149 - 152, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)We implanted 100 keV W in unpolished GC substrates at nominal fluences up to
in unpolished GC substrates at nominal fluences up to 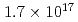 ions/cm
ions/cm . The implanted samples were electrochemically anodized in a NaOH aqueous solution to etch the surface layer. The analyses were performed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). XPS W 4f spectra indicated the formation of carbides as reported previously. The electrochemical etching clearly increased the W concentration on the surface. According to the RBS results, half of the implanted W atoms were retained in the substrate, while the rest should escape to the etching solution. The cross-sectional TEM image revealed a uniform distribution of WC particles with a diameter of less than 10 nm just near the surface region.
. The implanted samples were electrochemically anodized in a NaOH aqueous solution to etch the surface layer. The analyses were performed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). XPS W 4f spectra indicated the formation of carbides as reported previously. The electrochemical etching clearly increased the W concentration on the surface. According to the RBS results, half of the implanted W atoms were retained in the substrate, while the rest should escape to the etching solution. The cross-sectional TEM image revealed a uniform distribution of WC particles with a diameter of less than 10 nm just near the surface region.
Kato, Sho; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.81 - 84, 2013/03
Nanoparticles were formed by 100 keV tungsten-ion implantation in unpolished glassy carbon substrates at nominal fluences of 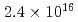 -
- 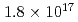 ions/cm
ions/cm . The implanted samples were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, hydrodynamic voltammetry using a rotating disk electrode, and field emission scanning electron microscopy. A significant sputtering effect changed the depth profile during the course of irradiation and limited the amount of tungsten retainable in the substrate in agreement with our calculated distributions. The nanoparticles were composed of tungsten carbide and dispersed uniformly with diameters of around 10 nm.
. The implanted samples were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, hydrodynamic voltammetry using a rotating disk electrode, and field emission scanning electron microscopy. A significant sputtering effect changed the depth profile during the course of irradiation and limited the amount of tungsten retainable in the substrate in agreement with our calculated distributions. The nanoparticles were composed of tungsten carbide and dispersed uniformly with diameters of around 10 nm.
 /Si by ion implantation
/Si by ion implantationTakahiro, Katsumi*; Ninakuchi, Yuki*; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Isshiki, Toshiyuki*; Nishio, Koji*; Sasase, Masato*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Nishiyama, Fumitaka*
Applied Surface Science, 258(19), p.7322 - 7326, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.02(Chemistry, Physical)A nanometer-sized metallic particle embedded in a transparent dielectric exhibits a nonlinear susceptibility, and going to be applied to nonlinear optical devices. In the present study, well-ordered arrangements of Ag nanoparticles have been found for Ag-implanted SiO . Thermally grown SiO
. Thermally grown SiO on Si were implanted with 350 keV-Ag ions to fluences of 0.37-1.2
on Si were implanted with 350 keV-Ag ions to fluences of 0.37-1.2  10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy reveal the presence of a two-dimensional array of Ag nanoparticles of 25-40 nm in diameter located at a depth of
. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy reveal the presence of a two-dimensional array of Ag nanoparticles of 25-40 nm in diameter located at a depth of  130 nm, together with the self-organization of tiny Ag nanoparticles aligned along the SiO
130 nm, together with the self-organization of tiny Ag nanoparticles aligned along the SiO /Si interface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction confirm the stability of these Ag nanoparticles embedded in the SiO
/Si interface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction confirm the stability of these Ag nanoparticles embedded in the SiO /Si is found to be stable against oxidation and sulfidation when stored in ambient conditions for more than one and a half year.
/Si is found to be stable against oxidation and sulfidation when stored in ambient conditions for more than one and a half year.
Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Saito, Masahiro*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Plasmonics, 6(3), p.535 - 539, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:28.2(Chemistry, Physical)Silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) have optical absorption bands due to localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) in visible range. The LSPR of Ag-NPs is being used for optical gas sensors. However, there have been differences in LSPR absorption band between most of the experimental data and calculations. We have demonstrated that plasma treatments for Ag NPs to clear the effect of contamination on surface of Ag NPs for LSPR absorption band. The results show that Ar plasma treatments to Ag NPs bring blue-shift and narrowing in their LSPR absorption band. Raman scattering analysis result that hydrocarbons adsorbed on silver surfaces were removed effectively by plasma exposure. It was found that the decrease in Raman line intensity for hydrocarbons was correlated well with the blue-shift. Our findings indicate that one of the most important factors for difference in LSPR absorption band between the experimental data and calculations is due to the impurity adsorption on silver surfaces.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Applied Surface Science, 257(5), p.1556 - 1561, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.83(Chemistry, Physical)Carbon-based films having nitrogen species on their surface were prepared on a glassy-carbon (GC) substrate as a non-platinum cathode catalyst for polymer electrolyte fuel cells by depositing cobalt and carbon in the presence of N gas using a pulse laser deposition method and then removing metal Co by HCl-washing treatment. The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity was electrochemically determined using a rotating disk electrode system where the film samples on the GC substrate were replaceable. The ORR activity increased with elevating temperature of the GC substrate during the deposition. A carbon-based film prepared at 600
gas using a pulse laser deposition method and then removing metal Co by HCl-washing treatment. The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity was electrochemically determined using a rotating disk electrode system where the film samples on the GC substrate were replaceable. The ORR activity increased with elevating temperature of the GC substrate during the deposition. A carbon-based film prepared at 600 C in the presence of 66.7 Pa N
C in the presence of 66.7 Pa N showed the highest ORR activity among the tested samples; its ORR potential was 0.66 V (vs. NHE). This film was composed of amorphous carbons doped with pyridine-type nitrogen atoms on its surface.
showed the highest ORR activity among the tested samples; its ORR potential was 0.66 V (vs. NHE). This film was composed of amorphous carbons doped with pyridine-type nitrogen atoms on its surface.
Sumita, Junya; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Mogi, Haruyoshi; ; Kitami, Takayuki; Akutsu, Yoichi; *; *; *
JAERI-Research 99-054, p.41 - 0, 1999/09
no abstracts in English
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Morimoto, Keiichi*; Yasuda, Kenji*; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 substrate by ion irradiation
substrate by ion irradiationKawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Yoshimura, Kimio; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Takahiro, Katsumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 substrate by ion irradiation
substrate by ion irradiationKawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Yoshimura, Kimio; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 films prepared by reactive sputtering
films prepared by reactive sputteringYamamoto, Shunya; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 substrates implanted with Ge ions
substrates implanted with Ge ionsShinagawa, Teruyoshi*; Umenyi, A. V.*; Kikuchi, Shusuke*; Aiba, Mizuki*; Inada, Kazuki*; Miura, Kenta*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
Light emission between ultraviolet and blue from SiO substrates implanted with Ge ions in comparatively shallow depth (
substrates implanted with Ge ions in comparatively shallow depth ( 100 nm) has been reported. In this paper, we report the photoluminescence (PL) properties of SiO
100 nm) has been reported. In this paper, we report the photoluminescence (PL) properties of SiO substrates implanted with Ge ions deeper than previous works (
substrates implanted with Ge ions deeper than previous works ( 200 nm depth) in order to enlarge the spot size of the photonic crystals waveguides. Ge ions were implanted into an SiO
200 nm depth) in order to enlarge the spot size of the photonic crystals waveguides. Ge ions were implanted into an SiO substrate with 350 keV, and the implantation amount was 1
substrate with 350 keV, and the implantation amount was 1 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . PL peaks around a wavelength of 400 nm were observed. Stronger PL peaks were measured after annealing (900
. PL peaks around a wavelength of 400 nm were observed. Stronger PL peaks were measured after annealing (900  C), which confirmed an effect of improving the emission intensity by the annealing process. Though Ge ions were implanted more deeply than the earlier reported depth, similar results were confirmed. The expectation for a new light-emitting waveguide device that combines Ge-ion-implanted SiO
C), which confirmed an effect of improving the emission intensity by the annealing process. Though Ge ions were implanted more deeply than the earlier reported depth, similar results were confirmed. The expectation for a new light-emitting waveguide device that combines Ge-ion-implanted SiO substrates with photonic crystal characteristics has risen.
substrates with photonic crystal characteristics has risen.
Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Yoshimura, Kimio; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 substrate
substrateKawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Yoshimura, Kimio; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Sanari, Takumi*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Nagata, Shinji*
no journal, ,
Silver (Ag) and gold (Au) nanoparticles have strong optical extinction band due to localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) in the visible range. These nanoparticles on transparent substrates are being applied to chemical and biological sensors, in which changes in the LSPR features, including resonance wavelength, width and intensity, are observed. In such applications, an intense and sharp absorption band is required for higher detection sensitivity. Our previous work showed that a plasma treatment could be an effective tool to control the LSPR features for Ag nanoparticles prepared by sputter deposition. In the treatment, argon (Ar) plasma cleans up impurities adsorbed on the Ag nanoparticles, resulting in the blue shift and sharpening of the LSPR. In the present work, sputter deposition, and plasma have been employed to fabricate Au nanoparticles with desired optical properties for plasmon-based sensors.
Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Sanari, Takumi*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Nagata, Shinji*
no journal, ,
Optical extinction spectrum of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) exhibits a strong peak due to the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR). The extinction peak by LSPR change in dependence on a medium surrounding Au NPs. Recently, new sensing materials have been developed for organic gas sensors using LSPR. The extinction peak by LSPR, however, often differs from the ideal values because of impurities adhered on Au NPs surface in air. In this study, plasma and ion sputtering treatments have been employed to eliminate impurities on the Au NPs surfaces. As the result, it was found that carbonaceous impurities decrease significantly from X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and the wavelength of the LSPR extinction peak close to ideal value. In addition, the observation by scanning electron microscopy was indicated no significant change in the morphology of Au NPs after the treatments. We concluded plasma and ion sputtering treatments were effective methods to obtain Au NPs with clean surfaces.