Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Hoshino, Kazutoyo*; Tsukada, Manabu*; Sawauchi, Fumiya*; Otake, Yoshinori; Ichise, Kenichi; Tagami, Susumu
JAEA-Technology 2022-034, 47 Pages, 2023/03
The Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF) was established in 1982 as an experimental facility for long-term storage of solidified high-level radioactive waste generated in the reprocessing of spent light water reactor fuel and the subsequent safety assessment of geological disposal. It is a historic facility that started operation in 1982. This facility consists of 5 concrete cells, 1 lead cell, 6 glove boxes, and 7 hoods, and is a large-scale facility that can use nuclear fuel materials including uranium and plutonium and radioactive isotopes including TRU. In this facility, research and development requested by the research department is carried out in the Hot Material Examination Section. In addition, patrol inspections, self-inspections, etc. are also carried out as maintenance management based on safety regulations. This report summarizes the overview of WASTEF facilities, the results of operation, maintenance and management work in FY2021, and the future outlook.
Suzuki, Kazuhiro; Motooka, Takafumi; Tsukada, Takashi; Terakawa, Yuto; Ichise, Kenichi; Numata, Masami; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2014-004, 29 Pages, 2014/03
By the effect of the Great East Japan Earthquake, seawater was injected into spent fuel pools in unit 2, 3 and 4 at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Plant in order to cool spent fuels. It is known that chloride ion contained in seawater could cause pitting corrosion for metallic materials. It was concerned that radioactive products inside of fuel cladding tubes might be escaped through the pits. Therefore we have investigated the pit initiation condition of fuel cladding tubes by measuring pitting potential in order to evaluate stability of the enclosure function of fuel cladding tubes in spent fuel pools containing sea salt. In this report, we describe the development of specimen preparation techniques for pitting measurement of spent fuel cladding tubes having high radioactivity. By accomplishing of the development of the specimen preparation techniques, we could evaluate pit initiation condition of spent fuel cladding tubes in water containing sea salt.
 and AmO
and AmO
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Ito, Akinori*; Ichise, Kenichi; Arai, Yasuo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 414(2), p.109 - 113, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:77.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal diffusivities of AmO and AmO
and AmO were measured using a laser flash method. The heat capacities of AmO
were measured using a laser flash method. The heat capacities of AmO and AmO
and AmO were measured using a drop calorimetry. The thermal conductivity was determined from the measured thermal diffusivity, heat capacity and bulk density. In these results, the heat capacity of AmO
were measured using a drop calorimetry. The thermal conductivity was determined from the measured thermal diffusivity, heat capacity and bulk density. In these results, the heat capacity of AmO was larger than that of AmO
was larger than that of AmO and close to those of UO
and close to those of UO and NpO
and NpO . The thermal conductivities of AmO
. The thermal conductivities of AmO and AmO
and AmO were found to decrease with increasing temperature in the temperature range investigated. The thermal conductivity of AmO
were found to decrease with increasing temperature in the temperature range investigated. The thermal conductivity of AmO from 473 to 773 K was slightly smaller than those of UO
from 473 to 773 K was slightly smaller than those of UO and PuO
and PuO and close to that of NpO
and close to that of NpO . On the other hand, the thermal conductivity of AmO
. On the other hand, the thermal conductivity of AmO with A-type rare earth oxide structure was smaller than that of AmO
with A-type rare earth oxide structure was smaller than that of AmO with fluorite structure and larger than that of non-stoichiometric AmO
with fluorite structure and larger than that of non-stoichiometric AmO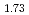 .
.
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Takano, Masahide; Ichise, Kenichi; Akabori, Mitsuo; Arai, Yasuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(3), p.359 - 365, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, we prepared the sintered samples of two kinds of (Zr,Pu,Am)N and (Zr,Np,Pu,Am,Cm)N solid solutions. The thermal diffusivity and heat capacity of Zr-based transuranium nitride solid solutions were measured by a laser flash method and a drop calorimetry, respectively. The thermal conductivities of (Zr,Pu,Am)N and (Zr,Np,Pu,Am,Cm)N were determined from the measured thermal diffusivity, heat capacity and bulk density. It was found that the thermal conductivities of (Zr,Pu,Am)N and (Zr,Np,Pu,Am,Cm)N were higher than that of (Pu,Am)N. It was also found that the thermal conductivities of (Zr,Pu,Am)N and (Zr,Np,Pu,Am,Cm)N obviously increased with temperature in comparison with (Pu,Am)N, although they were smaller than that of ZrN over the temperature range investigated.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Masaya; Nakata, Masahito; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Abe, Kazuyuki; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-072, 144 Pages, 2010/03
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from FY2006 in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupled irradiations or single irradiation by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 thermal reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we summarized about the overall plan, the work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Sakuraba, Naotoshi; Numata, Masami; Komiya, Tomokazu; Ichise, Kenichi; Nishi, Masahiro; Tomita, Takeshi; Usami, Koji; Endo, Shinya; Miyata, Seiichi; Kurosawa, Tatsuya; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-071, 34 Pages, 2010/03
As a part of maintenance technology of a large-sized glove box for handling of TRU nuclides, we developed replacement technology for front acrylic panels using the bag-in/bag-out method and applied this technology to replace the deteriorated front acrylic panels at Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF) in Nuclear Science Research Institute of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). As a consequence, we could safely replace the front acrylic panels under the condition of continuous negative pressure only with partial decontamination of the glove box. We also demonstrated that the present technology is highly effective in points of safety, workability and cost as compared to the usual replacement technology for front acrylic panels of a glove box, where workers in an air-line suit replace directly the front acrylic panels in a green house.
Endo, Shinya; Numata, Masami; Ichise, Kenichi; Nishi, Masahiro; Komiya, Tomokazu; Sakuraba, Naotoshi; Usami, Koji; Tomita, Takeshi
Proceedings of 46th Annual Meeting of "Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling" Working Group (HOTLAB 2009) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2009/09
For safety operation and maintenance of the large size glove box, the degraded acrylic panels of the box must be replaced by the new panels. As the conventional replacement technique, the decontamination of the glove box and installation of isolation tent are necessary to prevent the leak of contamination, because airtight condition of the box is broken down during replacement process. Therefore, the prerequisite works are required considerable manpower. The new replacement technique using bag-in / bag-out method was developed by JAEA. In this technique, for keeping the airtight condition of the box, the inside of degraded panel is covered with an airtight panel and the outside is covered over the large bag which is used to replace the acrylic panels. As the benefits of this technique, the prerequisite works are not required and the manpower is less than a third of the conventional technique.
Shirasu, Noriko; Kuramoto, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Ichise, Kenichi; Ono, Katsuto; Nihei, Yasuo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 352(1-3), p.365 - 371, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To evaluate irradiation behavior of the ROX fuel, irradiation experiment was carried out using 20% enriched U instead of Pu. Three fuels were prepared; a single phase fuel of YSZ containing UO (U-YSZ), two particle-dispersed fuels of U-YSZ particle in spinel or corundum matrix. The U-YSZ particles were prepared by crashing presintered U-YSZ pellets and by sieving them. These fuels were irradiated in Japan Research Reactor No.3 for 13 cycles, about 300 days. Though many cracks were observed in the pellets by X-ray photographs, significant appearance changes were not observed for all fuel pins. Distribution of typical FPs was analyzed by the
(U-YSZ), two particle-dispersed fuels of U-YSZ particle in spinel or corundum matrix. The U-YSZ particles were prepared by crashing presintered U-YSZ pellets and by sieving them. These fuels were irradiated in Japan Research Reactor No.3 for 13 cycles, about 300 days. Though many cracks were observed in the pellets by X-ray photographs, significant appearance changes were not observed for all fuel pins. Distribution of typical FPs was analyzed by the  scanning over the fuel pin. Non-volatile nuclide remained in the fuel pellet. On the other hand, a part of Cs moved to the gaps between the pellets and to the insulators.
scanning over the fuel pin. Non-volatile nuclide remained in the fuel pellet. On the other hand, a part of Cs moved to the gaps between the pellets and to the insulators.  Cs and
Cs and  Cs showed different distributions at the plenum. Fuel pellets were taken out from fuel pins without bonding. Spinel decomposition and subsequent restructuring were not observed probably due to low irradiation temperature.
Cs showed different distributions at the plenum. Fuel pellets were taken out from fuel pins without bonding. Spinel decomposition and subsequent restructuring were not observed probably due to low irradiation temperature.
; Nakata, Masahito; ; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki;
ASRR-V: Proc., 5th Asian Symp. on Research Reactors, 2, p.871 - 875, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Shirasu, Noriko; Kuramoto, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Honda, Junichi; Hatakeyama, Yuichi; Ichise, Kenichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwai, Takashi; Matsui, Hiroki; Ichise, Kenichi; Ono, Katsuto; Arai, Yasuo
no journal, ,
The results of post-irradiation destructive examinations of (Zr,Pu)N and (TiN,PuN) simulated of inert matrix nitiride fuel which is a candidate material for transmutation of minor actinides, are reported. From the observation of cross section of the fuel pins, a gap was existent between fuel pellet and cladding. As there is no large cruck in the fuel pellet, the structure of the pellet was very stable. Because reation zones and signs of the corrosion were not shown, the fuel clad chemical interaction did not occurred. Grain size of the fuel pellet did not change under irradiation as the temperature of the pellet was low.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Ichise, Kenichi; Usami, Koji; Endo, Shinya; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Yonekawa, Minoru; Ito, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Masaya; Soga, Tomonori; et al.
no journal, ,
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from 2006 fiscal year in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupling irradiations or single irradiations by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 fission reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are the very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we will present about the overall plan, work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Usami, Koji; Ichise, Kenichi; Numata, Masami; Endo, Shinya; Onozawa, Atsushi; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Kikuchi, Taiji; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Nakata, Masahito; et al.
no journal, ,
In the R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant, the specimens to be obtained by coupling irradiation between JOYO and JRR-3 is necessary to establish the evaluation method by using the irradiation damage indicator of them. Therefore, the techniques for assembling of JRR-3 re-irradiation capsule in the Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF) were developed to perform the coupling irradiation. The techniques contributed to the first coupling irradiation in the world.

Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Kashimura, Motoaki; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Ichise, Kenichi; Ito, Akinori; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
Heat capacity of MOX fuel is one of the important physical properties for fuel design and for evaluation of thermal conductivity by laser flash method. In this study, the enthalpies of PuO were measured as one of the evaluation of basic physical properties on MOX fuel. Additionally the temperature and O/Pu ratio dependencies on heat capacities were evaluated by analysing the enthalpy data.
were measured as one of the evaluation of basic physical properties on MOX fuel. Additionally the temperature and O/Pu ratio dependencies on heat capacities were evaluated by analysing the enthalpy data.
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Takano, Masahide; Ito, Akinori; Ichise, Kenichi; Kurosawa, Tatsuya; Akabori, Mitsuo; Arai, Yasuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ichise, Kenichi; Sakuraba, Naotoshi; Suzuki, Kazuhiro; Miyata, Seiichi; Komiya, Tomokazu; Nishi, Masahiro; Kitagawa, Isamu; Numata, Masami
no journal, ,
As a part of measures to reduce radioactive wastes, which are generated during operation and maintenance of Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF), we developed volume reduction equipment for 
 and
and  wastes. In this presentation, we report manufacture of an experimental model, its operativeness & verification of reduction effect in a mock-up test, improvements, and application to actual radioactive wastes.
wastes. In this presentation, we report manufacture of an experimental model, its operativeness & verification of reduction effect in a mock-up test, improvements, and application to actual radioactive wastes.
 and AmO
and AmO
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Ito, Akinori*; Ichise, Kenichi; Arai, Yasuo
no journal, ,
The thermal diffusivities of AmO and AmO
and AmO were measured by using a laser flash method. The heat capacities of AmO
were measured by using a laser flash method. The heat capacities of AmO and AmO
and AmO were measured by using a drop calorimetry. In these results, the heat capacity of AmO
were measured by using a drop calorimetry. In these results, the heat capacity of AmO was larger than that of AmO
was larger than that of AmO and close to that of UO
and close to that of UO . The thermal conductivities of AmO
. The thermal conductivities of AmO and AmO
and AmO were found to decrease with increasing temperature in the temperature range investigated. The thermal conductivity of AmO
were found to decrease with increasing temperature in the temperature range investigated. The thermal conductivity of AmO from 473 to 773 K was slightly smaller than those of UO
from 473 to 773 K was slightly smaller than those of UO and PuO
and PuO and close to that of NpO
and close to that of NpO . On the other hand, the thermal conductivity of AmO
. On the other hand, the thermal conductivity of AmO with A-type rare earth oxide structure was smaller than that of AmO
with A-type rare earth oxide structure was smaller than that of AmO with fluorite structure and larger than that of non-stoichiometric AmO
with fluorite structure and larger than that of non-stoichiometric AmO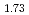 .
.
Suzuki, Kazuhiro; Motooka, Takafumi; Tsukada, Takashi; Terakawa, Yuto; Ichise, Kenichi; Numata, Masami; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Kazuhiro; Toyokawa, Takuya; Motooka, Takafumi; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Terakawa, Yuto; Suzuki, Miho; Ichise, Kenichi; Numata, Masami; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English