Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 blanket
blanketYokoyama, Kenji; Shono, Akira*
International Handbook of Evaluated Reactor Physics Benchmark Experiments (CD-ROM), 223 Pages, 2010/03
Under the framework of the International Reactor Physic Experimental Evaluation Project (IRPhEP) organized by OECD/NEA, eight types of nuclear characteristics parameters, criticality, control rod worth, sodium void reactivity, fuel replacement reactivity, isothermal temperature coefficient and burnup reactivity coefficients, measured in the experimental fast reactor JOYO MK-I core were evaluated. In the present evaluation, not only nominal values but also uncertainties of experiments and analytical models were fully re-investigated according to the evaluation policy of the IRPhEP. In addition, each evaluation provides a reactor physics benchmark problem, which are expected to utilize for validating analytical models and nuclear data.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Shono, Akira*; Ishikawa, Makoto
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 157(3), p.249 - 263, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental data acquired in the experimental fast reactor JOYO MK-I performance tests in the late 1970s have been revaluated and analyzed with a nuclear analysis system for fast reactors used in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). For the purpose of improving the prediction accuracy of nuclear characteristics, nominal values and uncertainties of the experimental data were revaluated by using knowledge obtained after the MK-I performance test and calculation results based on the latest reactor physics analysis methods. All the nominal values were corrected by using a formulation of control rod interaction effects proposed in the present paper, and all the possible uncertainty factors were evaluated and quantified. The analysis results agreed well with measured values within the experimental and nuclear-induced uncertainties for all the nuclear characteristics of the criticality, control rod worth sodium void reactivity, fuel replacement reactivity and isothermal temperature coefficient.
Hazama, Taira; Shono, Akira*; Yokoyama, Kenji
Proceedings of American Nuclear Society Topical Meeting on Physics of Reactors (PHYSOR 2006) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2006/09
Benchmark data have been created on reactor physics experiments performed in two reactors: the experimental fast reactor JOYO MK-I and Deuterium Critical Assembly (DCA). The data were prepared for the International Reactor Physics Experiment Evaluation Project (IRPhEP). In JOYO data, five kinds of reactivity data were evaluated: (1)criticality, (2)control rod worth, (3)sodium void reactivity, (4)fuel replacement reactivity, and (5)isothermal temperature coefficient. In particular, the control rod worth, a key quantity in all the reactivity evaluations, were evaluated in detail, considering interaction effects. In DCA data, three kinds of parameters were evaluated: (1)critical moderator level, (2)epithermal capture ratio of  U, (3)dysprosium thermal reaction rate distribution in a fuel assembly. Data are systematically arranged in eight kinds of core configurations, varying the assembly pitch and void fraction. Each of evaluated data has a unique feature and will be useful to validate reactor physics calculation schemes.
U, (3)dysprosium thermal reaction rate distribution in a fuel assembly. Data are systematically arranged in eight kinds of core configurations, varying the assembly pitch and void fraction. Each of evaluated data has a unique feature and will be useful to validate reactor physics calculation schemes.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Shono, Akira; Ishikawa, Makoto
JNC TN9400 2005-024, 372 Pages, 2005/05
"JOYO" MK-I has a typical fast breeder reactor core which was fuelled by plutonium-uranium mixed oxide (MOX) and the fuel region was surrounded by blanket consisting of depleted uranium oxide. Since it has a simple core geometry without any other special irradiation subassembly, it is suitable for the reactor physics analysis. The experimental data acquired in the "JOYO" MK-I performance tests are analyzed with the latest analysis methods in order to resister the data in the IRPhE (International Reactor Physics Benchmark Experiments) project. For this analysis, nominal values and uncertainties of the experimental data were reevaluated by using knowledge obtained after the MK-I performance test and calculation results based on the latest analysis methods. As the nuclear characteristics for the analysis, we selected the criticality, the control rod worth, the isothermal temperature coefficient, the fuel replacement reactivity worth and the sodium void reactivity worth, which were measured in unburnt cores prior to the first power ascension to 50MWth. In this evaluation, not only the measurement uncertainty but also geometry uncertainty and composition uncertainty are considered. All the uncertainties are evaluated with a classification into the random and the systematic components, according as the guideline of IRPhE. The analysis of "JOYO" MK-I was previously carried out in the fiscal year of 1999. In this report, the analysis is totally carried out again with the revised group constants and the latest analysis codes such as the ultra-fine group lattice calculation code. In order for use in the benchmark problem preparation, the analytical results are shown with various correction factors that are estimated from the difference between analytical models. The uncertainties of analysis results are also evaluated by considering the correction factors. Furthermore, a consistency evaluation with the other existing critical experiment data is carried out by performing ...
Hazama, Taira; Iwai, Takehiko*; Shono, Akira
JNC TN9400 2005-011, 114 Pages, 2004/10
A program is in progress to dispose excess weapon plutonium in BN-600 fast reactor. To support the program, a series of critical experiments that simulates plutonium loading in BN-600 (BFS critical experiment and analysis) was carried out, and has been analyzed in an international collaboration with Russian Institute of Physics and Power Engineering. This report describes analysis results of the critical experiments on the last core configurations BFS-62-5 and BFS-66-1. In addition, already-reported analysis results on BFS-62-1 to -4 cores are updated in a unified method. BFS-62-5 and 66-1 have different features such as use of MOX fuel in the central area and having the sodium plenum region above the fuel region, when compared with BFS-62-1 to -4 mainly consisting of uranium fuel. Despite the differences, major nuclear parameters were successfully analyzed with similarly good accuracy. Even the sodium void reactivity, an important safety parameter and sensitive to the core configuration change, was analyzed within nuclear data uncertainty. These results will contribute to the improvement in reliability of core design in the dismantled plutonium disposition program of Russia and the FBR feasibility study of Japan.
Shono, Akira; Hazama, Taira; Ishikawa, Makoto; Manturov, G.*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Fuel Cycles and Advanced Nuclear Systems; Global Developments (PHYSOR 2004), 95315 Pages, 2004/00
The present paper provides evaluation results of predicted uncertainty on nuclear parameters on the BN-600 hybrid core, a feasible option for Russian surplus weapons plutonium disposition. Covariance of nuclear group constant, analysis error, and experimental error are considered to predict uncertainties of the hybrid core nuclear parameters by applying the nuclear group constant adjustment method. Analysis results of BFS mockup and other fast reactor core experiments were reflected in the evaluation.
Shono, Akira; Sato, Wakaei*; Hazama, Taira; Iwai, Takehiko*; Ishikawa, Makoto
JNC TN9400 2003-074, 401 Pages, 2003/08
Nuclear design accuracy on the BN-600 hybrid core has been evaluated using the JNC's nuclear analysis system for FBR cores, by utilizing the critical experiment analysis results on BFS-62 configuration that had been obtained under JNC's efforts for Russian surplus weapons plutonium disposition. In the BN-600 hybrid core design, a part of the current UO2 fuel region is replaced by MOX fue1, and the Peripheral blanket region by stainless steel reflectors, respectively. These changes were simulated in a series of critical experiment configurations (BFS-62-1 to 4). Based on the analysis results on both BFS-62 configurations and other fast reactor cores, nuclear design accuracy on the BN-600 hybrid core has been evaluated by applying both the group constant adjustment method and the bias method. Evaluated nuclear parameters include, the criticality, fission rate distribution, sodium void reactivity, control rod worth, burn-up reactivity loss, etc. It is concluded, by applying the group constant adjustment method, that the evaluated accuracy (uncertainty) of most of the nuclear parameters can be decreased to less than half of those based on the basic nuclear constant without reflecting any experimental data. The improvement was mainly achieved by reducing the covariance of the iron elastjc cross section. This significant effect results from the feature of the BN-600 hybrid core, which has relatively larger power density, adopts U235 as the main fissile nucljde, and has the stainless steel reflector surrounding the fuel region. In addition, good consistency of analysis results between the BFS and other fast reactor cores is confirmed. Information obtained by BFS-62 experiment show significant contribution to the accuracy improvement. It is also found that the bias method shows less significant effects on the accuracy improvement than the group constant adjustment method. Furthermore, the bias method may degrade the accuracy for certain nuclear parameters that have large e
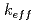 Analysis Results
Analysis ResultsShono, Akira; Mantourov, G.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 144(3), p.211 - 218, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
Hazama, Taira; Sato, Wakaei*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Shono, Akira
JNC TN9400 2003-035, 44 Pages, 2003/05
Collaboration between Russian Institute of Physics and Power Engineering (IPPE) and Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) named (Investigation of neutronic-physical characteristics and their change when introducing large quantity of neptunium (Np) at different BFS critical assemblies) is under progress. This is the first report of the collaboration to describe experimental information and JNC analysis results on BFS-67 critical experiment. In BFS-67 experiment, nuclear characteristics (criticality, control rod worth, sodium void reactivity, reaction ratio, etc) were measured in 4 different cores with various amounts of Np and location. JNC analysis was perfomed based on a JNC standard analysis scheme as in the analyses of BFS-62 critical experiments. (1)Sensitivity coefficients of Np capture cross section for the sodium void reactivity and control rod worth are large enough and comparable to those of U-238 and Pu-239. This indicates the experimental data can be used to improve design accuracy of Np loaded core. (2)C/E values for the criticality show high accuracy of 0.995 independent of core patterns, indicating accuracy of the calculation is high enough. (3)Calculated values for the sodium void reactivity agree with experimental values within 1cent and there is no influence of Np loading on calculation accuracy. (4)Calculated values for the control rod worth agree with experimental values within experimental errors for enriched B4C control rod. Those for naturaI B4C slightly overestimate. An influence of Np loading is not observed. (5)Calculated values for the reaction ratio agree with experimental values within 5% for fission reactions, whereas those for capture reactions show nearly 10% of differences. Positions of foils used in the measurement should be reflected.
; Chiba, Go; Numata, Kazuyuki*
JNC TN9400 2002-062, 39 Pages, 2002/11
The unfied cross-section set ADJ2000, which was produced by adjusting 70-energy-grouped JFS-3-J3.2 (JENDL-3.2-based group constant set) using its analysis accuracy on various critical experiments, had been used in JFY2001 for core design studies in the feasibility study on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. The ADJ2000 was published in June 2001, having 70 energy group structure as well. Calculated values from ADJ2000 would contain errors ("nuclear constant effects") which come from differences of weighting functions (neutron spectra) between that used for processing JFS-3-J3.2 and that of studied cores. In order to obtain more reliable results, the nuclear constant effects have to be corrected. Accordingly. nuclear constant effects on various fast reactor core concepts relating to application of unified cross-section set ADJ2000 have been evaluated for several nuclear parameters including criticality burnup reactivity loss, coolant void reactivity (depressurization reactivity in the case of gas-cooled reactor cores), Doppler reactivity and breeding ratio. Studied cores are listed below. (1)Sodium-cooled MOX-fuelled cores (large-size and middle-size) (2)Sodium-cooled metal-fuelled core (middle-size) (3)Lead-bismuth-cooled nitride-fuelled core (middle-size) (4)Carbon-dioxide-cooled MOX-fuelled core (large-size) (5)Helium-cooled coated-particle-fuelled core (large-size) (6)Helium-cooled enclosed-pin-fuelled core (large-size, 2 designs)
Shono, Akira; Okawachi, Yasushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.2), p.493 - 496, 2002/08
None
Hazama, Taira; ; Iwai, Takehiko*; Sato, Wakaei*
JNC TN9400 2002-036, 113 Pages, 2002/06
In order to support the Russian excess weapons plutonium disposition program, the intemational collaboration has started between Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) and Russian Institute of Physics and Power Engineering(IPPE). In the frame of the collaboration, analyses have been carried out for a series of critical experiments that simulate BN-600 (Russian commercial fast reactor). This report summarizes analysis results of the critical expeliments on BFS-62-3A and BFS-62-4 cores. BFS-62-3A core models BN-600 hybrid core in which the present BN-600 core is modified so as to partially load MOX fuel assemblies and replace the blanket region with stainless steel. BFS-62-4 core has the same layout as BFS-62-3A core except that the blanket region is not replaced. The analyses were performed with JNC standard method developed in the analysis of JUPITER experiment. The results show a good agreement with experimental values for the criticality and the reaction rate ratio. For the control rod worth and the reaction rate distribution, the results for BFS-62-4 core are also reasonable. However, for BFS-62-3A, analysis results overestimate the reaction rate in the stainless steel region by 20% and underestimate reactivity worth for one of the control rods by 10%. For the sodium void reactivity, underestimation of more than 20% were observed, but the disagreement were successfully solved by adopting a newly developed nuclear constant set with a fine group structure. In addition, analysis accuracies were compared among a series of analyses and it was confirmed that the introduction of MOX fuel assemblies does not affect the accuracy. The final goal of the work is to reflect the analysis results for designing BN-600 hybrid core. Then similarity was investigated between BFS-62-3A core and BN-600 hybrid core. A good similarity was found in the neutron spectrum, the fission reaction ratio, the fission reaction distribution, and the control rod worth. However, ...
Sugino, Kazuteru; ; Iwai, Takehiko*; Numata, Kazuyuki*
JNC TN9400 2002-008, 241 Pages, 2002/04
In order to support the Russian excess weapons plutonium disposition, the international collaboration has been started between Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) and Russian Institute of Physics and Power Engneering (IPPE). In the frame of the collaboration, JNC has carried out analyses on the BFS-62 assemblies that are constructed in the fast reactor critical experimental facility BFS-2 of IPPE. This report summarizes an experimental analysis on the BFS-62-1 and BFS-62-2 cores. The BFS-62-1 core models the present BN-600, and contains the enriched UO fuel surrounded by the UO
fuel surrounded by the UO blanket. The BFS-62-2 core has the same layout as the BFS-62-1 but the blanket region was replaced with stainless steel shield. For core parameter analyses, the 3-D Hexagonal-Z or XYZ geometry model was applied by not only diffusion calculation but also transport calculation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality, the reaction rate ratio and reaction rate distribution in BFS-62-1. In the reaction rate distribution of BFS-62-2 calculation without cross-section adjustment produced big radial dependency of calculation over experiment value (C/E value) in the core region and overestimation in the shield region. Cross-section adjustment technique procedure improved those estimation, however alternation of cross-section of Iron, which was dominant in above improvement, compared to the cross-section error, and further investigation was required. Concerning the control rod worth of BFS-62-1, radial dependency of the C/E value was observed whether cross-section adjustment technique was applied or not, therefore comparison with results of other BFS-62 ...
blanket. The BFS-62-2 core has the same layout as the BFS-62-1 but the blanket region was replaced with stainless steel shield. For core parameter analyses, the 3-D Hexagonal-Z or XYZ geometry model was applied by not only diffusion calculation but also transport calculation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality, the reaction rate ratio and reaction rate distribution in BFS-62-1. In the reaction rate distribution of BFS-62-2 calculation without cross-section adjustment produced big radial dependency of calculation over experiment value (C/E value) in the core region and overestimation in the shield region. Cross-section adjustment technique procedure improved those estimation, however alternation of cross-section of Iron, which was dominant in above improvement, compared to the cross-section error, and further investigation was required. Concerning the control rod worth of BFS-62-1, radial dependency of the C/E value was observed whether cross-section adjustment technique was applied or not, therefore comparison with results of other BFS-62 ...
Shono, Akira; Sugino, Kazuteru; Hazama, Taira; Ishikawa, Makoto
7C-04, 0 Pages, 2002/00
None
Shono, Akira; Iwai, Takehiko*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.2), p.1085 - 1088, 2002/00
None
Okawachi, Yasushi; ; Koshizuka, Seiichi*
JNC TY9400 2001-017, 117 Pages, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Okawachi, Yasushi; Shono, Akira
JAERI-Conf 2001-006, p.121 - 124, 2001/03
None
Okawachi, Yasushi;
JNC TN9400 2001-001, 100 Pages, 2000/08
Gamma-ray decay heat released from fission products has been measured for fast neutron fissions of U-235 and Np-237 using the radiation spectrometry method. The samples were irradiated at fast neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo. Gamma-ray energy spectra were measured using a NaI(TI) scintillation detector. And, the number of fission was evaluated from measured gamma spectra by Ge detector. For the measured gamma-ray, the background count was subtracted from the pulse height distribution of 1024 channels measured. The results were grouped by 340 channels to match the response matrix of the detector. This distribution was converted to energy spectra using the FERDO code and the response matrix of the detector. Normalized decay heat by the number of fission was obtained by integration of the energy spectra for each time step. The finite irradiation decay heat that is directly obtained by experiments can not be compared with experimental results and calculational results obtained under various irradiation conditions. So, the finite irradiation decay heat was converted to the fission burst decay heat. These results were compared with summation calculations using JNDC-V2 dacy data file. The present results on U-235 were compared with other experimental data using the same method. The present results agreed with other experimental data using the same method within 10%, suggesting the repeatability of experimental method. The present results on Np-237 were compared with the results of summation calculations using JNDC-V2 decay data file. As the result, the present results agreed with summation calculations within 8%. Probelms to be solved for the future are estimation of the experimental error, re-evaluation of the number of fission using updated nuclear data. To improve accuracy of decay heat data in shorter cooling time range, less irradiation experiment will be useful. Furthermore, to improve accuracy of decay heat data in longer cooloing ...
Sugino, Kazuteru; Iwai, Takehiko*;
JNC TN9400 2000-098, 182 Pages, 2000/07
In order to support the Russian excess weapons plutonium disposition, the international collaboration has been started between Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) and Russian Institute of Physics and Power Engineering (IPPE). In the frame of the collaboration, JNC has carried out analyses on the BFS-62 assemblies that are constructed in the fast reactor critical experimental facility BFS-2 of IPPE. This report summarizes an experimental analysis on the BFS-62-1 assembly, which is the first core of the BFS-62 series. The core contains the enriched U0 fuel surrounded by the U0
fuel surrounded by the U0 blanket. The standard analytical method for fast reactors has been applied, which was used for the JUPITER and other experimental analyses. Due to the lack of the analytical data the 2D RZ core calculation was mainly used. The 3D XYZ core calculation was applied only for the preliminary evaluation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality and the reaction rate ratio. However, it was found that accurate evaluation of the reaction rate distribution was impossible without exact consideration of the arrangement of the two types of sodium (with and without hydrogen impurity), which can be accommodated by the 3D core analysis, thus it was essentia1. In addition, it was clarifie that there was a room for an improvement of the result on the reaction rate distribution in the blanket and shielding regions. The application of the 3D core calculation improved the result on the control rod worth because 3D core model can more exactly consider the shape of the control rod. Furthermore it was judged that the result of the analysis on the sodium void reactivity .....
blanket. The standard analytical method for fast reactors has been applied, which was used for the JUPITER and other experimental analyses. Due to the lack of the analytical data the 2D RZ core calculation was mainly used. The 3D XYZ core calculation was applied only for the preliminary evaluation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality and the reaction rate ratio. However, it was found that accurate evaluation of the reaction rate distribution was impossible without exact consideration of the arrangement of the two types of sodium (with and without hydrogen impurity), which can be accommodated by the 3D core analysis, thus it was essentia1. In addition, it was clarifie that there was a room for an improvement of the result on the reaction rate distribution in the blanket and shielding regions. The application of the 3D core calculation improved the result on the control rod worth because 3D core model can more exactly consider the shape of the control rod. Furthermore it was judged that the result of the analysis on the sodium void reactivity .....
; Sato, Wakaei*; Iwai, Takehiko*
JNC TN9400 2000-096, 113 Pages, 2000/06
This report describes the updated analyses results on the BFS-58-1-I1 core. The experiment was conducted at BFS-2 of Russian Institute of Physics & Power Engineering (IPPE). The central region is "non-Uranium fuel zone", where only Pu can induce fission reaction. The non-U zone is surrounded by MOx fuel zone, which is surrounded by U0 fuel zone. Sodium is used for simulating the coolant material. As it was found that the lattice pitch had been incorrectly understood in the past analyses, all items have been re-calculated using the corrected number densities. Furthermore, significantly softened neutron spectrum in the central region caused problems in applying the plate-stretch model that has been established for fast reactor cores through JUPITER experimental analyses. Both keeping the pellet density and using SRAC library for the elastic cross section for lighter nuclides allow us to obtain reasonable analysis accuracy on the spectral indices that were measured at the center of the core. Application of such a cell model was justified through comparison among various cell models using continuous energy Monte-Carlo code MVP. It is confirmed that both the MOX zone and the U0
fuel zone. Sodium is used for simulating the coolant material. As it was found that the lattice pitch had been incorrectly understood in the past analyses, all items have been re-calculated using the corrected number densities. Furthermore, significantly softened neutron spectrum in the central region caused problems in applying the plate-stretch model that has been established for fast reactor cores through JUPITER experimental analyses. Both keeping the pellet density and using SRAC library for the elastic cross section for lighter nuclides allow us to obtain reasonable analysis accuracy on the spectral indices that were measured at the center of the core. Application of such a cell model was justified through comparison among various cell models using continuous energy Monte-Carlo code MVP. It is confirmed that both the MOX zone and the U0 zone can be correctly evaluated by the plate-stretch model. Based on the updated cell calculation, both the effective multiplication factor (k-eff)and the spectral indexes agree well with the measured values. The transport and mesh-size correction is made for the k-eff evaluation. Those results also agree well within reasonable difference between those obtained by IPPE and CEA, which were obtained by using sub-group method or continuous-energy Monte Carlo code. Evaluation by the nuclear data library adjustment confirmed that the analyses results of the BFS-58-1-I1 core have no significant inconsistency with JUPITER experimental analyses results. Those results are quite important for starting BFS-62 cores, which will be analyzed in the framework of supporting program for Russian ...
zone can be correctly evaluated by the plate-stretch model. Based on the updated cell calculation, both the effective multiplication factor (k-eff)and the spectral indexes agree well with the measured values. The transport and mesh-size correction is made for the k-eff evaluation. Those results also agree well within reasonable difference between those obtained by IPPE and CEA, which were obtained by using sub-group method or continuous-energy Monte Carlo code. Evaluation by the nuclear data library adjustment confirmed that the analyses results of the BFS-58-1-I1 core have no significant inconsistency with JUPITER experimental analyses results. Those results are quite important for starting BFS-62 cores, which will be analyzed in the framework of supporting program for Russian ...