Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ogawa, Rina; Totsuka, Masayoshi*; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2023-012, 57 Pages, 2023/07
Concrete vault disposal facility is assumed to be installed below the groundwater table because it is necessary to install them on the ground that has enough bearing capacity. Therefore, the flow rates of groundwater into and out of concrete vault were evaluated by taking into account the permeability coefficients of the geological environment surrounding the facility and of the engineered structure of the facility. Groundwater flow analysis was performed by using the groundwater flow analysis code MIG2DF based on finite element method. In the evaluation of considering the geological environment, since the flow rate of groundwater into and out of the bottom of concrete vault was larger than the flow rates into and out of other sides of the vault in previous technical studies, the evaluation of the flow rate was performed by varying the permeability coefficient of the bedrock adjacent to the bottom of concrete vault. In addition, the other evaluation of the flow rate was conducted assuming the deterioration of concrete vault and of bentonite-mixed soil. As a result, it was found that the permeability coefficient of bedrock adjacent to concrete vault greatly contributed to flow rates of groundwater into and out of concrete vault. In addition, as the permeability coefficient of the bentonite-mixed soil increased due to chemical deterioration, the flow rate of leachate into the surrounding cover soil increased. From the above results, it was found that these permeability coefficients were important influencing factors in the engineering design and safety evaluation of concrete vault disposal facilities.
Nagao, Rina; Namekawa, Maki*; Totsuka, Masayoshi*; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2021-009, 139 Pages, 2021/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is the implementing body of the near surface disposal of low-level radioactive waste (LLW) generated from research facilities and other facilities. Concrete-pit disposal are considered as a method of disposing of the LLW. Since the concrete-pits are placed at deeper position than the groundwater level, we need to consider that radionuclides might migrate with the flow of groundwater. Accordingly, in order to explain the safety of the concrete-pit disposal facility, it is necessary to investigate the flow of groundwater and the volumetric flow rate of leaching water from the facility. Therefore, in this report, sensitivity analysis of the volumetric flow rate of leaching water from concrete-pit was carried out by varying the permeability of cover-soil filled with in outside of the lateral sides of the bentonite mixed soil (BMS) and the conditions of the BMS on the upper part of the concrete-pits. As a result of the analysis, when the BMS is normal condition, the volumetric flow rate of leaching water from the concrete-pits is reduced by lowering permeability of the lateral cover-soil. However, in the case of occurring the deterioration of the function of BMS on the upper part of the concrete-pit, significant reduction of the volumetric flow rate of leaching water is not seen even if the permeability of the lateral cover-soil is lowered. Therefore, taking into consideration the possibility of the deterioration of the function of BMS on the upper part of the concrete-pit, it is necessary to consider that cover-soil with low permeability is equipped on the upper part of the BMS.
Totsuka, Masayoshi; Kurosawa, Ryohei*; Sakai, Akihiro; Nakata, Hisakazu; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Amazawa, Hiroya
JAEA-Technology 2017-001, 40 Pages, 2017/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is planning for the near surface disposal of low level radioactive wastes generated from research, industrial and medical facilities industry in Japan. This document provides the values of radioactivity concentrations equivalent to dose criterion for trench-type disposal. These values are derived based on the safety assessment for ground water scenarios by using a model which describes the release of radionuclides from wastes to a cover soil caused by elution. These concentrations are compared with the one calculated by a model that describes the nuclide release mechanisms as solid-liquid partitioning equilibrium. Additionally, the change in the concentrations is evaluated when the amount of water percolating into a disposal facility varies.
Sakai, Akihiro; Kurosawa, Ryohei*; Totsuka, Masayoshi; Nakata, Hisakazu; Amazawa, Hiroya
JAEA-Technology 2016-032, 117 Pages, 2017/02
JAEA has been planning to implement near surface disposal of low level waste generated from research, medical, and industrial facilities. JAEA plans to carry out 3d analysis of groundwater flow in geological model around the disposal site because of development of migration assessment modeling of radioactivity materials in the site. In the safety demonstration test in JAEA, 3d analysis of groundwater flow was carried out on 1999. The analysis was calculated by using the code "3D-SEEP". But it is necessary to improve the conditions of the model in the analysis. Therefore, we improved the geological model which had been developed carried out 3d analysis of groundwater flow by using the current 3D-SEEP for the specified disposal site in the future. From the result, we expect that 3d analysis of groundwater flow in the environment around the specified near surface disposal site will be able to be sufficiently conducted by developing an appropriate model for the disposal site.
 -concrete system
-concrete systemIzawa, Kazuhiko; Uchida, Yuriko; Okubo, Kiyoshi; Totsuka, Masayoshi; Sono, Hiroki; Tonoike, Kotaro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(11), p.1043 - 1047, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:66.54(Nuclear Science & Technology)Possibility of criticality of fuel debris in a form of UO -concrete mixture is evaluated by calculating infinite multiplication factor (
-concrete mixture is evaluated by calculating infinite multiplication factor (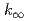 ) for a study of criticality control on the fuel debris generated through the molten core concrete interaction (MCCI) in a severe accident of a light water reactor (LWR). The infinite multiplication factor can be greater than unity, which means that handling of the mixture is subject to criticality control. This paper shows that concrete have efficient slowing-down capability of neutron and points out the necessity of further investigations on the criticality of low-enriched UO
) for a study of criticality control on the fuel debris generated through the molten core concrete interaction (MCCI) in a severe accident of a light water reactor (LWR). The infinite multiplication factor can be greater than unity, which means that handling of the mixture is subject to criticality control. This paper shows that concrete have efficient slowing-down capability of neutron and points out the necessity of further investigations on the criticality of low-enriched UO -concrete system for actual handling of fuel debris.
-concrete system for actual handling of fuel debris.
Totsuka, Masayoshi; Shirai, Nobutoshi; Takaya, Akikazu; Inano, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suyama, Kenya; Totsuka, Masayoshi; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Takada, Tomoyuki*
no journal, ,
Decommission of the Fukushima Daiichi NPP is under discussion. It is not possible for us to assure the fuel assemblies keep the original geometry, and the nuclide composition of the material of the damaged fuel and their positions in the reactor are also unknown now. So that, in this stage, it is difficult for us to judge whether the parameters adopted in the criticality safety evaluation is reasonable or on the contrary over conservative. Based on this view, for the further study on the criticality safety evaluation of the damaged nuclear fuel, we have stared evaluating the basic criticality parameters of such fuel materials.
Totsuka, Masayoshi; Suyama, Kenya; Uchiyama, Gunzo
no journal, ,
We have prepared a library for SWAT code based on JENDL-4 and carried out validation by comparison with burnup calculation results for LWR fuel using the previous library based on JENDL-3.3. Calculation results by adopting JENDL-4 showed improvement of C/E for  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm,
Cm,  Cm,
Cm, 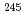 Cm,
Cm, 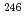 Cm,
Cm,  Cs,
Cs, 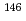 Nd,
Nd,  Eu,
Eu, 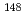 Sm,
Sm, 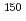 Sm,
Sm,  Sm of 3 to 20%.
Sm of 3 to 20%.
Ogawa, Rina; Totsuka, Masayoshi*; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sakai, Akihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kochiyama, Mami; Tomioka, Dai; Totsuka, Masayoshi*; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sakai, Akihiro
no journal, ,
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is proceeding with plans for the near surface disposal of low-level radioactive waste generated from research institutes and medical institutions in Japan. In order to dispose of the radioactive waste generated by the dismantling of the research reactor, it is necessary to evaluate the radioactivity concentration in the waste. We report on the status of study of radioactivity evaluation methods for dismantling waste generated from research reactors.