Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Ina, Takuya; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Fluid Dynamics Research, 55(6), p.065501_1 - 065501_25, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Mechanics)We investigate the applicability of the data assimilation (DA) to large eddy simulations (LESs) based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). We carry out the observing system simulation experiment of a two-dimensional (2D) forced isotropic turbulence, and examine the DA accuracy of the nudging and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) with spatially sparse and noisy observation data of flow fields. The advantage of the LETKF is that it does not require computing spatial interpolation and/or an inverse problem between the macroscopic variables (the density and the pressure) and the velocity distribution function of the LBM, while the nudging introduces additional models for them. The numerical experiments with 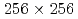 grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with
grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with 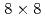 observation points (
observation points (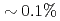 of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.
of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Asahi, Yuichi; Inagaki, Atsushi*; Shimose, Kenichi*; Hirano, Kohin*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 28, 4 Pages, 2023/05
We have developed a multi-scale wind simulation code named CityLBM that can resolve entire cities to detailed streets. CityLBM enables a real time ensemble simulation for several km square area by applying the locally mesh-refined lattice Boltzmann method on GPU supercomputers. On the other hand, real-world wind simulations contain complex boundary conditions that cannot be modeled, so data assimilation techniques are needed to reflect observed data in the simulation. This study proposes an optimization method for ground surface temperature bias based on an ensemble Kalman filter to reproduce wind conditions within urban city blocks. As a verification of CityLBM, an Observing System Simulation Experiment (OSSE) is conducted for the central Tokyo area to estimate boundary conditions from observed near-surface temperature values.
Asahi, Yuichi; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Shiba, Hayato*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 186(3), p.659 - 692, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)We develop a Transformer-based deep learning model to predict the plume concentrations in the urban area under uniform flow conditions. Our model has two distinct input layers: Transformer layers for sequential data and convolutional layers in convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image-like data. Our model can predict the plume concentration from realistically available data such as the time series monitoring data at a few observation stations and the building shapes and the source location. It is shown that the model can give reasonably accurate prediction with orders of magnitude faster than CFD simulations. It is also shown that the exactly same model can be applied to predict the source location, which also gives reasonable prediction accuracy.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Dai-36-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/12
This study implemented and tested the ensemble data assimilation (DA) of turbulent flows using the lattice Boltzmann method and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LBM-LETKF). The computational code was implemented fully on GPUs. The test was carried out for the 3D turbulent flow around a square cylinder with 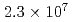 meshes and 32 ensemble members using 32 GPUs. The time interval of the DA in the test was a half of the period of the Kalman vortex shedding. The normalized mean absolute errors (NMAE) of the lift coefficient were 132%, 148%, and 13.2% for the non-DA case, the nudging case (a simpler DA algorithm), and the LETKF case, respectively. It was found that the LETKF achieved good DA accuracy even though the observation was not frequent enough for the small scale turbulence, while the nudging showed systematic delays in its solution, and could not keep the DA accurately.
meshes and 32 ensemble members using 32 GPUs. The time interval of the DA in the test was a half of the period of the Kalman vortex shedding. The normalized mean absolute errors (NMAE) of the lift coefficient were 132%, 148%, and 13.2% for the non-DA case, the nudging case (a simpler DA algorithm), and the LETKF case, respectively. It was found that the LETKF achieved good DA accuracy even though the observation was not frequent enough for the small scale turbulence, while the nudging showed systematic delays in its solution, and could not keep the DA accurately.
Asahi, Yuichi; Padioleau, T.*; Latu, G.*; Bigot, J.*; Grandgirard, V.*; Obrejan, K.*
Dai-36-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/12
We implement a kinetic plasma simulation code with multiple performance portable frameworks and evaluated its performance on Intel Icelake, NVIDIA V100 and A100 GPUs, and AMD MI100 GPU. Relying on the language standard parallelism stdpar and proposed language standard multi-dimensional array support mdspan, we demonstrate a performance portable implementation without harming the readability and productivity. With stdpar, we obtain a good overall performance for a kinetic plasma mini-application in the range of  20% to the Kokkos version on Icelake, V100, A100 and MI100. We conclude that stdpar can be a good candidate to develop a performance portable and productive code targeting Exascale era platforms, assuming this programming model will be available on AMD and/or Intel GPUs in the future.
20% to the Kokkos version on Icelake, V100, A100 and MI100. We conclude that stdpar can be a good candidate to develop a performance portable and productive code targeting Exascale era platforms, assuming this programming model will be available on AMD and/or Intel GPUs in the future.
Asahi, Yuichi; Padioleau, T.*; Latu, G.*; Bigot, J.*; Grandgirard, V.*; Obrejan, K.*
Proceedings of 2022 International Workshop on Performance, Portability, and Productivity in HPC (P3HPC) (Internet), p.68 - 80, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)This paper presents the performance portable implementation of a kinetic plasma simulation code with C++ parallel algorithm to run across multiple CPUs and GPUs. Relying on the language standard parallelism stdpar and proposed language standard multi-dimensional array support mdspan, we demonstrate that a performance portable implementation is possible without harming the readability and productivity. We obtain a good overall performance for a mini-application in the range of 20% to the Kokkos version on Intel Icelake, NVIDIA V100, and A100 GPUs. Our conclusion is that stdpar can be a good candidate to develop a performance portable and productive code targeting the Exascale era platform, assuming this approach will be available on AMD and/or Intel GPUs in the future.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 4 Pages, 2022/06
We developed GPU implementation of ensemble data assimilation (DA) using the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) with the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). The performance test was carried out upto 32 ensembles of two-dimensional isotropic turbulence simulations using the D2Q9 LBM. The computational cost of the LETKF was less than or nearly equal to that of the LBM upto eight ensembles, while the former exceeded the latter at larger ensembles. At 32 ensembles, their computational costs per cycle were respectively 28.3 msec and 5.39 msec. These results suggested that further speedup of the LETKF is needed for practical 3D LBM simulations.
Asahi, Yuichi; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Shiba, Hayato*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 5 Pages, 2022/06
We have ported the GPU accelerated Lattice Boltzmann Method code "CityLBM" to AMD MI100 GPU. We present the performance of CityLBM achieved on NVIDIA P100, V100, A100 GPUs and AMDMI100 GPU. Using the host to host MPI communications, the performance on MI100 GPU is around 20% better than on V100 GPU. It has turned out that most of the kernels are successfully accelerated except for interpolation kernels for Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method.
Maeyama, Shinya*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Asahi, Yuichi; Ishizawa, Akihiro*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.3166_1 - 3166_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:93.39(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Turbulent transport is a key physics process for confining magnetic fusion plasma. Recent theoretical and experimental studies of existing fusion experimental devices revealed the existence of cross-scale interactions between small (electron)-scale and large (ion)-scale turbulence. Since conventional turbulent transport modelling lacks cross-scale interactions, it should be clarified whether cross-scale interactions are needed to be considered in future experiments on burning plasma, whose high electron temperature is sustained with fusion-born alpha particle heating. Here, we present supercomputer simulations showing that electron scale turbulence in high electron temperature plasma can affect the turbulent transport of not only electrons but also fuels and ash. Electron-scale turbulence disturbs the trajectories of resonant electrons responsible for ion-scale micro-instability and suppresses large-scale turbulent fluctuations. Simultaneously, ion-scale turbulent eddies also suppress electron-scale turbulence. These results indicate a mutually exclusive nature of turbulence with disparate scales. We demonstrate the possibility of reduced heat flux via cross-scale interactions.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Ina, Takuya; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 13th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Heterogeneous Systems (ScalAH22) (Internet), p.10 - 17, 2022/00
The ensemble data assimilation of computational fluid dynamics simulations based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) is implemented and optimized on a GPU supercomputer based on NVIDIA A100 GPUs. To connect the LBM and LETKF parts, data transpose communication is optimized by overlapping computation, file I/O, and communication based on data dependency in each LETKF kernel. In two dimensional forced isotropic turbulence simulations with the ensemble size of 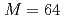 and the number of grid points of
and the number of grid points of 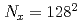 , the optimized implementation achieved
, the optimized implementation achieved 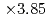 speedup from the naive implementation, in which the LETKF part is not parallelized. The main computing kernel of the local problem is the eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) of
speedup from the naive implementation, in which the LETKF part is not parallelized. The main computing kernel of the local problem is the eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) of 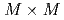 real symmetric dense matrices, which is computed by a newly developed batched EVD in EigenG. The batched EVD in EigenG outperforms that in cuSolver, and
real symmetric dense matrices, which is computed by a newly developed batched EVD in EigenG. The batched EVD in EigenG outperforms that in cuSolver, and 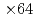 speedup was achieved.
speedup was achieved.
Asahi, Yuichi; Latu, G.*; Bigot, J.*; Grandgirard, V.*
Proceedings of 2021 International Workshop on Performance, Portability, and Productivity in HPC (P3HPC) (Internet), p.79 - 91, 2021/11
This paper presents optimization strategies dedicated to a kinetic plasma simulation code that makes use of OpenACC/OpenMP directives and Kokkos performance portable framework to run across multiple CPUs and GPUs. We evaluate the impacts of optimizations on multiple hardware platforms: Intel Xeon Skylake, Fujitsu Arm A64FX, and Nvidia Tesla P100 and V100. After the optimizations, the OpenACC/OpenMP version achieved the acceleration of 1.07 to 1.39. The Kokkos version in turn achieved the acceleration of 1.00 to 1.33. Since the impact of optimizations under multiple combinations of kernels, devices and parallel implementations is demonstrated, this paper provides a widely available approach to accelerate a code keeping the performance portability. To achieve an excellent performance on both CPUs and GPUs, Kokkos could be a reasonable choice which offers more flexibility to manage multiple data and loop structures with a single codebase.
Asahi, Yuichi; Hatayama, Sora*; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing (IEEE Cluster 2021) (Internet), p.686 - 691, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.38(Computer Science, Hardware & Architecture)We develop a convolutional neural network model to predict the multi-resolution steady flow. Based on the state-of-the-art image-to-image translation model pix2pixHD, our model can predict the high resolution flow field from the set of patched signed distance functions. By patching the high resolution data, the memory requirements in our model is suppressed compared to pix2pixHD.
Asahi, Yuichi; Hatayama, Sora*; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 4 Pages, 2021/05
We develop a convolutional neural network model to predict the multi-resolution steady flow. Based on the state-of-the-art image-to-image translation model Pix2PixHD, our model can predict the high resolution flow field from the signed distance function. By patching the high resolution data, the memory requirements in our model is suppressed compared to Pix2PixHD.
Asahi, Yuichi; Fujii, Keisuke*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 97(2), p.86 - 92, 2021/02
The 5D gyrokinetic simulation data has been analyzed with the data-driven analysis methods. By defining an entropy-like quantity with singular values, we have quantitatively evaluated the randomness of the plasma state. We found that the randomness of plasma increases after the avalanche like transport and then gradually decrease. Since the decrease of the randomness is expected to be relevant to the phase space structure formation, we have developed a method to extract the phase space structures from the time series of 5D data. The relationship between the avalanche-like transport and phase space structures is discussed based on the contribution of each principal component to the energy transport.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Obrejan, K.*; Asahi, Yuichi; Honda, Mitsuru*
Physics of Plasmas, 28(1), p.012501_1 - 012501_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.92(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Tracer impurity transport in ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence is investigated using a global full- gyrokinetic simulation including kinetic electrons, bulk ions, and low to medium
gyrokinetic simulation including kinetic electrons, bulk ions, and low to medium  tracer impurities, where
tracer impurities, where  is the charge number. It is found that in addition to turbulent particle transport, enhanced neoclassical particle transport due to a new synergy effect between turbulent and neoclassical transports makes a significant contribution to tracer impurity transport. Bursty excitation of the ITG mode generates non-ambipolar turbulent particle fluxes of electrons and bulk ions, leading to a fast growth of the radial electric field following the ambipolar condition. The divergence of
is the charge number. It is found that in addition to turbulent particle transport, enhanced neoclassical particle transport due to a new synergy effect between turbulent and neoclassical transports makes a significant contribution to tracer impurity transport. Bursty excitation of the ITG mode generates non-ambipolar turbulent particle fluxes of electrons and bulk ions, leading to a fast growth of the radial electric field following the ambipolar condition. The divergence of 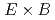 flows compresses up-down asymmetric density perturbations, which are subject to transport induced by the magnetic drift. The enhanced neoclassical particle transport depends on the ion mass, because the magnitude of up-down asymmetric density perturbation is determined by a competition between the
flows compresses up-down asymmetric density perturbations, which are subject to transport induced by the magnetic drift. The enhanced neoclassical particle transport depends on the ion mass, because the magnitude of up-down asymmetric density perturbation is determined by a competition between the 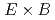 compression effect and the return current given by the parallel streaming motion. This mechanism does not work for the temperature, and thus, selectively enhances only particle transport.
compression effect and the return current given by the parallel streaming motion. This mechanism does not work for the temperature, and thus, selectively enhances only particle transport.
Asahi, Yuichi; Fujii, Keisuke*; Heim, D. M.*; Maeyama, Shinya*; Garbet, X.*; Grandgirard, V.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Masatoshi*
Physics of Plasmas, 28(1), p.012304_1 - 012304_21, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This article demonstrates a data compression technique for the time series of five dimensional distribution function data based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Phase space bases and corresponding coefficients are constructed by PCA in order to reduce the data size and the dimensionality. It is shown that about 83% of the variance of the original five dimensional distribution can be expressed with 64 components. This leads to the compression of the degrees of freedom from 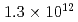 to
to 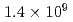 . One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
. One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Asahi, Yuichi; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Dai-34-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 2 Pages, 2020/12
We develop a multigrid preconditioned conjugate gradient (MG-CG) solver for the pressure Poisson equation in a two-phase flow CFD code JUPITER. The code is written in C++ and CUDA to keep the portability on multi-platforms. The main kernels of the CG solver achieve reasonable performance as 0.4  0.75 of the roofline performances, and the performances of the MG-preconditioner are also reasonable on NVIDIA GPU and Intel CPU. However, the performance degradation of the SpMV kernel on ARM is significant. It is confirmed that the optimization does not work if any functions are included in the loop.
0.75 of the roofline performances, and the performances of the MG-preconditioner are also reasonable on NVIDIA GPU and Intel CPU. However, the performance degradation of the SpMV kernel on ARM is significant. It is confirmed that the optimization does not work if any functions are included in the loop.
Asahi, Yuichi; Latu, G.*; Bigot, J.*; Grandgirard, V.*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.218 - 224, 2020/10
Performance portability is expected to be a critical issue in the upcoming exascale era. We explore a performance portable approach for a fusion plasma turbulence simulation code employing the kinetic model, namely the GYSELA code. For this purpose, we extract the key features of GYSELA such as the high dimensionality (more than 4D) and the semi-Lagrangian scheme, and encapsulate them into a mini-application which solves the similar but a simplified Vlasov-Poisson system as GYSELA. We implement the mini-app with OpenACC, OpenMP4.5 and Kokkos, where we suppress unnecessary duplications of code lines. Based on our experience, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of OpenACC, OpenMP4.5 and Kokkos, from the view point of performance portability, readability and productivity.
Asahi, Yuichi*; Latu, G.*; Bigot, J.*; Maeyama, Shinya*; Grandgirard, V.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Concurrency and Computation; Practice and Experience, 32(5), p.e5551_1 - e5551_21, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.03(Computer Science, Software Engineering)Two five-dimensional gyrokinetic codes GYSELA and GKV were ported to the modern accelerators, Xeon Phi KNL and Tesla P100 GPU. Serial computing kernels of GYSELA on KNL and GKV on P100 GPU were respectively 1.3x and 7.4x faster than those on a single Skylake processor. Scaling tests of GYSELA and GKV were respectively performed from 16 to 512 KNLs and from 32 to 256 P100 GPUs, and data transpose communications in semi-Lagrangian kernels in GYSELA and in convolution kernels in GKV were found to be main bottlenecks, respectively. In order to mitigate the communication costs, pipeline-based and task-based communication overlapping were implemented in these codes.
Asahi, Yuichi*; Grandgirard, V.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Donnel, P.*; Garbet, X.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Latu, G.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 61(6), p.065015_1 - 065015_15, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.12(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The role of poloidal convective cells on transport processes is studied with the full-F gyrokinetic code GYSELA. For this purpose, we apply a numerical filter to convective cells and compare the simulation results with and without the filter. The energy flux driven by the magnetic drifts turns out to be reduced by a factor of about 2 once the numerical filter is applied. A careful analysis reveals that the frequency spectrum of the convective cells is well-correlated with that of the turbulent Reynolds stress tensor, giving credit to their turbulence-driven origin. The impact of convective cells can be interpreted as a synergy between turbulence and neoclassical dynamics.