Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
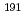 Pt-labeled platinum complex and evaluation of its biodistribution in healthy mice
Pt-labeled platinum complex and evaluation of its biodistribution in healthy miceOmokawa, Marina*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Kawashima, Hidekazu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Yagi, Yusuke*; Naito, Yuki*; Yasui, Hiroyuki*
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 97, p.117557_1 - 117557_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)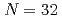 and
and 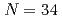 shell gap for Ti and V by the first high-precision multireflection time-of-flight mass measurements at BigRIPS-SLOWRI
shell gap for Ti and V by the first high-precision multireflection time-of-flight mass measurements at BigRIPS-SLOWRIIimura, Shun*; Rosenbusch, M.*; Takamine, Aiko*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Wada, Michiharu*; Chen, S.*; Hou, D. S.*; Xian, W.*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Yan, S.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(1), p.012501_1 - 012501_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:94.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 13(12), p.e0208909_1 - e0208909_12, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.05(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Imaging of  Tc radioisotope was conducted using an electron tracking-Compton camera (ETCC).
Tc radioisotope was conducted using an electron tracking-Compton camera (ETCC).  Tc emits 204, 582, and 835 keV
Tc emits 204, 582, and 835 keV  rays, and was produced in the
rays, and was produced in the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n) Tc reaction with a
Tc reaction with a  Mo-enriched target. The recycling of the
Mo-enriched target. The recycling of the  Mo-enriched molybdenum trioxide was investigated, and the recycled yield of
Mo-enriched molybdenum trioxide was investigated, and the recycled yield of  Mo was achieved to be 70% - 90%. The images were obtained with each of the three
Mo was achieved to be 70% - 90%. The images were obtained with each of the three  rays. Results showed that the spatial resolution increases with increasing
rays. Results showed that the spatial resolution increases with increasing  -ray energy, and suggested that the ETCC with high-energy
-ray energy, and suggested that the ETCC with high-energy  -ray emitters such as
-ray emitters such as  Tc is useful for the medical imaging of deep tissue and organs in the human body.
Tc is useful for the medical imaging of deep tissue and organs in the human body.
 = 100 with a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph
= 100 with a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrographIto, Yuta*; Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Arai, Fumiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kimura, Sota*; Koura, Hiroyuki; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 120(15), p.152501_1 - 152501_6, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:93.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Masses of 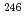 Es,
Es, 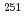 Fm and the transfermium nuclei
Fm and the transfermium nuclei 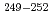 Md, and
Md, and  No, produced by hot- and cold-fusion reactions, in the vicinity of the deformed
No, produced by hot- and cold-fusion reactions, in the vicinity of the deformed 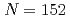 neutron shell closure, have been directly measured using a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph. The masses of
neutron shell closure, have been directly measured using a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph. The masses of 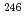 Es and
Es and 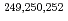 Md were measured for the first time. Using the masses of
Md were measured for the first time. Using the masses of 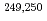 Md as anchor points for
Md as anchor points for  decay chains, the masses of heavier nuclei, up to
decay chains, the masses of heavier nuclei, up to  Bh and
Bh and  Mt, were determined. These new masses were compared with theoretical global mass models and demonstrated to be in good agreement with macroscopic-microscopic models in this region. The empirical shell gap parameter
Mt, were determined. These new masses were compared with theoretical global mass models and demonstrated to be in good agreement with macroscopic-microscopic models in this region. The empirical shell gap parameter 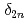 derived from three isotopic masses was updated with the new masses and corroborate the existence of the deformed
derived from three isotopic masses was updated with the new masses and corroborate the existence of the deformed 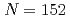 neutron shell closure for Md and Lr.
neutron shell closure for Md and Lr.
Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Ito, Yuta*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Kimura, Sota*; Koura, Hiroyuki; MacCormick, M.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 407, p.160 - 165, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:78.05(Instruments & Instrumentation)Various isotopes of Ac, Ra, Fr, and Rn were produced by fusion-evaporation reactions using a  Ca beam. The energetic ions were stopped in and extracted from a helium gas cell. The extracted ions were identified using a multi-reflection time-of-fight mass spectrograph. In all cases, it was observed that the predominant charge state for the extracted ions, including the alkali Fr, was 2+.
Ca beam. The energetic ions were stopped in and extracted from a helium gas cell. The extracted ions were identified using a multi-reflection time-of-fight mass spectrograph. In all cases, it was observed that the predominant charge state for the extracted ions, including the alkali Fr, was 2+.
Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Ito, Yuta*; Kaji, Daiya*; Arai, Fumiya*; MacCormick, M.*; Murray, I.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Jeong, S.*; Kimura, Sota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(1), p.011305_1 - 011305_6, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:96.07(Physics, Nuclear)Using a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph located after a gas cell coupled with the gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS-II, the masses of several  -decaying heavy nuclei were directly and precisely measured. The nuclei were produced via fusion-evaporation reactions and separated from projectilelike and targetlike particles using GARIS-II before being stopped in a helium-filled gas cell. Time-of-flight spectra for three isobar chains,
-decaying heavy nuclei were directly and precisely measured. The nuclei were produced via fusion-evaporation reactions and separated from projectilelike and targetlike particles using GARIS-II before being stopped in a helium-filled gas cell. Time-of-flight spectra for three isobar chains,  Fr-
Fr- Rn-
Rn- At-
At- Po,
Po,  Fr-
Fr-  Rn-
Rn- At-
At- Po-
Po- Bi, and
Bi, and  Fr-
Fr- Rn-
Rn- At, were observed. Precision atomic mass values were determined for
At, were observed. Precision atomic mass values were determined for 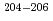 Fr,
Fr, 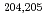 Rn, and
Rn, and 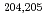 At. Identifications of
At. Identifications of  Bi,
Bi, 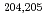 Po,
Po,  Rn, and
Rn, and  At were made with N
At were made with N 10 detected ions, representing the next step toward use of mass spectrometry to identify exceedingly low-yield species such as superheavy element ions.
10 detected ions, representing the next step toward use of mass spectrometry to identify exceedingly low-yield species such as superheavy element ions.
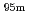 Tc for Compton camera imaging
Tc for Compton camera imagingHatsukawa, Yuichi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Nagai, Yasuki; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1283 - 1285, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Chemistry, Analytical)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is used in radioactive medical diagonostic tests, for example as a radioactive tracer that medical equipment can detect in the human body. It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 141 keV
Tc) is used in radioactive medical diagonostic tests, for example as a radioactive tracer that medical equipment can detect in the human body. It is well suited to the role because it emits readily detectable 141 keV  rays, and its half-life is 6.01 hours (meaning that about 94% of it decays to technetium-99 in 24 hours). There are at least 31 commonly used radiopharmaceuticals based on technetium-99m for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood, and tumors. Recent years, with the develop-ment of the Compton camera which can realize high position resolution, technetium isotopes emitting high energy
rays, and its half-life is 6.01 hours (meaning that about 94% of it decays to technetium-99 in 24 hours). There are at least 31 commonly used radiopharmaceuticals based on technetium-99m for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood, and tumors. Recent years, with the develop-ment of the Compton camera which can realize high position resolution, technetium isotopes emitting high energy  -rays are required. In this study, technetium-95m which emits some
-rays are required. In this study, technetium-95m which emits some  rays around 800 keV was produced by the
rays around 800 keV was produced by the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n)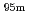 Tc reaction.
Tc reaction.
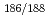 Re-labeled antibody (A7) for radioimmunotherapy with rhenium(I) tricarbonyl core as a chelate site
Re-labeled antibody (A7) for radioimmunotherapy with rhenium(I) tricarbonyl core as a chelate siteOgawa, Kazuma*; Kawashima, Hidekazu*; Kinuya, Seigo*; Shiba, Kazuhiro*; Onoguchi, Masahisa*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Odani, Akira*; Saji, Hideo*
Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 23(10), p.843 - 848, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:31.42(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Rhenium is one of the most valuable elements for internal radiotherapy because 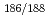 Re have favorable physical characteristics. However, there are problems when proteins such as antibodies are used as carriers of
Re have favorable physical characteristics. However, there are problems when proteins such as antibodies are used as carriers of 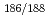 Re. Labeling methods require the complicated processes. Therefore, we planned the preparation by a simple method and evaluation of a stable
Re. Labeling methods require the complicated processes. Therefore, we planned the preparation by a simple method and evaluation of a stable 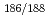 Re-labeled antibody. For this purpose, we selected
Re-labeled antibody. For this purpose, we selected 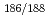 Re(I) tricarbonyl complex as a chelating site. A7 was used as a model protein.
Re(I) tricarbonyl complex as a chelating site. A7 was used as a model protein. 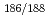 Re-labeled A7 was prepared by directly reacting a
Re-labeled A7 was prepared by directly reacting a 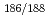 Re(I) tricarbonyl precursor with A7.
Re(I) tricarbonyl precursor with A7. 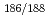 Re-(CO)
Re-(CO) -A7 were prepared with radiochemical yields of 23-28%. After purification,
-A7 were prepared with radiochemical yields of 23-28%. After purification, 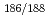 Re-(CO)
Re-(CO) -A7 showed a radiochemical purity of over 95%. In biodistribution experiments,
-A7 showed a radiochemical purity of over 95%. In biodistribution experiments, 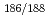 Re-labeled A7 showed high uptakes in the tumor.
Re-labeled A7 showed high uptakes in the tumor.
 Re-labeled antibody (A7) by a simple method using rhenium(I) tricarbonyl complex
Re-labeled antibody (A7) by a simple method using rhenium(I) tricarbonyl complexOgawa, Kazuma*; Kawashima, Hidekazu*; Kinuya, Seigo*; Yoshimoto, Mitsuyoshi*; Shiba, Kazuhiro*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Mori, Hirofumi*; Saji, Hideo*
no journal, ,
 Re is one of the most useful radionuclides for internal radiotherapy. However, there is a problem when protein such as antibody is used as a carrier of
Re is one of the most useful radionuclides for internal radiotherapy. However, there is a problem when protein such as antibody is used as a carrier of  Re. The labeling method using bifunctional chelating agents require the conjugation of
Re. The labeling method using bifunctional chelating agents require the conjugation of  Re-complex to protein after radiolabeling with the bifunctional chelating agent. Then, we planned the preparation of a stable
Re-complex to protein after radiolabeling with the bifunctional chelating agent. Then, we planned the preparation of a stable  Re-labeled protein by a simple method. A7 monoclonal antibody was labeled by reacting
Re-labeled protein by a simple method. A7 monoclonal antibody was labeled by reacting  Re(I) tricarbonyl precursor with A7 directly.
Re(I) tricarbonyl precursor with A7 directly.  Re labeled A7 was prepared with radiochemical yield of 23%. After purification,
Re labeled A7 was prepared with radiochemical yield of 23%. After purification,  Re labeled A7 showed radiochemical purity over 98%. After 24 hours of incubation, about 93% of
Re labeled A7 showed radiochemical purity over 98%. After 24 hours of incubation, about 93% of  Re-A7 remained intact, which indicates
Re-A7 remained intact, which indicates  Re-A7 is stable in vitro. In biodistribution experiment, 11.2% of the injected dose/g of
Re-A7 is stable in vitro. In biodistribution experiment, 11.2% of the injected dose/g of  Re-A7 accumulated in the tumor at 24 hours postinjection, and tumor to blood ratio was over 1.0 at the same time.
Re-A7 accumulated in the tumor at 24 hours postinjection, and tumor to blood ratio was over 1.0 at the same time.
 Re-labeled biotin as a labeling agent for antibodies
Re-labeled biotin as a labeling agent for antibodiesHirasawa, Makoto*; Kawashima, Hidekazu*; Ogawa, Kazuma*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Ono, Masahiro*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saji, Hideo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawashima, Hidekazu*; Hirasawa, Makoto*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Ono, Masahiro*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saji, Hideo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sonoda, Shinya*; Nabetani, Akira*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; Takada, Atsushi*; Kubo, Hidetoshi*; Komura, Shotaro*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; Tanimori, Toru*; Matsuoka, Yoshihiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
We present the performance results using this new ETCC such as the imaging test using F-18 in point-like and rod-like phantoms with varying the intense of radiation. In addition, the measurementof Tc-95m which is produced by Japan Atomic Energy Agency was performed. Tc-95m emitsthe  -rays with the energy, 204, 583, and 835 keV, and then an image with multi-energies is examined. The position resolution achieves less than about 8 degrees from 10 degrees at 511 keV by this improvement. Further improvement of the angular resolution (position resolution) will be presented until 2015 spring. Also, we are developing the next ETCC by increasing the thickness of the scintillator from 1 rad. to 2 rad. and the gas pressure from 1 atm to 3 atm which improvethe detection efficiency by a factor of
-rays with the energy, 204, 583, and 835 keV, and then an image with multi-energies is examined. The position resolution achieves less than about 8 degrees from 10 degrees at 511 keV by this improvement. Further improvement of the angular resolution (position resolution) will be presented until 2015 spring. Also, we are developing the next ETCC by increasing the thickness of the scintillator from 1 rad. to 2 rad. and the gas pressure from 1 atm to 3 atm which improvethe detection efficiency by a factor of  5 at 511 keV. By these improvements, the imaging time of mouse is expected to be reduced from several hours with to
5 at 511 keV. By these improvements, the imaging time of mouse is expected to be reduced from several hours with to  20 minutes for lots of kinds of RIs with the energy band from 0.1-2 MeV.
20 minutes for lots of kinds of RIs with the energy band from 0.1-2 MeV.
 Tc for Compton camera imaging
Tc for Compton camera imagingHatsukawa, Yuichi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Nagai, Yasuki; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
no journal, ,
In recent years, the Compton camera which is originally developed for the astrophysical studies was applied for medical diagnostic usage. For the Compton camera imaging require technetium isotopes emitting higher energy  -rays. Two Tc isotopes,
-rays. Two Tc isotopes,  Tc (T
Tc (T = 60 d; E
= 60 d; E = 204, 582 and 835 keV) and
= 204, 582 and 835 keV) and 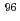 Tc(T
Tc(T = 4.28 d, E
= 4.28 d, E = 778 and 812 keV) are candidates for Compton camera imaging. Compton camera imaging can realize high position resolution without collimator. Because of no collimator using, the Compton camera makes higher
= 778 and 812 keV) are candidates for Compton camera imaging. Compton camera imaging can realize high position resolution without collimator. Because of no collimator using, the Compton camera makes higher  -ray detection efficiency. Compared with SPECT with
-ray detection efficiency. Compared with SPECT with  Tc, the Compton camera imaging technique can be expected that radiation exposure deduce to 1/5-1/10. In this study, technetium-95m was produced by the
Tc, the Compton camera imaging technique can be expected that radiation exposure deduce to 1/5-1/10. In this study, technetium-95m was produced by the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n) Tc reaction.
Tc reaction.
Nakamura, Satoshi; Ban, Yasutoshi; Sugimoto, Mie; Tambo, Masaki; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Hiruta, Kenta; Yoshida, Takuya; Uehara, Hiroyuki; Obata, Hiroki; Kimura, Yasuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
In Nuclear Science Research Institute at JAEA, detailed studies with regard to the elemental and nuclide compositions of fuel debris have been proceeding. We have conducted dissolution of the samples by alkaline fusion with sodium peroxide and chemical analysis by ICP-AES, alpha and gamma spectrometer, and TIMS. After studying the dissolution methods with various types of simulated debris, a demonstration test with TMI-2 debris was conducted. The elemental composition in the dissolved solution of TMI-2 debris consistent with the results of SEM/WDX and XRD analyses, and the validity of the present method was confirmed. In this presentation, the details of each analysis and the issues raised through the analysis will be introduced.