Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Ozaki, Toshinori*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Kudo, Masaki*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(2), p.023001_1 - 023001_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.16(Physics, Applied)We show that Xe ion irradiation with 80 MeV to GdBa Cu
Cu Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at
Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at 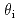 = 45
= 45 , whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (
, whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (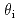 = 0
= 0 ) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density
) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density  .
.
Xu, P. G.; Tomota, Yo*; Arakaki, Yu; Harjo, S.; Sueyoshi, Hitoshi*
Materials Characterization, 127, p.104 - 110, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:93.45(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ishikawa, Nobuyuki*; Sueyoshi, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi
Yosetsu Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 29(3), p.218 - 224, 2011/08
Cold cracking test was conducted using Y-grooved constraint weld joint by intentionally introducing hydrogen gas, and critical hydrogen content in the weld metal to cold cracking was determined. Residual stress distribution in the weld meal was measured by neutron diffraction technique. The root portion showed highest tensile stress of over 1110 MPa in the transverse direction, which is the same as the crack opening direction.
Makino, Amane*; Sueyoshi, Kuni*; Suzuki, Yuji*; Kawachi, Naoki; Tawaraya, Keitaro*; Otsu, Naoko*; Nakanishi, Hiromi*; Fujiwara, Toru*
Nihon Dojo Hiryo Gaku Zasshi, 82(2), p.152 - 159, 2011/04
This paper is a proceeding of the fourth division (Plant nutrition) symposium theme of discussed in the annual conference of 2011 soil science and plant nutrition at Hokkaido University. N. Kawachi, an author who takes charge of third section, discuss nutritional physiology revealed by imaging analysis of element kinetics in plants. This section focuses on introducing a RI imaging system developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In addition, it is expressed that the analytical research conducted on nutritional physiology in plants as revealed by imaging of element kinetics.
Sueyoshi, Hitoshi*; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi
no journal, ,
Experiments of cold cracking on a 980 MPa class restraint weld joint were performed and the residual stress distribution in the joint was analyzed using neutron diffraction technique. The critical conditions for the cold cracking of the weld joint was determined from the obtained results.
Sueyoshi, Hitoshi*; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi
no journal, ,
Experiments of cold cracking on a hydrogen induced 980 MPa class restraint weld joint were performed and the residual stress distribution in the joint was analyzed using neutron diffraction technique. The critical conditions for the cold cracking of the weld joint was determined from the obtained results.