Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Omichi, Masaaki*; Asano, Atsushi*; Tsukuda, Satoshi*; Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Saeki, Akinori*; Sakamaki, Daisuke*; Onoda, Akira*; Hayashi, Takashi*; Seki, Shu*
Nature Communications (Internet), 5, p.3718_1 - 3718_8, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:78.11(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Protein nanowires exhibiting specific biological activities hold promise for interacting with living cells and controlling and predicting biological responses such as apoptosis, endocytosis and cell adhesion. Here we report the result of the interaction of a single high-energy charged particle with protein molecules. Degradation of the human serum albumin nanowires was examined using trypsin. The biotinylated human serum albumin nanowires bound avidin, demonstrating the high affinity of the nanowires. Human serum albumin-avidin hybrid nanowires were also fabricated from a solid state mixture and exhibited good mechanical strength. The biotinylated human serum albumin nanowires can be transformed into nanowires exhibiting a biological function such as avidin-biotinyl interactions and peroxidase activity. The present technique is a versatile platform for functionalizing the surface of any protein molecule with an extremely large surface area.
Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Sakai, Hideaki*; Okuyama, Daisuke*; Ishiwata, Shintaro*; Fujioka, Jun*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Hashizume, Daisuke*; Kagawa, Fumitaka*; Takahashi, Yoichiro*; Shimano, Ryo*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 407(11), p.1685 - 1688, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.98(Physics, Condensed Matter)*; *; *; *
PNC TN941 82-55, 284 Pages, 1982/03
The postdisassembly expansion phase of the Hypothetical Core Disruptive Accident (HCDA) in the MONJU reactor was analyzed by using the SIMMER-II code. Hitherto, the isentropic expansion of fuel vapor has been assumed after the core disassembly phase to estimate the system work energy following a postulated energetic disassembly. Recently, the SIMMER code was applied to analyze che postdisassembly expansion phase for the Clinch River Breeder Reactor (CRBR), and it was shown that the system work energy as a result of an HCDA was remarkably reduced compared with the isentropic expansion. The SIMMER code has attracted attension in the field of postdisassembly expansion analysis because of this possibility of work energy reduction. SIMMER-II was installed at PNC, the O-arai Engineering Center, in May 1980, and has been operational since November 1980. This report is divided into two parts. The first deals with the parameter survey based on the study of the MONJU postdisassembly expansion under simplified initial conditions by Kondo and Aizawa at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The other is based on the results of the initiating phase and of the core disassembly phase analyses by the SAS 3D and VENUS-PM codes, performed at PNC. In the latter, we adopted two cases which yielded largest system kinetic energy in the MONJU system, and we estimated the maximum energy released in the MONJU HCDA by using the SIMMER-II code. The main results obtained are shown below. (1)The maximum system kinetic energy released during the postdisassembly phase of the MONJU HCDA is at most 10 MJ when the active core, upper axial blanket and fission gas plenum are all voided at the initial state. (The maximum system work energy associated with isentropic expansion of the fuel vapor to 1 atm is 992 MJ.) (2)Under the same initial average core fuel temperature, a higher peaking factor of temperature distribution causes a larger system kinetic energy. For example, for temperature ...
Nagae, Daisuke; Takemuara, Makoto*; Ueno, Hideki*; Kameda, Daisuke*; Asahi, Koichiro*; Yoshimi, Akihiro*; Sugimoto, Takashi*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Uchida, Makoto*; et al.
no journal, ,
An electric quadrupole moment ( moment) is sensitive to collective aspects of nuclear structure. In the
moment) is sensitive to collective aspects of nuclear structure. In the  -moment measurement for unstable nuclei, we employ the
-moment measurement for unstable nuclei, we employ the  -detected nuclear-quadrupole resonance method. In this method, we need to supply
-detected nuclear-quadrupole resonance method. In this method, we need to supply 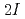 resonance frequencies, where
resonance frequencies, where  denotes the nuclear spin. We have developed a new RF-application system to induced all of the
denotes the nuclear spin. We have developed a new RF-application system to induced all of the 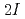 transitions. The application of the
transitions. The application of the 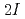 frequencies may be pursued in two different ways; the sequential RF pulse method and the mixed-wave RF pulse method. We confirmed the reversal of polarization for the both methods, from measurements of
frequencies may be pursued in two different ways; the sequential RF pulse method and the mixed-wave RF pulse method. We confirmed the reversal of polarization for the both methods, from measurements of  -ray asymmetry change for polarized
-ray asymmetry change for polarized  B. Using this system, the
B. Using this system, the  moments of
moments of 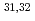 Al have been measured to be
Al have been measured to be 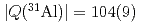
 mb and
mb and 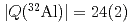
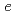
 mb by the sequential RF pulse method.
mb by the sequential RF pulse method.