Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsukuda, Satoshi*; Takahashi, Ryota*; Seki, Shuhei*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tanaka, Shunichiro*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 118, p.16 - 20, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.71(Chemistry, Physical)Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)-Pt nanoparticles (NPs) hybrid nanowires were fabricated by high energy ion beam irradiation to PVP thin films including H PtCl
PtCl . Single ion hitting caused crosslinking reactions of PVP and reduction of Pt ions within local cylindrical area along an ion trajectory (ion track); therefore, the PVP nanowires including Pt NPs were formed and isolated on Si substrate after wet-development procedure. The number of Pt NPs was easily controlled by the mixed ratio of PVP and H
. Single ion hitting caused crosslinking reactions of PVP and reduction of Pt ions within local cylindrical area along an ion trajectory (ion track); therefore, the PVP nanowires including Pt NPs were formed and isolated on Si substrate after wet-development procedure. The number of Pt NPs was easily controlled by the mixed ratio of PVP and H PtCl
PtCl . However, increasing the amount of H
. However, increasing the amount of H PtCl
PtCl led to decreasing the radial size and separation of the hybrid nanowires during the wet-development. Additional electron beam irradiation after ion beam improved separation of the nanowires and controlled radial sizes due to an increase in the density of crosslinking points inner the nanowires.
led to decreasing the radial size and separation of the hybrid nanowires during the wet-development. Additional electron beam irradiation after ion beam improved separation of the nanowires and controlled radial sizes due to an increase in the density of crosslinking points inner the nanowires.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki
IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 22(6), p.3197 - 3206, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:76.71(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The degradation of ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) sheets as a cable insulation material for nuclear power plants (NPP) was studied by accelerated thermal ageing, radiation ageing and thermal - radiation combined ageing. The oxidation of EPR proceeded with ageing and the decay of mechanical property was closely related to the content of oxidation products. The antioxidant as a stabilizer in EPR was effective for the thermal oxidation, but not for the radiation oxidation. For the thermal and radiation combined oxidation, the mechanical property and the content of oxidation products were different among the treatment sequences due to the decay of antioxidant. The lifetime of EPR cable is closely related to the remaining content of antioxidant, and the lifetime evaluation would be recommended by the reverse sequential combination (thermal ageing after radiation ageing).
Takeyama, Akinori; Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies (Internet), 3(4), p.402 - 406, 2015/12
Narisawa, Masaki*; Koka, Masashi; Takeyama, Akinori; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Sato, Takahiro; Hokazono, Hiroki*; Kawai, Taketoshi*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 123(9), p.805 - 808, 2015/09
 -ray irradiated polyethylene with KOH treatment and SEM-EDS
-ray irradiated polyethylene with KOH treatment and SEM-EDSShimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 30, 2015/03
In case of the accelerated ageing test on polymer cable insulation used for the nuclear power facility, it is very important to recognize whether oxygen penetrates in the polymer wholly or not. To confirm this, there are the method by which polymer is soaked in the KOH solution at 70 C for 5 minutes, dried and observed by a SEM-EDS, only for ethylene propylene rubber, one of the polymers. This study is to apply that method for polyethylene. Polyethylene sheet of 2 mm thickness was irradiated by
C for 5 minutes, dried and observed by a SEM-EDS, only for ethylene propylene rubber, one of the polymers. This study is to apply that method for polyethylene. Polyethylene sheet of 2 mm thickness was irradiated by  ray at a dose rate of 2 kGy/h for 400 h. A piece of irradiated polyethylene was picked up and the piece was soaked in the KOH solution for 24 h. After that, the piece was observed by a SEM-EDS. At the region within 70 micro meters from the surface, potassium is observed. It means that oxidation is occurred in this region. From now on, optimum soaking time will be examined.
ray at a dose rate of 2 kGy/h for 400 h. A piece of irradiated polyethylene was picked up and the piece was soaked in the KOH solution for 24 h. After that, the piece was observed by a SEM-EDS. At the region within 70 micro meters from the surface, potassium is observed. It means that oxidation is occurred in this region. From now on, optimum soaking time will be examined.
Omichi, Masaaki*; Asano, Atsushi*; Tsukuda, Satoshi*; Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Saeki, Akinori*; Sakamaki, Daisuke*; Onoda, Akira*; Hayashi, Takashi*; Seki, Shu*
Nature Communications (Internet), 5, p.3718_1 - 3718_8, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:78.11(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Protein nanowires exhibiting specific biological activities hold promise for interacting with living cells and controlling and predicting biological responses such as apoptosis, endocytosis and cell adhesion. Here we report the result of the interaction of a single high-energy charged particle with protein molecules. Degradation of the human serum albumin nanowires was examined using trypsin. The biotinylated human serum albumin nanowires bound avidin, demonstrating the high affinity of the nanowires. Human serum albumin-avidin hybrid nanowires were also fabricated from a solid state mixture and exhibited good mechanical strength. The biotinylated human serum albumin nanowires can be transformed into nanowires exhibiting a biological function such as avidin-biotinyl interactions and peroxidase activity. The present technique is a versatile platform for functionalizing the surface of any protein molecule with an extremely large surface area.
Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Miyashita, Atsumi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 29, 2014/03
Recovery from the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) is a matter of great urgency. In order to realize safe and secure operation for decontamination and decommissioning of NPP, it is indispensable to use equipments with sufficient radiation resistance (RR). In JAEA as well as other agency, various studies on RR of various materials and equipments have been conducted and a number of reports and papers have been published. Then, we started construction of a database named as "Database of Radiation Resistance on Polymer Materials and Equipments" and announced this database in a press release on June 1, 2012. At present, the database includes 878 data of materials, which are consisted of 423 data of polymer materials, 223 data of equipments and parts, 103 data of oils, fats and paintcoatings and 129 data of organic composite materials. The database will be extended and expected to be utilized for safe and secure operation.
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 42, 2014/03
A macroporous SiC material was synthesized from polycarbosilane (PCS) by direct foaming and radiation curing. A mixture of PCS and biurea, a blowing agent, was heat-treated in Ar to obtain foamed PCS body, irradiated by  -rays to fix the shaped body and finally pyrolyzed at 1000
-rays to fix the shaped body and finally pyrolyzed at 1000 C in Ar. In this work, effects of foaming temperature (280-320
C in Ar. In this work, effects of foaming temperature (280-320 C) and biurea content (0-1wt%) on the properties of obtained porous SiC material such as average cell size, porosity, compressive strength were investigated. It was found that the average cell size increased as foaming temperature and/or biurea content increased. Corresponding to increasing in average cell size, total porosity and open porosity increased and bulk density, closed porosity and compressive strength decreased. In case of the foaming at 280
C) and biurea content (0-1wt%) on the properties of obtained porous SiC material such as average cell size, porosity, compressive strength were investigated. It was found that the average cell size increased as foaming temperature and/or biurea content increased. Corresponding to increasing in average cell size, total porosity and open porosity increased and bulk density, closed porosity and compressive strength decreased. In case of the foaming at 280 C with biurea content of 1wt%, obtained porous SiC material showed average cell size of 0.5 mm, total porosity of 74% and compressive strength of 3.2 MPa.
C with biurea content of 1wt%, obtained porous SiC material showed average cell size of 0.5 mm, total porosity of 74% and compressive strength of 3.2 MPa.
Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Seguchi, Tadao*
IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 21(1), p.16 - 23, 2014/02
The thermal and radiation ageing behaviors and degradation mechanisms of SiR for the cable insulation of nuclear power plants were studied. The thermal ageing and radiation ageing in air were conducted up to 235 C and 195
C and 195 C, respectively. The dose rate of radiation ageing is 1 kGy/h. Thermal ageing in vacuum as well as in air was also conducted. The degraded SiR is evaluated by tensile test, gel fraction measurement, swelling ratio measurement and weight measurement, and then the results are analyzed. It is appeared that the radiation degradation of SiR at high temperature is much more severe than that of SiR at low temperature at the same dose. Focusing on the molecular structure, it is supposed that crosslinking reagents which are included in SiR are removed, oxygen atom is attached instead of the reagents and new crosslinking is foamed. Their behaviors are different from the polymer of hydrocarbon.
C, respectively. The dose rate of radiation ageing is 1 kGy/h. Thermal ageing in vacuum as well as in air was also conducted. The degraded SiR is evaluated by tensile test, gel fraction measurement, swelling ratio measurement and weight measurement, and then the results are analyzed. It is appeared that the radiation degradation of SiR at high temperature is much more severe than that of SiR at low temperature at the same dose. Focusing on the molecular structure, it is supposed that crosslinking reagents which are included in SiR are removed, oxygen atom is attached instead of the reagents and new crosslinking is foamed. Their behaviors are different from the polymer of hydrocarbon.
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Innovative Processing and Manufacturing of Advanced Ceramics and Composites II; Ceramic Transactions, Vol.243, p.61 - 69, 2014/01
A macroporous SiC material was synthesized from polycarbosilane (PCS) by direct foaming and radiation curing. A mixture of PCS and biurea, a blowing agent, was heat-treated in Ar to obtain foamed PCS body, irradiated by  -rays to fix the shaped body and finally pyrolyzed at 1000
-rays to fix the shaped body and finally pyrolyzed at 1000 C in Ar. In this work, effects of foaming temperature (280-320
C in Ar. In this work, effects of foaming temperature (280-320 C) and biurea content (0-1wt%) on the properties of obtained porous SiC material such as average cell size, porosity, compressive strength were investigated. It was found that the average cell size increased as foaming temperature and/or biurea content increased. Corresponding to increasing in average cell size, total porosity and open porosity increased and bulk density, closed porosity and compressive strength decreased. In case of the foaming at 280
C) and biurea content (0-1wt%) on the properties of obtained porous SiC material such as average cell size, porosity, compressive strength were investigated. It was found that the average cell size increased as foaming temperature and/or biurea content increased. Corresponding to increasing in average cell size, total porosity and open porosity increased and bulk density, closed porosity and compressive strength decreased. In case of the foaming at 280 C with biurea content of 1wt%, obtained porous SiC material showed average cell size of 0.5 mm, total porosity of 74% and compressive strength of 3.2 MPa.
C with biurea content of 1wt%, obtained porous SiC material showed average cell size of 0.5 mm, total porosity of 74% and compressive strength of 3.2 MPa.
Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Seguchi, Tadao*
IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 20(6), p.2107 - 2116, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.85(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The degradation of cables by the accelerated thermal and radiation ageing for nuclear power plant was studied. The thermal oxidation of crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) as a cable insulation showed the heterogeneous features along the depth of sheet specimens. The degree of oxidation was closely related to the distribution of antioxidant content due to the decay of antioxidant content by the evaporation and radiation decomposition during accelerated ageing. The specific relations were observed between the tensile properties and the yield of oxidation products and also between the oxidation products and antioxidant content in XLPE specimens. The yields and the content and their distribution were detected by FTIR. The oxidation of XLPE containing antioxidant of enough content proceeded proportionally with ageing time or radiation dose at any ageing conditions. When the antioxidant content decreased less than a limited content by thermal and/or radiation ageing, the oxidation rate by thermal ageing increased sharply with ageing time. Therefore, the oxidation at surface of XLPE was much accelerated when the antioxidant decreased to result the heterogeneous oxidation. The mechanical properties depend closely on the degree of oxidation at the surface. The behavior of oxidation was also affected by the types of antioxidant.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Haruyama, Yasuyuki; Sugimoto, Masaki
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 85, p.124 - 129, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.02(Chemistry, Physical)The yields of gas evolution from various types of polyethylene and ethylene-propylene copolymer by radiation were precisely measured after  ray irradiation under vacuum at the wide range of temperatures (-196
ray irradiation under vacuum at the wide range of temperatures (-196  200
200 C). For all polymers the major gas was H
C). For all polymers the major gas was H and the minor products were C
and the minor products were C , C
, C , C
, C hydrocarbons and oxidation compounds as CO
hydrocarbons and oxidation compounds as CO and CO. The total gas yield increased with the increase of irradiation temperature. The yield of total gas increased with irradiation temperature, and the behavior was closely related to the molecular motion of polymer matrix during irradiation.
and CO. The total gas yield increased with the increase of irradiation temperature. The yield of total gas increased with irradiation temperature, and the behavior was closely related to the molecular motion of polymer matrix during irradiation.
Sugimoto, Masaki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Seguchi, Tadao*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 82, p.69 - 73, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:97.76(Chemistry, Physical)The oxidation products formed by thermal and radiation ageing of crosslinked polyethylene for cable insulation were analyzed by FTIR-ATR spectrometry. The most of products were composed of carboxylic acid, carboxylic ester, and carboxylic anhydride. The carboxylic acid was the primal product, and the others were the secondary products by the thermal reaction of carboxylic acids. The carboxylic acid as the primal oxidation product supports the proposed new oxidation mechanisms that the main chain scission should occur directly by oxidation of polyethylene radicals.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Watashi, Katsumi; Suzuki, Masahide; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Oshima, Takeshi; Kudo, Hisaaki*
JAEA-Research 2012-029, 158 Pages, 2012/12
The degradation mechanisms of ethylene-propylene rubber (EPR), crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE), polyvinylchloride (PVC), and silicone rubber (SiR) as the cable insulation materials were investigated for the cable ageing research of the nuclear power plant. The materials as same insulations for the practical cable (practical formulation) and as the model formulation containing specific additive were selected. They were exposed to the accelerated radiation and thermal environments. The mechanical properties, the crosslinking and chain scission, and the distribution of antioxidant and of oxidative products were measured and analyzed.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kudo, Hisaaki*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 81(11), p.1747 - 1751, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:94.85(Chemistry, Physical)The mechanism of polymer oxidation by radiation and thermal ageing was investigated for the life evaluation of cables installed in radiation environments. The antioxidant as a stabilizer was much effective for thermal oxidation with a small content in polymers, but was not effective for radiation oxidation. The ionizing radiation induced the oxidation to result chain scission even at low temperature, because the free radicals were produced and the antioxidant could not stop the oxidation of radicals with the chain scission. A new mechanism of antioxidant effect for polymer oxidation was proposed. The effect of antioxidant was not the termination of free radicals in polymer chains such as peroxy radicals, but was the depression of initial radical formation in polymer chains by thermal activation. The antioxidant molecule was assumed to delocalize the activated energy in polymer chains by Boltzmann statics (distribution) to result decrease the probability of radical formation at a given temperature. The interaction distance (delocalization area) by one antioxidant molecule was estimated to be 5-10 nm in polymer matrix, though the value would depend on the chemical structure of antioxidant.
Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Seguchi, Tadao*
IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 19(5), p.1768 - 1773, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:59.03(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The life of cables installed in nuclear power plant was evaluated by the accelerated ageing tests of thermal and radiation degradation. For radiation degradation, the dose rate was the important points, because the oxidation distribution in the insulation was much affected by dose rate due to oxygen penetration limitation during irradiation. The oxidation distribution was observed by FTIR for crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) and ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) of cable insulation degraded at various irradiation conditions and compared with the mechanical degradation. The oxidation profile was almost same between a low dose rate at room temperature and a high dose rate at elevated temperature (100  C), and the degradation was same for both irradiations. By increasing the irradiation temperature the oxygen penetration rate increased exponentially and the thermal degradation during irradiation was negligible at around 100
C), and the degradation was same for both irradiations. By increasing the irradiation temperature the oxygen penetration rate increased exponentially and the thermal degradation during irradiation was negligible at around 100  C. Therefore, the dose rate could be increased by 15 times by irradiation at 100
C. Therefore, the dose rate could be increased by 15 times by irradiation at 100  C instead of the irradiation at room temperature for the adequate oxidation throughout insulation. The experimental result was coincident with the theoretical analysis.
C instead of the irradiation at room temperature for the adequate oxidation throughout insulation. The experimental result was coincident with the theoretical analysis.
Omichi, Masaaki*; Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Sato, Takahiro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Okubo, Takeru; Koka, Masashi; Kada, Wataru; Sugimoto, Masaki; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 12, p.7401 - 7404, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.57(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Oshima, Takeshi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2012-027, 46 Pages, 2012/08
The research on cable degradation mechanisms was conducted for 5 years in 2006 - 2010 as the project research of plant life management for nuclear power plant by NISA (Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency) of METI (Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry). At the finish of above research, the degradation mechanisms were reviewed on the analysis of many reports on cable degradation. The reports published after 1970 were mainly surveyed and the facts or data containing the experimental accuracy were selected. The verified facts, the reasonable interpretation of the facts, unresolved aspects were checked on the view points of recent techniques or analysis, and proposed the new model of degradation mechanisms was proposed.
Maeyoshi, Yuta*; Saeki, Akinori*; Suwa, Shotaro*; Omichi, Masaaki*; Marui, Hiromi*; Asano, Atsushi*; Tsukuda, Satoshi*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kishimura, Akihiro*; Kataoka, Kazunori*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 2, p.600_1 - 600_6, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:72.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The development of organic semiconducting nanowires that act as charge carrier transport pathways in flexible and lightweight nano-electronics is a major scientific challenge. We report on the fabrication of fullerene nanowires that is universally applicable to its derivatives (pristine C , methanofullerenes of C
, methanofullerenes of C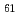 and C
and C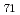 , and indene C
, and indene C bis-adduct). Nanowires with radii of 8
bis-adduct). Nanowires with radii of 8 11 nm were formed via a chain polymerization reaction induced by a high-energy ion beam. Fabrication of a poly(3-hexylthiophene): [6,6]-phenyl C
11 nm were formed via a chain polymerization reaction induced by a high-energy ion beam. Fabrication of a poly(3-hexylthiophene): [6,6]-phenyl C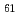 butyric acid methyl ester (PC
butyric acid methyl ester (PC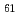 BM) bulk heterojunction organic photovoltaic cell including PC
BM) bulk heterojunction organic photovoltaic cell including PC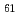 BM nanowires with precisely-controlled length and density demonstrates how application of this methodology can improve the power conversion efficiency of these inverted cells.
BM nanowires with precisely-controlled length and density demonstrates how application of this methodology can improve the power conversion efficiency of these inverted cells.
Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Asano, Atsushi*; Maeyoshi, Yuta*; Marui, Hiromi*; Omichi, Masaaki*; Saeki, Akinori*; Seki, Shu*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; et al.
Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 25(1), p.43 - 46, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.57(Polymer Science)