Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Islam, M. A.*; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Toh, Yosuke; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Harada, Hideo
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 70(8), p.1531 - 1535, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.14(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In this study, the MPGA system was characterized for nondestructive multi-element analysis of geological and cosmochemical samples. Among the three offline sorting modes of coincidence data in MPGA, the add-back mode resulted in relatively high analytical sensitivity and the lowest detection limit. The system is highly sensitive to Sm, Gd and Cd. When MPGA detection limits of the studied elements were compared with other cold neutron facilities, MPGA detection limits for Mg, K, S and Cl were improved around one order of magnitude than other facilities under the present experimental conditions, which consists of 8 Clover and BGO detectors. Analysis of the meteorite Orgueil by both MPGA and PGA imply that MPGA can be used for elemental analysis with sufficient accuracy. For some elements (such as Sm, K and Mg) which can Gnot be determined by conventional PGA, due to the spectral interference or lower sensitivity, it was observed that they could be determined accurately (3%) by MPGA.
 Ni via cold neutron capture reaction, 1; Nuclear structure of
Ni via cold neutron capture reaction, 1; Nuclear structure of  Ni
NiOshima, Masumi; Kin, Tadahiro*; Nakamura, Shoji; Homma, Michio*; Minato, Futoshi; Hayakawa, Takehito; Hara, Kaoru; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Harada, Hideo; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(8), p.084201_1 - 084201_15, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The  -radiation has been investigated produced by cold neutron capture in an enriched
-radiation has been investigated produced by cold neutron capture in an enriched  Ni sample. The 315
Ni sample. The 315  -rays have been placed in the
-rays have been placed in the  Ni level scheme of which 272 placements are new. We have determined excitation energies with 0.2-0.8 keV error and branching ratios of 62 bound levels in
Ni level scheme of which 272 placements are new. We have determined excitation energies with 0.2-0.8 keV error and branching ratios of 62 bound levels in  Ni, including 30 new levels. The Q-value of the
Ni, including 30 new levels. The Q-value of the  Ni (n,
Ni (n, )
)  Ni reaction amounts to 6837.75 (18) keV. A large-scale shell-model calculation has been performed and the energies of the low-lying
Ni reaction amounts to 6837.75 (18) keV. A large-scale shell-model calculation has been performed and the energies of the low-lying  Ni states are successfully reproduced. A mean-field statistical model calculation has been also made by using a self-consistent interaction between the Hartree-Fock + BCS method and the statistical calculation. The calculation result is consistent with the experimental level density of
Ni states are successfully reproduced. A mean-field statistical model calculation has been also made by using a self-consistent interaction between the Hartree-Fock + BCS method and the statistical calculation. The calculation result is consistent with the experimental level density of  Ni.
Ni.
 -ray analysis
-ray analysisToh, Yosuke; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Hara, Kaoru; Kin, Tadahiro; Nakamura, Shoji; Harada, Hideo
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 70(6), p.984 - 987, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.96(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)By applying the multiple  -ray detection method to prompt
-ray detection method to prompt  -ray analysis, called MPGA (multiple prompt
-ray analysis, called MPGA (multiple prompt  -ray analysis), the interference from hydrogen contained in a sample can be reduced. Therefore, this method can improve the signal-to-noise ratio, and provide a rapid screening method of toxic elements. We developed a neutron beam line and a detector system for MPGA, which consists of eight Clover Ge detectors, was constructed at the cold neutron guide C2-3-2 of JRR-3. Protein is an important nutrient in foods. The classical total protein analysis method is the Kjeldahl technique, which is time-consuming and inconvenient. As a convenient method to quantify total protein content in biological samples, the feasibility of application of MPGA to the quantification was studied. The results obtained with reference materials are in good agreement with the certified value. MPGA provides a tool for the rapid and non-destructive quantification of total protein content.
-ray analysis), the interference from hydrogen contained in a sample can be reduced. Therefore, this method can improve the signal-to-noise ratio, and provide a rapid screening method of toxic elements. We developed a neutron beam line and a detector system for MPGA, which consists of eight Clover Ge detectors, was constructed at the cold neutron guide C2-3-2 of JRR-3. Protein is an important nutrient in foods. The classical total protein analysis method is the Kjeldahl technique, which is time-consuming and inconvenient. As a convenient method to quantify total protein content in biological samples, the feasibility of application of MPGA to the quantification was studied. The results obtained with reference materials are in good agreement with the certified value. MPGA provides a tool for the rapid and non-destructive quantification of total protein content.
 -ray analysis
-ray analysisShozugawa, Katsumi*; Matsuo, Motoyuki*; Sano, Yuji*; Toh, Yosuke; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kimura, Atsushi; Hara, Kaoru; Kin, Tadahiro; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 291(2), p.341 - 346, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.98(Chemistry, Analytical)Multiple prompt  -ray analysis (MPGA), a new quantification method with high energy resolution, was applied to sediments from a marine shallow-water hydrothermal mound. Surface sediments around mounds were collected from the Wakamiko submarine crater located in Kagoshima Bay, southwest Japan, where the hydrothermal system was different from those at other marine shallow-water hydrothermal mounds. All samples were desalted and MPGA measurements were performed for 4,500 s (real time). Event data were obtained using eight CLOVER Ge detectors. We could obtain concentrations of
-ray analysis (MPGA), a new quantification method with high energy resolution, was applied to sediments from a marine shallow-water hydrothermal mound. Surface sediments around mounds were collected from the Wakamiko submarine crater located in Kagoshima Bay, southwest Japan, where the hydrothermal system was different from those at other marine shallow-water hydrothermal mounds. All samples were desalted and MPGA measurements were performed for 4,500 s (real time). Event data were obtained using eight CLOVER Ge detectors. We could obtain concentrations of  S,
S,  Mn,
Mn,  As,
As,  Gd,
Gd, 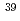 K,
K,  Sm,
Sm,  Fe, and
Fe, and  Rb with high sensitivity by MPGA. Furthermore,
Rb with high sensitivity by MPGA. Furthermore,  S,
S,  Rb, and
Rb, and  Mn have characteristic concentrations only at a mound, suggesting that sediments were sulfated by magmatic fluids at this mound.
Mn have characteristic concentrations only at a mound, suggesting that sediments were sulfated by magmatic fluids at this mound.
 -ray analysis (MPGA) to geochemical and cosmochemical samples
-ray analysis (MPGA) to geochemical and cosmochemical samplesOura, Yasuji*; Watanabe, Ryo*; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Oshima, Masumi; Hara, Kaoru; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 291(2), p.335 - 339, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.96(Chemistry, Analytical)We applied multiple prompt  -ray analysis (MPGA) method to geochemical and cosmochemical samples to evaluate its analytical performance on signal to noise (S/N) ratio, sensitivity, and detection limit. The S/N ratio measured by MPGA system was larger than that by normal prompt
-ray analysis (MPGA) method to geochemical and cosmochemical samples to evaluate its analytical performance on signal to noise (S/N) ratio, sensitivity, and detection limit. The S/N ratio measured by MPGA system was larger than that by normal prompt  ray activation analysis (PGAA) at JRR3. For some elements, the S/N ratio was improved more than ten times. Several elements that are not detected by PGAA were detected by MPGA. In the present experiment, concentrations of major elements and trace elements with high neutron capture cross section in geochemical and cosmochemical samples were determined accurately by the MPGA system. It is expected that it will determine a lot of trace elements after appropriate adjustments and modifications.
ray activation analysis (PGAA) at JRR3. For some elements, the S/N ratio was improved more than ten times. Several elements that are not detected by PGAA were detected by MPGA. In the present experiment, concentrations of major elements and trace elements with high neutron capture cross section in geochemical and cosmochemical samples were determined accurately by the MPGA system. It is expected that it will determine a lot of trace elements after appropriate adjustments and modifications.
 -ray detection
-ray detectionOshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Murakami, Yukihiro*
Bunseki, 2009(7), p.362 - 368, 2009/07
We have developed the multiple  -ray detection method which provide a tool for high-resolution and high-sensitivity elemental quantification. By applying this method to neutron activation analysis (NAA) and prompt
-ray detection method which provide a tool for high-resolution and high-sensitivity elemental quantification. By applying this method to neutron activation analysis (NAA) and prompt  -ray analysis (PGA) we have succeeded in the improvement of these analysis methods. We will review the principle of the multiple
-ray analysis (PGA) we have succeeded in the improvement of these analysis methods. We will review the principle of the multiple  -ray detection method, experimental apparatuses for NAA and MPGA and expected performances in those analyses.
-ray detection method, experimental apparatuses for NAA and MPGA and expected performances in those analyses.
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Oshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Kin, Tadahiro; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Ando, Shingo*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 80(1), p.016102_1 - 016102_3, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.53(Instruments & Instrumentation)In order to reduce time and effort of the daily task of refilling Dewar vessels of Ge detectors with LN , we have developed an automatic LN
, we have developed an automatic LN filling system equipped with an LN
filling system equipped with an LN plant. With the system, our multiple Ge detector system became almost maintenance free. Such an LN
plant. With the system, our multiple Ge detector system became almost maintenance free. Such an LN filling system is useful for moderate-scale Ge detector arrays consisting of less than 20 Ge detectors.
filling system is useful for moderate-scale Ge detector arrays consisting of less than 20 Ge detectors.
 -
- coincidence method to instrumental neutron activation analysis and prompt
coincidence method to instrumental neutron activation analysis and prompt  -ray analysis
-ray analysisOshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kin, Tadahiro; Kimura, Atsushi; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Goto, Jun*
Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Applications of Nuclear Techniques (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/06
The  -
- coincidence techniques developed for nuclear structure study has proved to be useful for nuclear quantification. The applications to Neutron Activation Analysis and Prompt
coincidence techniques developed for nuclear structure study has proved to be useful for nuclear quantification. The applications to Neutron Activation Analysis and Prompt  -ray Analysis are presented.
-ray Analysis are presented.
 -ray detector array for multiple prompt
-ray detector array for multiple prompt  -ray analysis
-ray analysisOshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kin, Tadahiro; Kimura, Atsushi; Goto, Jun*
no journal, ,
Prompt  -ray analysis (PGA) is a versatile element quantification method with non-destructive, rapid, high-precision and multi-element determination. PGA usually utilizes a single detector to measure
-ray analysis (PGA) is a versatile element quantification method with non-destructive, rapid, high-precision and multi-element determination. PGA usually utilizes a single detector to measure  -rays depopulating a neutron-captured state. Since the number of
-rays depopulating a neutron-captured state. Since the number of  -rays from the sample with multiple elements often exceeds one thousand, the energy resolution is not sufficient and it is impossible to resolve all the
-rays from the sample with multiple elements often exceeds one thousand, the energy resolution is not sufficient and it is impossible to resolve all the  rays. To meet this situation, we try to apply the
rays. To meet this situation, we try to apply the  -ray coincidence measurement method to PGA (Multiple Prompt
-ray coincidence measurement method to PGA (Multiple Prompt  -ray Analysis, MPGA). We have constructed a new
-ray Analysis, MPGA). We have constructed a new  -ray detector array for MPGA at a cold neutron beam line in Japan Research Reactor, JRR-3M, at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). It is one of the most efficient
-ray detector array for MPGA at a cold neutron beam line in Japan Research Reactor, JRR-3M, at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). It is one of the most efficient  -ray detector array composed of high resolution Ge detectors at present. A new analysis method of triple
-ray detector array composed of high resolution Ge detectors at present. A new analysis method of triple  coincidence has been attempted together with the present double
coincidence has been attempted together with the present double  coincidence. The results of Ir concentration in rock samples in NAA and also of Cd concentration in foods in MPGA will be presented at the conference.
coincidence. The results of Ir concentration in rock samples in NAA and also of Cd concentration in foods in MPGA will be presented at the conference.
 -ray
-rayToh, Yosuke; Oshima, Masumi; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray analysis
-ray analysisOshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Toh, Yosuke; Oshima, Masumi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kimura, Atsushi; Murakami, Yukihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray apparatus
-ray apparatusOshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo
no journal, ,
To achieve the new trace element analysis method of Multiple Prompt  -ray Analysis (MPGA) we have completed the construction of the MPGA apparatus, STELLA, at C2-3-2 beam line at the neutron guide hall in JAEA Research Reactor, JRR-3. The MPGA system made of twelve Ge detectors has been completed. A fast data acquisition system for this system has been developed. An automatic liquid nitrogen supply system for Ge detectors and an automatic sample changer enable the automatic measurement. Furthermore, rapid
-ray Analysis (MPGA) we have completed the construction of the MPGA apparatus, STELLA, at C2-3-2 beam line at the neutron guide hall in JAEA Research Reactor, JRR-3. The MPGA system made of twelve Ge detectors has been completed. A fast data acquisition system for this system has been developed. An automatic liquid nitrogen supply system for Ge detectors and an automatic sample changer enable the automatic measurement. Furthermore, rapid  -ray energy calibration and on-line quantification software is developed as well as necessary
-ray energy calibration and on-line quantification software is developed as well as necessary  -ray database for them. In July 2008, we have started the application of STELLA to MPGA based on the Interorganization Atomic Energy Research program by University of Tokyo, Toray Research Center and JAEA. In the talk we present the performance and status of STELLA as well as those of the apparatus at the new facility of J-PARC MLF.
-ray database for them. In July 2008, we have started the application of STELLA to MPGA based on the Interorganization Atomic Energy Research program by University of Tokyo, Toray Research Center and JAEA. In the talk we present the performance and status of STELLA as well as those of the apparatus at the new facility of J-PARC MLF.
 -rays
-raysOshima, Masumi; Kin, Tadahiro; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Murakami, Yukihiro*
no journal, ,
To derive neutron capture cross sections we are developing the ground state transition method, which is a kind of the prompt  -ray detection method. At the first step a level construction method has been developed. Based on the analysis with this method highly excited levels of Ni-63 have been newly assigned. By measuring the prompt
-ray detection method. At the first step a level construction method has been developed. Based on the analysis with this method highly excited levels of Ni-63 have been newly assigned. By measuring the prompt  -rays of Ni-63 at JAEA research reactor, JRR-3, we derived the thermal neutron capture cross section of Ni-62, which is in accordance with the previously known value.
-rays of Ni-63 at JAEA research reactor, JRR-3, we derived the thermal neutron capture cross section of Ni-62, which is in accordance with the previously known value.
Oshima, Masumi; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Toh, Yosuke
no journal, ,
So far we have demonstrated that the  -ray coincidence method (the multiple
-ray coincidence method (the multiple  -ray detection method) is a versatile method to achieve high resolution and high signal-to-noize ratio in nuclide determination. To extend this method we propose the X-ray coincidence method (the multiple X-ray detection method). We present a result of this method by using two low energy photon spectrometers and a standard
-ray detection method) is a versatile method to achieve high resolution and high signal-to-noize ratio in nuclide determination. To extend this method we propose the X-ray coincidence method (the multiple X-ray detection method). We present a result of this method by using two low energy photon spectrometers and a standard  -ray source of
-ray source of 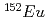 for activation of atoms. We could observe a peak in two dimensional X-ray matrix, which originates from coincidence of K-X and L-X rays. We demonstrated that background is reduced on the matrix.
for activation of atoms. We could observe a peak in two dimensional X-ray matrix, which originates from coincidence of K-X and L-X rays. We demonstrated that background is reduced on the matrix.
 ray analysis (MPGA) to geochemical and cosmochemical samples
ray analysis (MPGA) to geochemical and cosmochemical samplesWatanabe, Ryo*; Oura, Yasuji*; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Oshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Murakami, Yukihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 coincidence in prompt
coincidence in prompt  -ray analysis and neutron activation analysis
-ray analysis and neutron activation analysisOshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kin, Tadahiro; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi
no journal, ,
Prompt  -ray analysis (PGA) is a versatile element quantification method with non-destructive, rapid, high-precision and multi-element determination. In actual application, however, the energy resolution of commercial Ge detectors is not sufficient and it is impossible to resolve all the
-ray analysis (PGA) is a versatile element quantification method with non-destructive, rapid, high-precision and multi-element determination. In actual application, however, the energy resolution of commercial Ge detectors is not sufficient and it is impossible to resolve all the  -rays, since the number of
-rays, since the number of  -rays from the sample with multiple elements often exceeds one thousand. In a similar situation in Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA), we have applied a
-rays from the sample with multiple elements often exceeds one thousand. In a similar situation in Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA), we have applied a  -ray coincidence method (multiple
-ray coincidence method (multiple  -ray detection method), and developed a new method of NAA coupled with Multiple
-ray detection method), and developed a new method of NAA coupled with Multiple  -ray detection (NAAMG). Its high sensitivity is demonstrated in nuclide quantification. We apply the multiple
-ray detection (NAAMG). Its high sensitivity is demonstrated in nuclide quantification. We apply the multiple  -ray detection method to prompt
-ray detection method to prompt  -ray analysis (Multiple Prompt
-ray analysis (Multiple Prompt  -ray Analysis, MPGA) by using a new
-ray Analysis, MPGA) by using a new  -ray detector array at a cold neutron beam line in Japan Research Reactor, JRR-3, at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In MPGA analysis we have used so far the
-ray detector array at a cold neutron beam line in Japan Research Reactor, JRR-3, at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In MPGA analysis we have used so far the  -ray double coincidence measurement. We firstly try to apply a triple coincidence measurement. The present detector system can afford the double and triple coincidence measurement as well as the singles measurement in PGA and NAA. In the presentation we compare the detection limits for those measurements. Based on the results we demonstrated that the triple
-ray double coincidence measurement. We firstly try to apply a triple coincidence measurement. The present detector system can afford the double and triple coincidence measurement as well as the singles measurement in PGA and NAA. In the presentation we compare the detection limits for those measurements. Based on the results we demonstrated that the triple  coincidence is effective in some applications such as Ir concentration in rock samples. We also discuss results of applications to environmental samples.
coincidence is effective in some applications such as Ir concentration in rock samples. We also discuss results of applications to environmental samples.
 -ray detection method
-ray detection methodOshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kin, Tadahiro; Hara, Kaoru; Kimura, Atsushi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Sushida, Kazuyoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A new trace element analysis method is proposed on the basis of multiple  -ray detection, which is two or higher fold
-ray detection, which is two or higher fold  -ray coincidence method. We apply this method for prompt
-ray coincidence method. We apply this method for prompt  -ray activation analysis (PGAA) and instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA). The advantage of the methods consists of high energy resolution and high sensitivity. The principle of the multiple
-ray activation analysis (PGAA) and instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA). The advantage of the methods consists of high energy resolution and high sensitivity. The principle of the multiple  -ray detection method and actual applications to cosmological chemistry, earth chemistry, environmental chemistry, etc, will be presented.
-ray detection method and actual applications to cosmological chemistry, earth chemistry, environmental chemistry, etc, will be presented.
Toh, Yosuke; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hara, Kaoru; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; Kin, Tadahiro; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Nakamura, Shoji; Oshima, Masumi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray spectrometer: STELLA
-ray spectrometer: STELLAOshima, Masumi; Kin, Tadahiro; Hara, Kaoru; Nakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Minato, Futoshi; Harada, Hideo; Homma, Michio*; Goto, Jun*; et al.
no journal, ,
Prompt  -rays from the neutron capture reaction of Ni-62 have been measured by using the multiple prompt
-rays from the neutron capture reaction of Ni-62 have been measured by using the multiple prompt  -ray spectrometer, STELLA, installed at the Research Reactor, JRR-3, of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. A highly-excited level structure below the neutron separation energy of 6838 keV in Ni-63 has been reported, including 35 new levels and 272 new
-ray spectrometer, STELLA, installed at the Research Reactor, JRR-3, of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. A highly-excited level structure below the neutron separation energy of 6838 keV in Ni-63 has been reported, including 35 new levels and 272 new  -ray transitions. The experimentally observed level structure is compared and discussed with a shell model calculation and a Mean-field statistical model calculation.
-ray transitions. The experimentally observed level structure is compared and discussed with a shell model calculation and a Mean-field statistical model calculation.