Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Doda, Norihiro; Igawa, Kenichi*; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Murakami, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 410, p.112377_1 - 112377_15, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)To enhance the safety of sodium-cooled fast reactors, the decay heat in the core must be removed by natural circulation even if the AC power supply to the forced circulation equipment is lost. Under natural circulation conditions, sodium flow is driven by buoyancy, and flow velocity and temperature distribution influence each other. Thus, it is difficult to evaluate the core hot spot temperature by deterministically considering the uncertainties affecting flow and heat. In this study, a statistical evaluation method is developed for the core hot spot temperature by using Monte Carlo sampling methods. The applicability of the core hotspot evaluation method was confirmed in three representative events during natural circulation decay heat removal operations in loop-type sodium-cooled fast reactors.
Doda, Norihiro; Nakamine, Yoshiaki*; Igawa, Kenichi*; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Murakami, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 6 Pages, 2022/06
As a part of the development of the "Advanced Reactor Knowledge- and AI-aided Design Integration Approach through the whole plant lifecycle (ARKADIA)" to automatically optimize the life cycle of innovative nuclear reactors including fast reactors, ARKADIA-design is being developed to support the optimization of fast reactor design in the conceptual stage. ARKADIA-Design consists of three systems (Virtual plant Life System (VLS), Evaluation assistance and Application System (EAS), and Knowledge Management System (KMS)). A design optimization framework controls the cooperation between the three systems through the interfaces in each system. This paper reports on the development status of the "VLS interface," which has a control function of coupling analysis codes in VLS.
Yoshimura, Kazuo; Doda, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Murakami, Satoshi*; Vilim, R. B.*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 16 Pages, 2022/03
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency, the multilevel simulation system which enables consistent evaluation from the whole plant behavior to the local phenomena is being developed to optimize plant design and enhance the safety of sodium-cooled fast reactors. To validate the coupling method in the MLS system, the 1D-CFD coupling method using Super-COPD for 1D plant dynamics analysis and Fluent for multi-dimensional CFD analysis was applied to the analyses of loss of flow tests in EBR-II. It was confirmed that it could predict multi-dimensional thermal-hydraulic phenomena such as thermal stratification in the upper plenum, Z-shaped pipe, and cold pool, holding the whole plant behavior simultaneously. Moreover, the applicability of the 1D-CFD coupling method to the evaluation of the phenomena in natural circulation conditions was confirmed by comparing the results of the 1D-CFD couple analyses and the measured data.
 SO
SO and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)
and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Komori, Yukiko*; Murakami, Masashi; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Daisuke*; Asai, Masato; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 317(1), p.421 - 430, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.93(Chemistry, Analytical)We have studied extraction behavior of group-6 elements Mo and W to search for suitable conditions for an on-line extraction experiment of their heavier homolog, seaborgium (Sg). Batch-wise extraction of carrier-free radiotracers  Mo and
Mo and 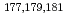 W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H
W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H SO
SO and 1.0
and 1.0 10
10 - 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H
- 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H SO
SO solutions with concentrations of [H
solutions with concentrations of [H SO
SO ]
]  2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Murakami, Satoshi*
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/07
Thermal striping on the core instrumentation plate (CIP) around the primary control rod (PCR) and backup control rod (BCR) channels and the radial blanket fuel assemblies (RBAs) may be caused. Since the interaction between neighbor areas exists in the UIS and the cold sodium flowing from the RBA is affected by the external flow around the UIS, a spatial connection method consisting of the numerical model for the whole upper plenum and the local target area has been developed. The numerical results were compared with the experimental results to confirm applicability of the method to the practical problem. And, sensitivity of mesh arrangement to the numerical results was discussed by using wide and narrow area models with two different spatial resolutions in each model. Through the examinations, appropriate local model for the spatial connection mothed could be proposed.
Eichler, R.*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Chiera, N. M.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Dressler, R.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.07005_1 - 07005_7, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:72.98(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In recent years gas-phase chemical studies assisted by physical pre-separation allowed for the productions and investigations of fragile single molecular species of superheavy elements. The latest highlight is the formation of very volatile hexacarbonyl compound of element 106, Sg(CO) . Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO)
. Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO) , W(CO)
, W(CO) , and Sg(CO)
, and Sg(CO) .
.
 and W(CO)
and W(CO)
Usoltsev, I.*; Eichler, R.*; Wang, Y.*; Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 104(3), p.141 - 151, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:95.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Conditions of the production and decomposition of hexacarbonyl complexes of short-lived Mo and W isotopes were investigated to study thermal stability of the heaviest group 6 hexacarbonyl complex Sg(CO) . A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO)
. A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO) and W(CO)
and W(CO) , indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO)
, indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO) could be determined with this technique.
could be determined with this technique.
Even, J.*; Ackermann, D.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(3), p.2457 - 2466, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.56(Chemistry, Analytical)Rapid In situ synthesis of metal carbonyl complexes has been demonstrated using short-lived isotopes produced in nuclear fission and fusion reactions. The short-lived isotopes with high recoil energy directly react with carbon-monoxides and form carbonyl complexes. Only highly volatile complexes were fast transported in a gas stream to counting and chemistry devices. Short-lived Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, W, Re, Os, and Ir were found to form volatile carbonyl complexes, while no volataile complex of Hf and Ta were detected. This technique has been applied to a chemical investigation of the superheavy element Sg (atomic number 106), and will be applicable to various fields of nuclear science with short-lived transition metal isotopes.
Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F. L.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F. L.*; et al.
Science, 345(6203), p.1491 - 1493, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:83.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A new superheavy element complex, a seaborgium carbonyl, has been successfully synthesized, and its adsorption property has been studied using a cryo-thermochromatography and  -detection apparatus COMPACT. Nuclear reaction products of short-lived
-detection apparatus COMPACT. Nuclear reaction products of short-lived  Sg preseparated with a gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS at RIKEN were directly injected into a gas cell filled with He/CO mixture gas, and chemical reaction products of volatile carbonyl complexes were trasported to COMPACT. The Sg carbonyl complex detected with COMPACT was found to be very volatile with adsorption enthalpy of
Sg preseparated with a gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS at RIKEN were directly injected into a gas cell filled with He/CO mixture gas, and chemical reaction products of volatile carbonyl complexes were trasported to COMPACT. The Sg carbonyl complex detected with COMPACT was found to be very volatile with adsorption enthalpy of  50 kJ/mol, from which we have concluded that this complex should be a Sg hexacarbonyl Sg(CO)
50 kJ/mol, from which we have concluded that this complex should be a Sg hexacarbonyl Sg(CO) . This is the first synthesis of organometallic compounds of transactinide elements for which only simple inorganic comounds have been synthesized so far.
. This is the first synthesis of organometallic compounds of transactinide elements for which only simple inorganic comounds have been synthesized so far.
 SO
SO /HNO
/HNO mixed solution
mixed solutionLi, Z.*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Sato, Nozomi; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Pershina, V.*; et al.
del, M.; Pershina, V.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 100(3), p.157 - 164, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Tanaka, Masaaki; Murakami, Satoshi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of ASME-JSME-KSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference 2011 (AJK 2011-FED) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2011/07
Authors have been developed a numerical simulation code MUGTHES by using the LES to investigate thermal striping phenomena in FBRs. In this paper, numerical simulations by the MUGTHES in T-junction piping system appear. The boundary conditions are chosen from an existing water experiment in JAEA. Numerical results are validated by comparisons with measured velocity and temperature profiles. Through the numerical simulations, generation mechanism of temperature fluctuation in thermal mixing process is revealed in the relation with the large-scale eddy motion.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Murakami, Satoshi*; Oki, Hiroshi*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of Joint International Conference of 7th Supercomputing in Nuclear Application and 3rd Monte Carlo (SNA + MC 2010) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2010/10
Strategy of the numerical estimation method development for the thermal fatigue in JSFR at JAEA is explained from the numerical simulation code development step to the application step for practical problems. Numerical simulation codes prepared for the study and outlines of the verification and validation study are briefly described. Numerical results in a T-junction piping system and typical numerical results around typical control rod channels and the blanket fuel subassemblies simulating the JSFR are shown as examples in recent progress.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Murakami, Satoshi*
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2009/09
This paper deals with numerical simulations focusing on several areas around typical CR channels in order to reveal thermal mixing phenomena and to confirm effect of mitigation measures to the thermal striping phenomena around the CR channel. By the numerical simulation, generation mechanism of influential temperature fluctuation on the CIP integrity is revealed and effect of mitigation measure based on the mixing mechanism is confirmed.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Murakami, Satoshi; Hibara, Hideki*; Sudo, Kozo*
Proceedings of International Conference on Jets, Wakes and Separated Flows (ICJWSF 2005), p.623 - 627, 2005/10
Numerical simulation to investigate the mixing characteristics in T-junction pipe with turbulence promoter was conducted. T-junction piping system is used to mix the fluids in different temperature. If the temperature fluctuation generated in the mixing process is transmitted to the structure, it can be bring thermal fatigue in the structure. Therefore,
Senda, Mamoru*; Inaoka, Kyoji*; Yoshimura, Shinya*; Muramatsu, Toshiharu; Murakami, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Masaaki
JNC TY9400 2005-003, 66 Pages, 2004/12
Heat transfer experiments have been carried out in order to clarify the effect of the low-frequency fluid temperature fluctuation on the unsteady heat transfer in a channel, which is related to the thermal striping phenomena. In this study, fluid temperature fluctuation was realized by the periodic large-scale shedding vortices in the channel with a rectangular cylinder, where the hot and cold water flows into the test section from the lower and upper parts of the contraction. The frequency of fluid temperature fluctuation was controlled by changing the width-to-height ratio of the cylinder. The unsteady heat transfer coefficient of the channel wall was measured by the thin-film heat flux sensor. The experiments were made for the Reynolds number of 9000 and the Strouhal numbers ranging from about 0.16 to about 0.2. It is found that the time averaged Nusselt numbers in the fluid temperature fluctuation field are almost equal to those of the constant fluid temperature regardless of the Strouhal number under the present experimental conditions.And numerical simulation was carried out for typical experiment condition. By the numerical simulation, dominant frequency of Nusselt number fluctuation and fluid temperature fluctuation showed good agreement between experiment and calculation.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Murakami, Satoshi*; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
JNC TN9400 2004-032, 50 Pages, 2004/06
It is important to evaluate thermal-striping phenomena, which the thermal-fatigue inside the structure material is generated by the temperature fluctuation due to the fluid mixing with different temperature. Especially, the high amplitude and the high number of repetitions of the temperature fluctuation are needed to take into consideration. Moreover, it is necessary to consider the comparatively low frequency components of fluid temperature fluctuation, since the influence to structure material is large. Therefore, it is required to know the generating mechanism and conditions of the high amplitude and the low frequency component of fluid temperature fluctuation. In Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute, basic research on the promote system for fluid mixing is conducted, which system ("Turbulence promoter") is expected to reduce the large amplitude and low frequency components of fluid temperature fluctuation in T-junction pipe. In this investigation, it is aimed to validate the effect and to generalize the mixing characteristics of "Turbulence promoter" on the fluid mixing in T-junction pipe, and to contribute the knowledge to the rational design of LMFBR. In this report, numerical simulation for the existing experiment was conducted using a quasi-direct simulation code (DINUS-3).
Murakami, Satoshi*; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
JNC TN9400 2003-038, 59 Pages, 2003/05
A large-scale sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor in feasibility studies on commercialized fast reactors which has a tendency of cosideration of thorough simplified and compacted system is being investigated, however special attention should be paid to thermohydraulic designs for a gas entrainment behavior from free surfaces, a flow-induced vibration of in-vessel components, a thermal shock for various structures due to to high-speed coolant flows, nonsymmetrical coolant flows, etc. in the reactor vessel. As thus a lot of thermal-hydraulic issues relate to each other complicatedly on the reactor designs, multiple-criteria decision-making on the understanding of relationship among thermal-hydraulic issues is indispensable to design the reactor efficiently. Genetic Algorithm (GA),which is one of the methods, for multjple-criteria decision-making, was applied to the typical simPle objective optimization problems and then was confirmed its basic performance. From the Analyses, the following results have been obtained: (1)In the unimodal optimization problem, it was confirmed that GA is capable of sufficient searching ability. (2)It was confirmed that GA can be also applied to the discrete optimization problems. (3)In the case of applying GA to the combinational optimization problem, the searching efficiency is improved better by increasing the number of experiment times than the maximum of generation. (4)In the case of applying GA to the multimodal optimization problem, the searching ability is improved by using the two genetic operators (i.e., the mutation, and the elite strategy)at the same time.
*;
JNC TN9400 2002-011, 37 Pages, 2002/05
Numerical analyses for turbulence thermal mixing, the aim of which is to evaluate relationship between hydrodynamics and temperature distribution of an archedvortex, were carried out using the direct numerical simulation code DINUS-3. From the analyses, the following results have been obtained: (1)Transportation period of the arched-vortex and distance between the arched--vortices were kept constant in isothermal and non-isothermal conditions. (2)The transportation period of afched-vortex was decreased with increasing Reynolds number under the condition of the constant flow velocity ratio between both coolant pipes. (3)One of the main reasons for this behavior was considered that the motion of the cold fluid flowing out of the branch pipe was restricted by the difference of fluid density between the branch and the main pipes. The amplitudes of the cross flow velocity fluctuation in the leg region of the arched-vortex were larger than those under isothermal condition. (4)It was confirmed that the arched-vortex consists of two kinds of vortexes, i.e., a longitudinal vortex generated by a shear motion at the top of the arched-vortex, and a horizontal vortex by shedding motion at both sides of the branch jet flow.
; *; Yamaguchi, Akira
JNC TN9400 2001-129, 51 Pages, 2002/03
A large-scale sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor investigated in the feasibility studies on commercialized fasat reactors has a tendency of consideration of thorough simplified and compacted system designs to realize drastic economical improvements. Therefore, special attention should be paid to thermohydraulic designs for gas entrainment behavior from free surfaces, a flow-induced vibration of in-vessel components, thermal shock for various structures due to high-speed coolant flows, nonsymmetrical coolant flows, etc. in the reactor vessel. In-vessel thermohydraulic analyses were carried out using a multi-dimensional code AQUA to contribute to a planning of water scaled-model experiments for the separated upper plena of the reactor vessel. From the analysis, the following results were obtained. (1)It can be considered that there is little effect of volumetric flow rate between the upper plenum and the free surfase plenum on hydrodynamic characteristics in the whole upper plenum. Because the affected area is limited in the neighborhood of gaps of hot/cold leg pipes. (2)Change in flow velocity components is limited around the outer wall of hot leg pipes if the gap width of the dipped plate and penetrating components changes. From the above results, it was concluded that the assumption seems to be valid that the free surface plenum hydrodynamic characteristics is independent of the upper plenum flows. However it is necessary to consider jet effects due to the hot leg intake flows affecting vortex concentrations in the upper plenum.
; *; Yamaguchi, Akira
JNC TN9400 2001-117, 60 Pages, 2002/02
A large-scale sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor in feasibility studies on commercialized fast reactors has a tendency of consideration of thorough simplified and compacted system designs to realize drastic economical improvements. Therefore, special attention should be paid to thermohydraulic designs for a gas entrainment behavior from free surfaces, a flow-induced vibration of in-vessel components, a thermal shock for various structures due to high-speed coolant flows, nonsymmetrical coolant flows, etc. in the reactor vessel. In-vessel thermohydraulic analyses were carried out using a multi-dimensional code AQUA to understand the thermohydraulic characteristics in the upper plenum, and to investigate suitable in-vessel structure for the elimination of gas entrainment possiblity. From the analysis, the following results were obtained. (1)It is difficult to rationale in-vessel flow patterns through adjustments of porous ratio and pressure loss for a hold down plate and baffle plates installed in an upper core structure. (2)Dummy plug insertion to a slit of the upper core structure is one of effective measures to stabilize in-vessel flow patterns. (3)Flow guide devices such as a baffle ring and a partial inner barrel are also effective measures to eliminate impinging jet to a dipped plate (D/P) and to reduce horizontal flow velocity components at free surface. (4)Installations of labyrinth structures to a R/V - D/P gap is successful for decreasing of free surface horizontal flows. (5)Gap closing of an in-vessel fuel pot and two cold trap components has the effects of reductions for free surface horizontal flows and for the difference of free surface levels. Following future investigations are important preventive measures against the gas entrainment from the free surface. (1)Flattening of spatial axial velocity distributions at the R/V - D/P gap. (2)Alleviation measures of vortex concentration at free surface. (3)Separation measures of 3-dimensional vortex distributi