Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Tsuzuki, Takayuki*; Murai, Tetsuro*
JAEA-Technology 2022-023, 128 Pages, 2022/11
In a mercury target of the J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex), pulsed proton beams repeatedly bombard the flowing mercury which is confined in a stainless-steel vessel (target vessel). Cavitation damage caused by the propagation of the pressure waves is a factor of the life of the target vessel. As a measure to reduce damages, we developed a bubbler to inject the gas microbubbles into the flowing mercury, which can reduce the pressure waves. To operate the mercury target vessel stably with the 1 MW high-intensity proton beams, further reduction of the damage is required. The bubbler setting position should be closer to the beam window to increase the bubble population, which could enhance the reduction effect on the pressure waves and damage. However, the space at the beam window of the target vessel is restricted. The bubbler design and setting position as well as the vane design for the mercury flowing pattern are optimized by means of a machine learning technique to get more suitable bubble distribution, increasing in bubble population and optimizing bubble size nearby the beam window of the target vessel. The results of CFD analyses performed with 1000 cases were used for machine learning. Since the flow rate of mercury affects the temperature of the target vessel, this was used for the constraint condition. As a result, we found a design of mercury target vessel that can increase the bubble population by ca. 20% higher than the current design.
Murai, Naoki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Kawamura, Mitsuaki*; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Tajima, Setsuko*; Baron, A. Q. R.*
Physical Review B, 101(3), p.035126_1 - 035126_6, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:32.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report an inelastic X-ray scattering investigation of phonons in FeSe superconductor. Comparing the experimental phonon dispersion with density functional theory (DFT) calculations in the non-magnetic state, we found a significant disagreement between them. A better overall agreement was obtained by allowing for spin-polarization in DFT calculations, despite the absence of magnetic order in FeSe. This calculation gives a realistic approximation, at DFT level, of the disordered paramagnetic state of FeSe, in which strong spin fluctuations are present.
 K
K Fe
Fe As
As
Ideta, Shinichiro*; Murai, Naoki; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*
Physical Review B, 100(23), p.235135_1 - 235135_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)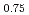 K
K Fe
Fe As
As as seen via time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering
as seen via time-of-flight inelastic neutron scatteringMurai, Naoki; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; Ideta, Shinichiro*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Ikeda, Hiroaki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi
Physical Review B, 97(24), p.241112_1 - 241112_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We use inelastic neutron scattering (INS) to investigate the effect of electron correlations on spin dynamics in iron-based superconductor Ba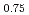 K
K Fe
Fe As
As . Our INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A first principles analysis of dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the mass renormalization factor of 3, as determined by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that electron correlations in the Fe-3d bands yield enhanced effective electron masses, and consequently, induce substantial narrowing of the spin excitation bandwidth. Our results highlight the importance of electron correlations in an itinerant description of the spin excitations in iron-based superconductors.
. Our INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A first principles analysis of dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the mass renormalization factor of 3, as determined by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that electron correlations in the Fe-3d bands yield enhanced effective electron masses, and consequently, induce substantial narrowing of the spin excitation bandwidth. Our results highlight the importance of electron correlations in an itinerant description of the spin excitations in iron-based superconductors.
 studied by neutron scattering and their relation with thermal conductivities
studied by neutron scattering and their relation with thermal conductivitiesKajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Murai, Naoki; Shamoto, Shinichi; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Hata, Hiroto*; Eto, Takahiro*; Noda, Masaaki*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 8(1), p.9651_1 - 9651_8, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.02(Multidisciplinary Sciences) As
As using high-resolution inelastic X-ray scattering
using high-resolution inelastic X-ray scatteringMurai, Naoki*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Uchiyama, Hiroshi*; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Miyasaka, Shigeki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 93(2), p.020301_1 - 020301_5, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:33.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Murai, Yuichi*; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Toda, Shinichi*; Ishikawa, Masaaki*; Yamamoto, Fujio*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 236(1), p.94 - 106, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:96.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)Air-water two-phase flow in helicallly coiled tube of 20mm in the internal diameter is investigated ezperimentally to elucidate the effect of centrifugal acceleration on the flow regime map and the local instantaneous flow structure. Three kinds of test tubes including a straight tube are used to compare the flow structure under turbulent flow condition. The superficial velocity up to 6 m/s is tested so that centrifugal Froude number covers a range from 0 to 3. The inter facial structure is visualized from two directions by a high-speed video system with a synchronized measurement of local pressure fluctuation. The results reveral that the flow transition line alters due to centrifugal force acting on liquid phase in the tube. Especially the bubbly fow regime is narrwed significantly. The pressure fluctuation amplitude gets large relatively to the average presure loww as void fraction increases. The Frequency spectra of the pressure fluctuation have plural peaks in the case of strong curvature, implying that the periodicity of slugging two-phase flow is collapsed by internal secondary flow actibated inside liquid phase. Moreover, the substantial velocity of gas phase is slower than the total superficial velocity in case of large Froude number because of biased distribution to the inner surface allowing liquid flow passing outside as like a radial stratified flow.
Murai, Yuichi*; Yamamoto, Fujio*; Ishikawa, Masaaki*; Sakai, Kosuke*; Oiwa, Hiroshi*; Toda, Shinichi; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Tamayama, Kiyoshi
JNC TY4400 2003-006, 75 Pages, 2003/06
None
; ; Kaneko, Masaaki*; *; *
JNC TJ6400 2001-012, 51 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Makoto; *; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Nakajima, Hideo; Kato, Takashi; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Matsui, Kunihiro; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Ando, Toshinari; et al.
Proc. of 15th Int. Conf. on Magnet Technology (MT-15), p.409 - 412, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
; *; *; *; *
Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 47, p.1427 - 1438, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:72.1(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English
 As
As via inelastic X-ray scattering
via inelastic X-ray scatteringMurai, Naoki*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Uchiyama, Hiroshi*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Miyasaka, Shigeki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Co
Co )
) As
As by inelastic X-ray scattering
by inelastic X-ray scatteringMurai, Naoki*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Uchiyama, Hiroshi*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Miyasaka, Shigeki*; et al.
no journal, ,
 As
As via high-resolution inelastic X-ray scattering
via high-resolution inelastic X-ray scatteringMurai, Naoki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Uchiyama, Hiroshi*; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Miyasaka, Shigeki*; et al.
no journal, ,
We report the first IXS study of single crystals of SrFe As
As that have been detwinned via application of in-plane uniaxial stress. Our results clearly show anisotropy in phonon structure below
that have been detwinned via application of in-plane uniaxial stress. Our results clearly show anisotropy in phonon structure below 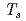 =
= 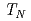 characterized by mode splitting at tetragonally-equivalent momentum transfers. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first observation of phonon anisotropy in iron-pnictides at finite momentum transfers. We obtain good agreement with our results using calculations that are modified to account for a reduced magnetic moment and fluctuating magnetism. Previous efforts using either non-magnetic calculations or static magnetism tend to either get the dispersion wrong from non-magnetic calculations or strongly over-estimate the phonon mode splitting when static magnetism is included. Our model for the response below
characterized by mode splitting at tetragonally-equivalent momentum transfers. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first observation of phonon anisotropy in iron-pnictides at finite momentum transfers. We obtain good agreement with our results using calculations that are modified to account for a reduced magnetic moment and fluctuating magnetism. Previous efforts using either non-magnetic calculations or static magnetism tend to either get the dispersion wrong from non-magnetic calculations or strongly over-estimate the phonon mode splitting when static magnetism is included. Our model for the response below 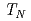 incorporates a phenomenological reduction in force constant anisotropy, by about 65%, that can be attributed to residual fast magnetic fluctuations. Above
incorporates a phenomenological reduction in force constant anisotropy, by about 65%, that can be attributed to residual fast magnetic fluctuations. Above 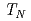 , all fluctuations are assumed to be fast and the response becomes the average of the results from the static magnetism. This serves as a starting point for a general model of phonons in iron-pnictides applicable to both non-magnetic and magnetic phases.
, all fluctuations are assumed to be fast and the response becomes the average of the results from the static magnetism. This serves as a starting point for a general model of phonons in iron-pnictides applicable to both non-magnetic and magnetic phases.
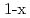 K_
K_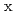 Fe_
Fe_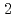 As_
As_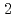 (x = 0.25) as seen via inelastic neutron scattering
(x = 0.25) as seen via inelastic neutron scatteringMurai, Naoki; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Ideta, Shinichiro*; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*
no journal, ,
We report an inelastic neutron scattering (INS) study of underdoped Ba_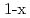 K_
K_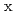 Fe_
Fe_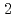 As_
As_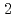 that shows the presence of double-resonance at the same commensurate wave vector in the superconducting (SC) state. By comparing our INS data with the SC gap structure of the same crystal, as measured by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), we show that the observed double-resonance feature originates neither from SC gap anisotropy nor from multiple SC gaps on different Fermi-surface sheets. This suggests that the double-resonance feature in iron-pnictides cannot be interpreted within a spin-exciton scenario.
that shows the presence of double-resonance at the same commensurate wave vector in the superconducting (SC) state. By comparing our INS data with the SC gap structure of the same crystal, as measured by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), we show that the observed double-resonance feature originates neither from SC gap anisotropy nor from multiple SC gaps on different Fermi-surface sheets. This suggests that the double-resonance feature in iron-pnictides cannot be interpreted within a spin-exciton scenario.
Yoshida, Junya; Ohashi, Masaki*; Goto, Ryosuke*; Nagase, Yuichi*; Murai, Rina*; May, S.*; Aye, M. M. T.*; Kimbara, Shinji*; Yoshimoto, Masahiro*; Nakazawa, Kazuma*
no journal, ,
J-PARC E07 collaboration has been performed K- beam exposure to all the emulsion sheet detector. The analysis for double strangeness nuclei is ongoing. We'll discuss the current status, performance, speed, and future prospects.
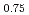 K
K Fe
Fe As
As due to electron correlation effects
due to electron correlation effectsMurai, Naoki; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; Ideta, Shinichiro*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Ikeda, Hiroaki*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*
no journal, ,
Using inelastic neutron scattering (INS) and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), we investigate the spin dynamics of iron-based superconductor Ba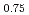 K
K Fe
Fe As
As . The INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A random phase approximation (RPA) treatment of the dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the band renormalization factor of 3 derived from the ARPES measurements on the same crystals, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that the experimental spin excitation peak lies at a much lower energy than the bare value, reflecting a strong renormalization of the quasiparticle band dispersion near the Fermi level due to electron correlation effect. The present results point to a unified framework that connects the magnetic response to the underlying electronic structure of the materials.
. The INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A random phase approximation (RPA) treatment of the dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the band renormalization factor of 3 derived from the ARPES measurements on the same crystals, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that the experimental spin excitation peak lies at a much lower energy than the bare value, reflecting a strong renormalization of the quasiparticle band dispersion near the Fermi level due to electron correlation effect. The present results point to a unified framework that connects the magnetic response to the underlying electronic structure of the materials.
 K
K Fe
Fe As
As due to electron correlation effects
due to electron correlation effectsMurai, Naoki; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; Ikeda, Hiroaki*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Ideta, Shinichiro*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
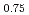 K
K Fe
Fe As
As due to electron correlation effects
due to electron correlation effectsMurai, Naoki; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Ikeda, Hiroaki*; Ideta, Shinichiro*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*
no journal, ,
We report inelastic neutron scattering (INS) study of hole-doped iron-based superconductor Ba K
K Fe
Fe As
As (x = 0.25). The INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A random phase approximation (RPA) treatment of the dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the band renormalization factor of 3 derived from angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) measurements on the same sample, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that the Fe-3d bandwidth narrowing due to electron correlation is directly reflected in the spin excitation energy scale. We will discuss the current state of our analysis relating the magnetic response to the underlying electronic structure of the materials.
(x = 0.25). The INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A random phase approximation (RPA) treatment of the dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the band renormalization factor of 3 derived from angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) measurements on the same sample, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that the Fe-3d bandwidth narrowing due to electron correlation is directly reflected in the spin excitation energy scale. We will discuss the current state of our analysis relating the magnetic response to the underlying electronic structure of the materials.
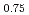 K
K Fe
Fe As
As as seen via time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering
as seen via time-of-flight inelastic neutron scatteringMurai, Naoki; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; Ikeda, Hiroaki*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Ideta, Shinichiro*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*
no journal, ,
We use inelastic neutron scattering (INS) to investigate the effect of electron correlations on spin dynamics in iron-based superconductor Ba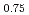 K
K Fe
Fe As
As . Our INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A first principles analysis of dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the mass renormalization factor of 3, as determined by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that electron correlations in the Fe-3d bands yield enhanced effective electron masses, and consequently, induce substantial narrowing of the spin excitation bandwidth. Our results highlight the importance of electron correlations in an itinerant description of the spin excitations in iron-based superconductors.
. Our INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A first principles analysis of dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the mass renormalization factor of 3, as determined by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that electron correlations in the Fe-3d bands yield enhanced effective electron masses, and consequently, induce substantial narrowing of the spin excitation bandwidth. Our results highlight the importance of electron correlations in an itinerant description of the spin excitations in iron-based superconductors.