Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
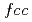 -base GdO
-base GdO precipitations in a Mg-Zn-Gd alloy
precipitations in a Mg-Zn-Gd alloyIto, Yuto*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Transactions, 64(8), p.2022 - 2025, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have found that, during 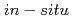 scanning transmission electron microscopy observations, heating of a Mg
scanning transmission electron microscopy observations, heating of a Mg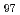 Zn
Zn Gd
Gd (at.%) alloy at 623K leads to dynamic precipitations of face-centered-cubic (
(at.%) alloy at 623K leads to dynamic precipitations of face-centered-cubic (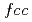 )-based Gd nanoparticles. With the aid of density-functional theory (DFT) calculations, the observed lattice constant of 5.32
)-based Gd nanoparticles. With the aid of density-functional theory (DFT) calculations, the observed lattice constant of 5.32 , which is larger than that expected for pure
, which is larger than that expected for pure 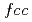 -Gd of 5.06
-Gd of 5.06 , is likely to be due to oxygen atoms inserted at tetrahedral interstitial sites with essentially a fractional occupation. Systematic DFT calculations show possible occurrences of
, is likely to be due to oxygen atoms inserted at tetrahedral interstitial sites with essentially a fractional occupation. Systematic DFT calculations show possible occurrences of 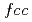 -Gd-based oxide phase with a wide non-stoichiometry range by occupying either tetrahedral or octahedral interstitial positions, being represented as GdO
-Gd-based oxide phase with a wide non-stoichiometry range by occupying either tetrahedral or octahedral interstitial positions, being represented as GdO .
.
 to extreme environments
to extreme environmentsHorikawa, Daiki*; Yamaguchi, Ayami*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Tanaka, Daisuke*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Yukuhiro, Fumiko*; Kuwahara, Hirokazu*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; et al.
Astrobiology, 12(4), p.283 - 289, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:68.76(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We examined the hatchability of hydrated and anhydrobiotic eggs of the tardigrade  to hatch after ionizing irradiation (helium ions), extremely low and high temperatures, and high vacuum. Anhydrobiotic eggs (50% lethal dose; 1690 Gy) were substantially more radioresistant than hydrated ones (50% lethal dose; 509 Gy). Anhydrobiotic eggs also have a broader temperature resistance compared with hydrated ones. Over 70% of the anhydrobiotic eggs treated at high and low temperatures, but all of the hydrated eggs failed to hatch. After exposure to high vacuum conditions, the hatchability of the anhydrobiotic eggs was comparable to that of untreated control eggs.
to hatch after ionizing irradiation (helium ions), extremely low and high temperatures, and high vacuum. Anhydrobiotic eggs (50% lethal dose; 1690 Gy) were substantially more radioresistant than hydrated ones (50% lethal dose; 509 Gy). Anhydrobiotic eggs also have a broader temperature resistance compared with hydrated ones. Over 70% of the anhydrobiotic eggs treated at high and low temperatures, but all of the hydrated eggs failed to hatch. After exposure to high vacuum conditions, the hatchability of the anhydrobiotic eggs was comparable to that of untreated control eggs.
 ; A New model animal for astrobiology
; A New model animal for astrobiologyHorikawa, Daiki*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Abe, Wataru*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Yukuhiro, Fumiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Astrobiology, 8(3), p.549 - 556, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:94 Percentile:90.99(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report the successful rearing of the herbivorous tardigrade,  , by supplying the green alga
, by supplying the green alga 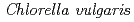 as food. The life span was 35 d, deposited eggs required 5.7 d to hatch, and animals began to deposit eggs 9 d after hatching. The reared individuals of this species had an anhydrobiotic capacity throughout their life cycle in egg, juvenile, and adult stages. Furthermore, the reared adults in an anhydrobiotic state were tolerant of temperatures of 90
as food. The life span was 35 d, deposited eggs required 5.7 d to hatch, and animals began to deposit eggs 9 d after hatching. The reared individuals of this species had an anhydrobiotic capacity throughout their life cycle in egg, juvenile, and adult stages. Furthermore, the reared adults in an anhydrobiotic state were tolerant of temperatures of 90 C and -196
C and -196 C and exposure to 99.8% acetonitrile or irradiation with 4000 Gy
C and exposure to 99.8% acetonitrile or irradiation with 4000 Gy  He ions. Based on their life history traits and tolerance to extreme stresses,
He ions. Based on their life history traits and tolerance to extreme stresses,  might be a suitable model for astrobiological studies of multicellular organisms.
might be a suitable model for astrobiological studies of multicellular organisms.
 -ray on the tardigrade
-ray on the tardigrade 
Horikawa, Daiki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Katagiri, Chihiro*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Higashi, Seigo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 116, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Horikawa, Daiki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Katagiri, Chihiro*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Higashi, Seigo*; et al.
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 82(12), p.843 - 848, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:130 Percentile:99.14(Biology)no abstracts in English
Fujikawa, Seigo; Kitamura, Toshikatsu; *; *; *; *
Techno Marine, 0(797), p.853 - 857, 1995/11
no abstracts in English
 -rays tolerance in water bears
-rays tolerance in water bearsHorikawa, Daiki*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Okuda, Takashi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Horikawa, Daiki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Katagiri, Chihiro*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Higashi, Seigo*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Wadachi, Hiroki*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Abe, Wataru*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Higashi, Seigo*; Okuda, Takashi*
no journal, ,
We collected some kinds of tardigrade to develop multi-cellular model oraganism for extremotolerant. Among four kinds of collected tardigrade, we found that a tardigrade  at Sapporo-city feeded
at Sapporo-city feeded  and could breed. The life-time of
and could breed. The life-time of  in an artificial culture condition is about 35 days and 5.7 days for hatching. During the whole life-time, one animal laids 8 eggs. In addition, it was observed that
in an artificial culture condition is about 35 days and 5.7 days for hatching. During the whole life-time, one animal laids 8 eggs. In addition, it was observed that  could enter an ametabolic dry state called anhydrobiosis in all stages of life-time. Furthermore, we observed a high surviving-rate even if
could enter an ametabolic dry state called anhydrobiosis in all stages of life-time. Furthermore, we observed a high surviving-rate even if  exposed in various kinds of extreme environments.
exposed in various kinds of extreme environments.
 ; A Model for astrobiological studies
; A Model for astrobiological studiesHorikawa, Daiki*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Abe, Wataru*; Koshikawa, Shigeyuki*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Iwata, Kenichi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Higashi, Seigo*; et al.
no journal, ,
We report the first successful rearing of the herbivorous tardigrade,  , by supplying a green alga
, by supplying a green alga  as a food. The reared individuals of this species had an anhydrobiotic capacity throughout their life cycle, from eggs, to juveniles, and to adults. Reared adults, while in an anhydrobiotic state, were tolerant to temperatures -196
as a food. The reared individuals of this species had an anhydrobiotic capacity throughout their life cycle, from eggs, to juveniles, and to adults. Reared adults, while in an anhydrobiotic state, were tolerant to temperatures -196 C and 100
C and 100 C. Furthermore, they were shown to be tolerant to the exposure to 99.8% acetonitrile, 1 GPa of hydrostatic pressure, or 5000 Gy of He ion radiation. We will report the details of these results, along with the description of their life history. Due to the observed tolerance to such extreme environmental conditions, we propose R. varieornatus to be included as a suitable model for astrobiological studies of multicellular organisms.
C. Furthermore, they were shown to be tolerant to the exposure to 99.8% acetonitrile, 1 GPa of hydrostatic pressure, or 5000 Gy of He ion radiation. We will report the details of these results, along with the description of their life history. Due to the observed tolerance to such extreme environmental conditions, we propose R. varieornatus to be included as a suitable model for astrobiological studies of multicellular organisms.
Ito, Yuto*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Abe, Eiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Yuto*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Abe, Eiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Yuto*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Abe, Eiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Yuto*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Abe, Eiji*
no journal, ,
Among HCP metals, Zn and Cd, which exhibit high c/a ratios, exhibit a peculiar deformation mode with crystal rotation called kink deformation under conditions where the main slip system is suppressed. Although a model of kink deformation has been proposed based on collective rearrangement of dislocations, the details of the kink deformation have not been clarified. In this study, we evaluate the phonon dispersion relation using first-principles calculations for HCP metals under uniaxial compression in the basal plane, where kink deformation is known to occur, and verify the generalized stacking fault energy, which is considered important for characterization of dislocations.
Ito, Yuto*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Abe, Eiji*
no journal, ,
Among hcp metals, Zn and Cd, which have high c/a ratios, exhibit kink deformation characterized by crystal rotation under conditions of suppressed basal slip under in-basal compression. Kink deformation has recently attracted attention because it compensates for the plastic deformation of the hcp structure, which has a limited independent slip system, and also contributes to high strength in some Mg alloys. In this study, we evaluated the structural stability of hcp metals under uniaxial compression conditions where basal slip is suppressed, using first-principles calculations of the Phonon dispersion relation and generalized stacking fault energy (GSFE) to understand the kink deformation mechanism.