Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kimura, Masanori; Hato, Shinji*; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2017/11
The authors developed a new metabolic model for iodine by combining the respiratory tract model (Publ.66), the gastrointestinal tract model (Publ.30) of the ICRP and the metabolic model for iodine (Johnson's model) in order to evaluate the behavior of radioiodine and stable iodine in the body more realistically. The developed metabolic model indicated that a reduction factor (RF) depends on dosage of stable iodine, timing of the administration of stable iodine, different iodine isotopes ( I -
I -  I), and age groups. Therefore, the RF was calculated by changing these parameters and then a database of the RF was constructed for the application to the OSCAAR code.
I), and age groups. Therefore, the RF was calculated by changing these parameters and then a database of the RF was constructed for the application to the OSCAAR code.
Kato, Nobuyoshi*; Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Nago, Makito*; Yamagami, Masahito*; Matsubara, Makoto*; Shigehiro, Michiko*; Aizawa, Takao*; Kamemura, Katsumi*
Chishitsu To Chosa, (139), p.17 - 22, 2014/04
no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Norihiro; Nishida, Akemi; Matsubara, Hitoshi*; Hazama, Osamu*; Suzuki, Yoshio; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Iigaki, Kazuhiko
Transactions of 22nd International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-22) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2013/08
It is not convenient to experimentally analyze its behavior under strong loads of earthquakes, since the facility is extremely huge and complex. The proposed system performs numerical simulations to evaluate the behaviors of an assembly like a nuclear facility. This system projects the components of an assembly onto both/either a distributed and/or a parallel computing environment in order to conduct a simulation of the behavior of an assembly such as a nuclear facility. In a result discussion, a numerical experiment was carried out with a cantilever model and its result was compared with theoretical data. A good corresponding among them was obtained as a structural analysis of an assembly by using a parallel computer. As a conclusion, a suggested methodology has shown to calculate a behavior of an assembly with High Temperature engineering Test Reactor.
Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Inagaki, Daisuke; Nago, Makito*; Kamemura, Katsumi*; Matsubara, Makoto*; Shigehiro, Michiko*
Proceedings of ITA-AITES World Tunnel Congress 2013 (WTC 2013)/39th General Assembly, p.2014 - 2021, 2013/05
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been constructing three shafts to a depth of 500 m in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project. In this study, in consideration of support patterns installed, a relationship between the rock mass properties and mechanical response to excavation was investigated in detail during the construction of the East Access Shaft below a depth of 250 m. Since the shaft has intersected several faults with the size greater than the shaft diameter, some amounts of rock spalling have occurred and cracks have severely developed in a concrete lining in highly fractured zones. The results of pre-excavation grouting were compared with the results of fracture mapping in the shaft wall obtained during the shaft sinking. Applicability of several support patterns installed to control massive spalling during the shaft sinking was also analysed using the results of geometry profiling of shaft wall using a three-dimensional laser scanner and convergence measurements. As a result, based the empirical relationships among the characteristics of rocks, dimension of spalling, damage of a concrete lining and support patterns, a flow chart for selection of span of a concrete lining was proposed to control its severe damage prior to shaft excavation.
 Fe
FeShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Homma, Michio*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
Physical Review C, 87(2), p.024301_1 - 024301_7, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.29(Physics, Nuclear)Electro-magnetic dipole transitions in  Fe were measured in photon scattering experiments with a linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
Fe were measured in photon scattering experiments with a linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. While the summed magnetic dipole (
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. While the summed magnetic dipole ( ) strength was determined as
) strength was determined as 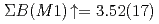
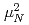 at excitation energies between 7 and 10 MeV, the summed electric dipole (
at excitation energies between 7 and 10 MeV, the summed electric dipole ( ) strength below 10 MeV was obtained as
) strength below 10 MeV was obtained as 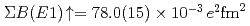 . The observed
. The observed  strength was compared with shell-model predictions in the
strength was compared with shell-model predictions in the 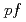 -shell using the GXPF1J and KB3G effective interactions. In addition, the
-shell using the GXPF1J and KB3G effective interactions. In addition, the  strength was compared with random-phase approximation calculations with the Skyrme interaction.
strength was compared with random-phase approximation calculations with the Skyrme interaction.
Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Inagaki, Daisuke; Nago, Makito*; Koike, Masashi*; Matsubara, Makoto*; Sugawara, Kentaro*
Dai-13-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.911 - 916, 2013/01
A repository for high-level radioactive waste in deep underground consists of several underground structures such as access and disposal drifts and shafts. In deep geological disposal project, a shaft is the first underground structure to be constructed and the last one to be backfilled. Therefore, the stability of shaft is one of key factors to steadily manage the project in the construction and operation phases. In this paper, the authors discuss influence of rock spalling on concrete lining in shaft sinking. Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been constructing three shafts (one is for ventilation and the others are for access use) up to a depth of 500 m in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. During the construction of the Ventilation Shaft (4.5 m in diameter) below a depth of 250 m, rock spalling occurred at several depths and an open crack has developed in a concrete lining installed just above rock spalling. The authors have measured geometry of shaft wall by using three-dimensional laser scanner. They also conducted numerical analysis in order to calculate change in stress distribution and deformation induced by rock spalling in a concrete lining and the surrounding rock. As a result, it was clarified that rock spalling induced tensile stress in the vertical direction in a concrete lining. Especially, the tensile stress in a concrete lining was likely to exceed tensile strength of a concrete lining in the case that it developed more than 100 cm in depth.
Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Matsubara, Makoto*; Ishikawa, Taiki*; Ogawa, Daisuke*
Geoscience Frontiers, 4(1), p.105 - 111, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:23.68(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)This paper focuses on the formation mechanism of fractures induced by excavation of a gallery in soft sedimentary rocks in the Horonobe area of Japan. Detailed fracture mapping of the gallery indicates that the fractures consist of both pre-existing fractures (shear fractures) and EDZ fractures (extension fractures). EDZ fractures correspond to bedding planes or potential joints inferred by paleo-stress field, and the EDZ fractures terminate against pre-existing fractures. Therefore, even for excavations in soft sedimentary rocks, formation of the EDZ fractures are controlled by pre-existing fractures and weakness planes associated with bedding planes and potential joints.
Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Shinichiro; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Sugaya, Takeyoshi*; Matsubara, Koji*; Niki, Shigeru*
Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 108, p.263 - 268, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.45(Energy & Fuels)GaAs solar cells which have a PiN structure with 50 self-organized In Ga
Ga As Quantum Dot (QD) layers were irradiated with 1 MeV electrons up to 1
As Quantum Dot (QD) layers were irradiated with 1 MeV electrons up to 1 10
10 /cm
/cm . After irradiation at 1
. After irradiation at 1 10
10 /cm
/cm , the remaining factor of I
, the remaining factor of I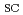 , V
, V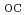 and P
and P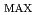 for the InGaAs 50 QD solar cell becomes 80, 90 and 55% of the initial values, respectively. On the other hand, those values for non QD GaAs solar cells decrease to 95, 80 and 63% of the initial values, respectively. Since the i-layer for the 50 QD solar cells (1.1
for the InGaAs 50 QD solar cell becomes 80, 90 and 55% of the initial values, respectively. On the other hand, those values for non QD GaAs solar cells decrease to 95, 80 and 63% of the initial values, respectively. Since the i-layer for the 50 QD solar cells (1.1  m) is thicker than the non QD solar cells (660 nm), the larger degradation of I
m) is thicker than the non QD solar cells (660 nm), the larger degradation of I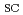 for the 50 QD solar cells than the non QD ones can be interpreted in terms that the carrier recombination in the i-layer for the 50 QD solar cells is larger than that for the non QD solar cells. For V
for the 50 QD solar cells than the non QD ones can be interpreted in terms that the carrier recombination in the i-layer for the 50 QD solar cells is larger than that for the non QD solar cells. For V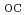 , the 50 QD solar cells showes better radiation resistance than the non QD solar cells. Furthermore, the annealing behavior of the electrical characteristics for the 50 QD and the non QD solar cells was investigated at RT under AM 0 immediately after the irradiation. As a result, the recovery of the electrical characteristics for both solar cells was observed, and the GaAs solar cells shows relatively larger recovery compared to the 50 QD solar cells. Although the mechanism of this recovery has not yet been clarified, the origin of this recovery is thought not to come from the existence of QDs because the GaAs solar cell without QD layers also shows the recovery.
, the 50 QD solar cells showes better radiation resistance than the non QD solar cells. Furthermore, the annealing behavior of the electrical characteristics for the 50 QD and the non QD solar cells was investigated at RT under AM 0 immediately after the irradiation. As a result, the recovery of the electrical characteristics for both solar cells was observed, and the GaAs solar cells shows relatively larger recovery compared to the 50 QD solar cells. Although the mechanism of this recovery has not yet been clarified, the origin of this recovery is thought not to come from the existence of QDs because the GaAs solar cell without QD layers also shows the recovery.
Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Inagaki, Daisuke; Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Yokota, Hideharu; Nago, Makito*; Matsubara, Makoto*; Shigehiro, Michiko*
Proceedings of ITA-AITES World Tunnel Congress 2012 (WTC 2012)/38th General Assembly (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2012/05
In the Horonobe URL Project, three shafts are planned to be excavated up to the depth of 500 m in the Neogene sedimentary rocks. The host rock of the URL site is comprised of diatomaceous and siliceous mudstones, which are the Koetoi and Wakkanai Formations, respectively. Approximately 100 m thick fracture zone with high hydraulic conductivity develops above about 400 m in depth in the Wakkanai Formation. The shaft sinking through the fracture zone is the most challenging issue from the aspect of tunnel engineering in the project. In the fracture zone, there is high possibility of severe breakout and spalling in shaft wall because the shafts might be intersecting faults with the size greater than shaft diameter in addition to low intact rock strength at great depth. In practice, prior to the construction of the Ventilation Shaft through the fracture zone below a depth of 250 m, the three dimensional fault distribution were predicted by integrating borehole investigation results and geological response to pre-excavation grouting operation. The countermeasure was also designed against massive spalling. During the shaft sinking, fracture mapping of shaft wall was carried out in order to evaluate the prediction of fault distribution. Roughness of shaft wall was also measured by three dimensional laser scanner in order to investigate the shape and volume of spalling resulting from the excavation work. Consequently, the Ventilation Shaft has successfully been constructed through the fracture zone. This is because the prediction of fault distribution was accurate, and the countermeasure against concrete lining damage due to spalling was promptly applied.
Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Inagaki, Daisuke; Nago, Makito*; Matsubara, Makoto*
Chika Kukan Shimpojiumu, Rombunshu, 17, p.155 - 162, 2012/01
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been constructing an underground research laboratory in order to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies of high-level radioactive waste in Horonobe, Hokkaido. A ventilation shaft (4.5 m in diameter) and two access shafts (6.5 m in diameter) are being excavated through the Neogene sedimentary rocks until the depth of 500 m. Based on the results of borehole investigation and pre-grounting operation in bedrock with high permeability from 250 m to 375 m in depth, the three dimensional fracture distribution map were built and the locations with high possibility of spalling in shaft wall in response to excavation were predicted prior to the shaft sinking from a depth of 250 m. Some amounts of spalling has occurred in several depths during shaft sinking from 250 m to 280 m in depth. The shape of each spalling was measured by means of three dimensional laser scaning system. As a result, spalling in shaft wall occurred along the faults predicted based on the three dimensional fracture distribution. In addition, spalling by brittle failure in shaft wall was also observed with a few extensile fractures which were expected to be induced by excavation. Based on the shape of spalling, it was confirmed that the applied shaft sinking procedure properly prevented a massive spalling.
 Pb
PbShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Tamii, Atsushi*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
Physical Review C, 78(6), p.061303_1 - 061303_4, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:77 Percentile:95.33(Physics, Nuclear)Spin-flip  strength in
strength in  Pb has been measured in photon scattering experiments with a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The data resolve an
Pb has been measured in photon scattering experiments with a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The data resolve an  giant resonance into at least seven, possibly eight, discrete transitions at excitation energies between 7.1 and 7.4 MeV below the neutron separation energy. The measured
giant resonance into at least seven, possibly eight, discrete transitions at excitation energies between 7.1 and 7.4 MeV below the neutron separation energy. The measured  strength in this region is found to be larger than the previous report. The experimental results are compared with an estimation of self-consistent random phase approximation using a semi-realistic interaction.
strength in this region is found to be larger than the previous report. The experimental results are compared with an estimation of self-consistent random phase approximation using a semi-realistic interaction.
 )lti-monitoring (
)lti-monitoring ( )elf (
)elf ( )nteraction (
)nteraction ( )ondition in (
)ondition in ( )ata (
)ata ( )xplorer for (
)xplorer for ( )valuation (
)valuation ( )rocessing
)rocessingNakajima, Norihiro; Araya, Fumimasa; Suzuki, Yoshio; Nishida, Akemi; Matsubara, Hitoshi; Nakajima, Kohei
Dai-27-Kai Nihon Shimyureshon Gakkai Taikai Happyo Rombunshu, p.511 - 514, 2008/06
A real space simulator for vibration table targeted to a nuclear power station has been proposed, which generates over tera-byte amount of calculated result. In order to analyze a huge size data, a data analyzer and data analyzing monitor system is suggested in this paper. A result of finite element analysis is examined by the system taking into account relation among neighboring elements' results. It is operated by multi-monitoring to view analyzing process. The system is implemented on a grid computing environment, AEGIS (atomic energy grid infrastructure) with coupling a large data visualization system.
Takahara, Shogo; Kimura, Masanori; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Homma, Toshimitsu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(Suppl.5), p.714 - 717, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is recognized that good preparedness and arrangement in advance of an emergency can improve the emergency response to a nuclear and radiological emergency. In the preparedness, comprehensive threat assessment is very important to provide technical guidance for developing the protective actions. Probabilistic safety assessment method is useful for assessing accident consequences comprehensively and quantitatively. In this study, an accident consequence assessment code OSCAAR, which was developed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, is used to provide the information for the guideline of intervention and return criteria for relocation on the long-term emergency situation.
Nishida, Akemi; Araya, Fumimasa; Matsubara, Hitoshi; Hazama, Osamu; Nakajima, Norihiro
Anzen Kenkyu Foramu 2008 Sanko Shiryoshu, p.93 - 94, 2008/02
The development of a vibration simulator has been planned for used in a full-scale nuclear power station; this simulator will implement the latest computational technologies and will allow comparisons to be made among the conventional spring-mass models and the actually observed data obtained from experiment and practice. This simulator will be used for evaluating the conservativeness of conventional models and the fragility of components through a seismic PSA (probabilistic safety assessment). This simulator will be used for analyzing the seismic responses of the entire nuclear facility by modeling each component independently.
Homma, Toshimitsu; Kimura, Masanori; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Ishikawa, Jun
Proceedings of 9th International Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (PSAM-9) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/00
Hazama, Osamu; Kushida, Noriyuki; Matsubara, Hitoshi; Nishida, Akemi; Suzuki, Yoshio; Araya, Fumimasa; Aoyagi, Tetsuo; Nakajima, Norihiro; Kondo, Makoto
Proceedings of 9th MpCCI User Forum, p.118 - 124, 2008/00
In order to safely and stably supply energy by nuclear means, structural integrity and design standards of the plant including factors such as aging must be confirmed, and its future conditions must be predicted with high reliability. Although full-scale experimentations are favorable for acquiring necessary information and carrying out investigative studies of the nuclear structures, such experiments are for most cases physically and financially impossible. Our objective is to establish an integrated full-scale simulation framework for simulating and quantitatively investing the vibration behavior of nuclear power plant equipments under earthquakes.
Nishida, Akemi; Matsubara, Hitoshi; Tian, R.; Hazama, Osamu; Suzuki, Yoshio; Araya, Fumimasa; Nakajima, Norihiro; Tani, Masayuki; Kondo, Makoto
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(3), p.376 - 382, 2007/09
Unexpected accidents such as oil-tank fires caused by the earthquake and breakage of pipes of nuclear plants have occurred over the past several years. Higher reliability is thus now increasingly expected to maintain the safety of infrastructures. We have been intensely focused on the construction of an analysis system called the "three-dimensional virtual vibration testbed," which is a numerical simulation system for a nuclear plant which considers the interconnection of machines, pipes, buildings, and their foundations under real operating conditions. In this paper, the "part-wise analysis method" is proposed in which each structural component is treated independently and analyzed as an assembly structure. Further, the system configurations in a parallel distribution environment are described. This study shows one of the successful examples of the application of this method to a nuclear-plant cooling system that has tens of millions of degrees of freedom.
Matsubara, Hitoshi; Yagawa, Genki
Oyo Rikigaku Rombunshu, 10, p.201 - 209, 2007/08
The present paper discusses the accuracy of patch-by-patch approximation of mixed-type finite element scheme. In the approximation, not only a displacement field for each element but also stress and strain fields for each patch are defined. In order to determine unknown parameters of stress/strain fields of a patch, the Hu-Washizu principle is employed. In this paper, the accuracy of the generalized finite element functions implemented in the proposed approximation is shown. Furthermore, to show the effectiveness of the approximation in the fracture mechanics that have singular stress fields, the approximation is applied to linear fracture problem.
Tani, Masayuki; Nakajima, Norihiro; Nishida, Akemi; Suzuki, Yoshio; Matsubara, Hitoshi; Araya, Fumimasa; Kushida, Noriyuki; Hazama, Osamu; Kondo, Makoto; Kawasaki, Kozo
Proceedings of Joint International Topical Meeting on Mathematics & Computations and Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (M&C+SNA 2007) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2007/04
Kimura, Masanori; Matsubara, Takeshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Homma, Toshimitsu
Proceedings of International Symposium on Environmental Modeling and Radioecology, p.348 - 351, 2007/03
no abstracts in English