Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O
Yoshioka, Satoru*; Tsuruta, Konosuke*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Sugiyama, Takeharu*; Oba, Yojiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kobayashi, Eiichi*; Okudaira, Koji*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 103(8), p.4654 - 4663, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:23.05(Materials Science, Ceramics)X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) reveal the damaged structures in MgAl O
O spinel induced by swift heavy ions. SAXS indicates the formation of ion tracks with cylindrical shape with a diameter of 5 nm. XANES indicates the cationic disordering between tetrahedral and octahedral sites by the irradiation. Quantitative analysis of XANES also reveals that cations preferably occupy the octahedral sites at high fluence.
spinel induced by swift heavy ions. SAXS indicates the formation of ion tracks with cylindrical shape with a diameter of 5 nm. XANES indicates the cationic disordering between tetrahedral and octahedral sites by the irradiation. Quantitative analysis of XANES also reveals that cations preferably occupy the octahedral sites at high fluence.
 O
O induced by swift heavy ions
induced by swift heavy ionsYoshioka, Satoru*; Tsuruta, Konosuke*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito; Kobayashi, Eiichi*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 20(7), p.4962 - 4969, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.21(Chemistry, Physical)Cationic disorder in the MgAl O
O spinel induced by swift heavy ions was investigated using the X-ray absorption near edge structure. With changes in the irradiation fluences of 200 MeV Xe ions, the Mg K-edge and Al K-edge spectra were synchronously changed. The calculated spectra based on density function theory indicate that the change in the experimental spectra was due to cationic disorder between Mg in tetrahedral sites and Al in octahedral sites. These results suggest a high inversion degree to an extent that the completely random configuration is achieved in MgAl
spinel induced by swift heavy ions was investigated using the X-ray absorption near edge structure. With changes in the irradiation fluences of 200 MeV Xe ions, the Mg K-edge and Al K-edge spectra were synchronously changed. The calculated spectra based on density function theory indicate that the change in the experimental spectra was due to cationic disorder between Mg in tetrahedral sites and Al in octahedral sites. These results suggest a high inversion degree to an extent that the completely random configuration is achieved in MgAl O
O induced by the high density electronic excitation under swift heavy ion irradiation.
induced by the high density electronic excitation under swift heavy ion irradiation.
Takaki, Seiya*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 326, p.140 - 144, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:94.83(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated atomic structure of ion tracks in CeO irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). TEM observations under inclined conditions showed continuous ion tracks with diffraction and structure factor contrast, and the decrease in the atomic density of the ion tracks was evaluated. High resolution STEM with high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) technique showed that the crystal structure of the Ce cation column is retained at the core region of ion tracks, although the signal intensity of the Ce cation lattice is reduced over a region nm in size. Annular bright field (ABF) STEM observation has detected that the O anion column is preferentially distorted at the core region of ion tracks within a diameter of 4 nm.
irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). TEM observations under inclined conditions showed continuous ion tracks with diffraction and structure factor contrast, and the decrease in the atomic density of the ion tracks was evaluated. High resolution STEM with high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) technique showed that the crystal structure of the Ce cation column is retained at the core region of ion tracks, although the signal intensity of the Ce cation lattice is reduced over a region nm in size. Annular bright field (ABF) STEM observation has detected that the O anion column is preferentially distorted at the core region of ion tracks within a diameter of 4 nm.
 irradiated with swift heavy ions
irradiated with swift heavy ionsYasuda, Kazuhiro*; Eto, Motoki*; Sawada, Kenichi*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 314, p.185 - 190, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:92.6(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated microstructure evolution in CeO irradiated with 210 MeV Xe ions by using transmission electron microscopy to gain the fundamental knowledge on radiation damage induced by fission fragments in nuclear fuel and transmutation target.
irradiated with 210 MeV Xe ions by using transmission electron microscopy to gain the fundamental knowledge on radiation damage induced by fission fragments in nuclear fuel and transmutation target.
 O
O under swift heavy ion irradiation
under swift heavy ion irradiationYasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Eto, Motoki*; Kawasoe, Shinji*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito
International Journal of Materials Research, 102(9), p.1082 - 1088, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:52.23(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Accumulation and recovery of radiation-induced damage with swift heavy ions instoichiometric magnesium aluminate spinel, MgAl O
O , has been investigated. Microstructural change and atomic disordering was examined through transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques, with bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) TEM images, and high angular resolution electron channelling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS), for single crystal MgAl
, has been investigated. Microstructural change and atomic disordering was examined through transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques, with bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) TEM images, and high angular resolution electron channelling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS), for single crystal MgAl O
O irradiated with 200 MeV Xe, and 340 or 350 MeV Au ions. The density of core damage region, detected by BFTEM with Fresnelcontrast, increased proportionally with ion fluence at the early stage of accumulation. This result is discussed with a balance between the formation and recovery of the core damage region under irradiation, and the influence region to induce the recovery was evaluated to be 7-9 nm in radius. The structure of the core damage region is found from HR and BFTEM images to be a columnar vacancy-rich region with a low atomic density.
irradiated with 200 MeV Xe, and 340 or 350 MeV Au ions. The density of core damage region, detected by BFTEM with Fresnelcontrast, increased proportionally with ion fluence at the early stage of accumulation. This result is discussed with a balance between the formation and recovery of the core damage region under irradiation, and the influence region to induce the recovery was evaluated to be 7-9 nm in radius. The structure of the core damage region is found from HR and BFTEM images to be a columnar vacancy-rich region with a low atomic density.
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Masukawa, Fumihiro; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 168(2), p.482 - 486, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental studies of shielding and radiation effects have been started using 120-GeV proton synchrotron at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) under collaboration between FNAL and Japan. The first campaign of the experiment was carried out at the Pbar target station and Numi experimental station at FNAL, using antiproton and neutrino production targets irradiated by 120-GeV protons. The generated secondary particles passing through steel, concrete and rock were measured by activation methods as well as by other detectors such as scintillator with a veto counter, phoswich detector and a Bonner ball counter on trial. Preliminary experimental results are presented.
Kinoshita, Motoyasu*; Geng, H. Y.*; Chen, Y.*; Kaneta, Yasunori*; Iwasawa, Misako*; Onuma, Toshiharu*; Sonoda, Takeshi*; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 2006 International Meeting on LWR Fuel Performance (TopFuel 2006) (CD-ROM), p.248 - 254, 2006/10
The New Crossover Project (NXO) is studying effect of fission irradiation on fuel material that research activity is crossing over universities, national and private laboratories. Simulation studies are being performed to find principal and triggering processes of the rim-structure formation in high burnup LWR fuel pellet, using accelerator irradiation and computational calculations. Accelerator irradiation, high energy electron irradiation, fission energy particle beam and ion implantation (ragegas atoms) and combined overlapping irradiations are being performed. For the target of irradiation, CeO isused as simulation of nuclear fuel. The initial results were such as planar structure made by Oxygen defects created by high energy electrons, and surface modification similar to grain-sub-division created by high fluence high energy particle irradiations.
isused as simulation of nuclear fuel. The initial results were such as planar structure made by Oxygen defects created by high energy electrons, and surface modification similar to grain-sub-division created by high fluence high energy particle irradiations.
Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Shimada, Mikio*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.235 - 238, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.83(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the microstructure change and atomic disordering process in magnesium aluminate spinel, MgO  Al
Al O
O with
with  =1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe
=1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe and 350-MeV Au
and 350-MeV Au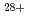 . Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12
. Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12 2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
Sataka, Masao; Ishikawa, Norito; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Okubo, Nariaki; Sonoda, Takeshi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Shiiyama, Kenichi*; Abe, Hiroaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsumura, Sho*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Shiiyama, Kenichi*; Sonoda, Takeshi*; Abe, Hiroaki*; Iwai, Takeo*; Sataka, Masao; Ishikawa, Norito; Chimi, Yasuhiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 pre-implanted with Xe ions
pre-implanted with Xe ionsYasunaga, Kazufumi*; Sonoda, Takeshi*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Shiiyama, Kenichi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Sataka, Masao; Ishikawa, Norito; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Okubo, Nariaki; Iwase, Akihiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
Irradiation experiments were performed for CeO using ion accelerators. CeO
using ion accelerators. CeO were first pre-implanted with 2at.% Xe and furthermore heavily irradiated with high-energy heavy ions, and as a result restructuring of dislocation has been found.
were first pre-implanted with 2at.% Xe and furthermore heavily irradiated with high-energy heavy ions, and as a result restructuring of dislocation has been found.
Sonoda, Takeshi*; Ishikawa, Norito; Sataka, Masao; Okubo, Nariaki; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Shiiyama, Kenichi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Kinoshita, Motoyasu*
no journal, ,
In order to elucidate the radiation damage in nuclear fuel, simulation material CeO has been irradiated with ions and its damage has been investigated. It is found that by 210MeV Xe irradiation subdivision of crystals is promoted, and Xe-preimplantation accelerates it.
has been irradiated with ions and its damage has been investigated. It is found that by 210MeV Xe irradiation subdivision of crystals is promoted, and Xe-preimplantation accelerates it.
Kinoshita, Motoyasu; Chen, Y.*; Sonoda, Takeshi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Nishiura, Yasumasa*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jinichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kinoshita, Motoyasu; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Sonoda, Takeshi*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Ishikawa, Norito; Sataka, Masao; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Geng, H. Y.*; Ichinomiya, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We show the outline of achievements of New Cross Over (NXO) project. Concerning the grain subdivision of ceramics fuel at high burnup, we are trying to clarify the mechanisms and to develop the simulation methods. The main high lights are as follow as: (1) We have reproduced the grain subdivision of CeO , by means of ion implanter and TUNDEM accelerator. (2) We performed computational science study concerning the relocation of oxygen. In case of oxygen exess conditions, first principal calculation reproduced the orderring structure. TAD calculation shows that the exess oxygen compose clusters and diffuses rapidly even if low temperature.
, by means of ion implanter and TUNDEM accelerator. (2) We performed computational science study concerning the relocation of oxygen. In case of oxygen exess conditions, first principal calculation reproduced the orderring structure. TAD calculation shows that the exess oxygen compose clusters and diffuses rapidly even if low temperature.
Kinoshita, Motoyasu; Chen, Y.*; Abe, Hiroaki*; Nishiura, Yasumasa*; Matsumura, Sho*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Sonoda, Takeshi*; Sataka, Masao; Kaburaki, Hideo; Nakamura, Jinichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 and CeO
and CeO for clarification of grain sub-division mechanism in high burnup fuels
for clarification of grain sub-division mechanism in high burnup fuelsSonoda, Takeshi*; Ishikawa, Norito; Sataka, Masao; Okubo, Nariaki; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Shiiyama, Kenichi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Kinoshita, Motoyasu
no journal, ,
Ion irradiation was performed for CeO and UO
and UO . Same kind of microstructure change is observed for both of the oxide materials.
. Same kind of microstructure change is observed for both of the oxide materials.
 irradiated with swift heavy ions
irradiated with swift heavy ionsYasunaga, Kazufumi*; Sonoda, Takeshi*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Shiiyama, Kenichi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Sataka, Masao; Ishikawa, Norito; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kinoshita, Motoyasu
no journal, ,
In order to study the elementary damage process of high burnup structure of light water reactor, ion implantation and ion irradiation were performed for CeO . It is suggested from the observation of electron microscopy that Xe gas suppress movement of dislocation in CeO
. It is suggested from the observation of electron microscopy that Xe gas suppress movement of dislocation in CeO .
.
Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Arakawa, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
A gold activation detector was studied as a high energy neutron detector at high radiation field in a series of shielding experiment at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. We could measure spallation residual nuclei with wide threshold energy by using a combination method with radiological chemical separation and X-X- coincidence detection methods. It was shown the detector was effective for high energy neutron detector.
coincidence detection methods. It was shown the detector was effective for high energy neutron detector.
Takaki, Seiya; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito
no journal, ,
Advanced nuclear application materials are irradiated by fast neutrons, electrons, a particles and fission fragments, so formation of radiation damage and microstructure evolution are induced by pile-up effect of those radiation. Behavior of point defects in materials which has ion and covalent bonding is influenced by electronic excitation. Especially, high-density electronic excitation damage induced by fission fragments, induce to form cylindrical defect, so called ion track in the materials to result in influence for microstructural evolution in fuel materials. This study aims to clarify the structure of ion tracks in CeO and cubic ZrO
and cubic ZrO (YSZ) irradiated with swift heavy ions by using several transmission electron microscopies. It was shown that the density of vacancy at the core damage region of ion tracks is increased and the O anion lattice is preferentially disordered at such region. In addition to, high density dislocation was formed in CeO
(YSZ) irradiated with swift heavy ions by using several transmission electron microscopies. It was shown that the density of vacancy at the core damage region of ion tracks is increased and the O anion lattice is preferentially disordered at such region. In addition to, high density dislocation was formed in CeO with irradiated by high fluence. This result support STEM observation. In case of YSZ, the size and the areal density of ion tracks is smaller than those of CeO
with irradiated by high fluence. This result support STEM observation. In case of YSZ, the size and the areal density of ion tracks is smaller than those of CeO . The difference of ion tracks between CeO
. The difference of ion tracks between CeO and YSZ is presumably due to the difference in the recovery process from the thermal spike regime, which is influenced by the presence of structural vacancy in oxide sublattice.
and YSZ is presumably due to the difference in the recovery process from the thermal spike regime, which is influenced by the presence of structural vacancy in oxide sublattice.
Suzuki, Akihiro*; Mizusako, Fumiki*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; Hoshino, Kuniyoshi*; Muroya, Yusa*; Matsumura, Tatsuro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English