Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mn
MnShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 245, p.116051_1 - 116051_6, 2024/05
Hydrogen at the mass ppm level causes hydrogen embrittlement in metallic materials, but it is extremely difficult to experimentally elucidate the hydrogen trapping sites. We have taken advantage of the fact that positive muons can act as light isotopes of hydrogen to study the trapping state of hydrogen in matter. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments and the density functional theory (DFT) calculations for hydrogen trapping energy are carried out for Al Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al
Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width (
Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width ( ) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed
) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed  change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
 muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations
muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculationsTsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 54(6), p.2374 - 2383, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Although hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high-strength Al alloys is recognized as a critical issue in the practical use of Al alloys, identifying the hydrogen trapping or distribution has been challenging. In the present study, an effective approach based on experiment and simulation is proposed to explore the potential trap sites in Al alloys. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were carried out for Al-0.5%Mg, Al-0.2%Cu, Al-0.15%Ti, Al-0.011%Ti, Al-0.28%V, and Al-0.015%V (at.%) in the temperature range from 5 to 300 K. The temperature variations of the dipole field widths have revealed three peaks for Al-0.5%Mg, four peaks for Al-0.2%Cu, three peaks for Al-0.011%Ti and Al-0.015%V. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon
peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon  peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
Toda, Hiroyuki*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*
Kagaku, 75(10), p.48 - 53, 2020/10
Highly-concentrated precipitations play therefore dominant role in mechanical properties and hydrogen embrittlement of aluminum alloys. It has been considered that the coherent interface between matrix and precipitation does not contribute to the crack initiation and embrittlement due to its coherency. Here, we discovered the origin of unprecedented quasi-cleavage fracture mode. Hydrogen partitioning at various defect sites is investigated comprehensively combined with experiment, theory and first-principles calculations. We demonstrate that despite low excess free volume, the aluminum-precipitation interface is more preferable trap site than void and grain boundary. The cohesivity of the interface deteriorates significantly with increasing occupancy while hydrogen atoms are trapped stably up to extremely high occupancy equivalent to spontaneous cleavage.
 Si and Al
Si and Al FeCu
FeCu intermetallic compounds in aluminum alloy; First-principles calculations
intermetallic compounds in aluminum alloy; First-principles calculationsYamaguchi, Masatake; Tsuru, Tomohito; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Materials Transactions, 61(10), p.1907 - 1911, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:55.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Materials Science and Technology, 36(15), p.1621 - 1627, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable phases in aluminum alloys are the primary nano-scale precipitates which have the biggest contribution to the increase in the tangible mechanical properties. The continuous increase in hardness in the 7xxx aluminum alloys is associated with the phase transformation from clusters or GP-zones to the metastable  phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of
phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of  phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Ebihara, Kenichi; Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.1998_1 - 1998_8, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:82.42(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Age-hardening has been one and only process to achieve high strength aluminum alloys since unlike iron and titanium, pure aluminum does not have other solid phases during heat treatment. Highly-concentrated precipitations play therefore dominant role in mechanical properties and hydrogen embrittlement of aluminium alloys. It has been considered that the coherent interface between matrix and precipitation does not contribute to the crack initiation and embrittlement due to its coherency. Here, we discovered the origin of unprecedented quasi-cleavage fracture mode. Hydrogen partitioning at various defect sites is investigated comprehensively combined with experiment, theory and first-principles calculations. We demonstrate that despite low excess free volume, the aluminum-precipitation interface is more preferable trap site than void and grain boundary. The cohesivity of the interface deteriorates significantly with increasing occupancy while hydrogen atoms are trapped stably up to extremely high occupancy equivalent to spontaneous cleavage.
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lervik, A.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Holmestad, R.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Materials Characterization, 158, p.109958_1 - 109958_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Characterization of precipitates in Al-Zn-Mg alloys, using a combination of electron diffraction, bright field transmission electron microscopy and atomic scale scanning transmission electron microscopy imaging revealed the presence of an unreported 
 orientation relationship between the
orientation relationship between the  -MgZn
-MgZn phase and the Al lattice with the following orientation relationship (0001)
phase and the Al lattice with the following orientation relationship (0001)
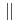 (120)
(120)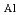 and (
and (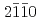 )
)
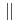 (001)
(001)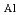 , plate on (120)
, plate on (120)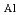 . The precipitate interfaces were observed and analyzed along two projections 90
. The precipitate interfaces were observed and analyzed along two projections 90 to one-another. The precipitate coarsening was through the common thickening ledge mechanism. The ledges were significantly stepped along one lateral direction. An interface relaxation model using density functional theory was carried out to explain the precipitate behavior.
to one-another. The precipitate coarsening was through the common thickening ledge mechanism. The ledges were significantly stepped along one lateral direction. An interface relaxation model using density functional theory was carried out to explain the precipitate behavior.
Kokabu, Hiroki*; Yoon, S.*; Lee, H.*; Nakajima, Kaoru*; Matsuda, Makoto; Sataka, Masao*; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Toulemonde, M.*; Kimura, Kenji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 460, p.34 - 37, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)Matsuda, Kenji*; Yasumoto, Toru*; Bendo, A.*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Marioara, C. D.*; Lervik, A.*; Holmestad, R.*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 60(8), p.1688 - 1696, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:63.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Bendo, A.*; Maeda, Tomoyoshi*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lervik, A.*; Holmestad, R.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; et al.
Philosophical Magazine, 99(21), p.2619 - 2635, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:82.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lee, S.*; Nunomura, Norio*; Shimano, Tomoki*; Bendo, A.*; Watanabe, Katsumi*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 774, p.405 - 409, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.96(Chemistry, Physical) hydrogen partitioning control
hydrogen partitioning controlToda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Su, H.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Tetsu To Hagane, 105(2), p.240 - 253, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Computational Materials Science, 156, p.368 - 375, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:78.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The segregation of multiple hydrogen atoms along aluminum (Al) grain boundaries (GBs) and fracture surfaces (FSs) was investigated through first-principles calculations considering the characteristics of GBs. The results indicate that hydrogen segregation is difficult along low-energy GBs. The segregation energy of multiple hydrogen atoms along GBs and FSs and the cohesive energy was obtained for three types of high-energy Al GBs. With increasing hydrogen segregation along the GBs, the cohesive energy of the GB decreases and approaches zero with no decrease in GB segregation energy. The GB cohesive energy decreases in parallel with the volume expansion of the region of low electron density along the GB.
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake
Materialia, 3, p.50 - 56, 2018/11
 precipitate in Al-Mg-Zn alloys
precipitate in Al-Mg-Zn alloysTsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Computational Materials Science, 148, p.301 - 306, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:82.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high strength 7xxx series Al alloys has been recognized as the critical issues in the practical use of Al alloys. Focusing on the interface between MgZn precipitates and an Al matrix, which is considered as one of the important segregation sites in these alloys, we investigated the stable
precipitates and an Al matrix, which is considered as one of the important segregation sites in these alloys, we investigated the stable  -MgZn
-MgZn -Al interface, and the possible hydrogen trap sites in MgZn
-Al interface, and the possible hydrogen trap sites in MgZn and at the
and at the  -MgZn
-MgZn -Al interface via first-principles calculation. Most of the interstitial sites inside the MgZn
-Al interface via first-principles calculation. Most of the interstitial sites inside the MgZn crystal were not possible trap sites because their energy is relatively higher than that of other trap sites. The trap energy of the most favorable site at the
crystal were not possible trap sites because their energy is relatively higher than that of other trap sites. The trap energy of the most favorable site at the  -MgZn
-MgZn -Al is approximately -0.3 eV/H, which is more stable that of the interstitial site at the grain boundary. The interface between MgZn
-Al is approximately -0.3 eV/H, which is more stable that of the interstitial site at the grain boundary. The interface between MgZn and Al is likely to be a possible trap site in Al alloys.
and Al is likely to be a possible trap site in Al alloys.
Matsuzaki, Shota*; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Nakajima, Kaoru*; Matsuda, Makoto; Sataka, Masao*; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Toulemonde, M.*; Kimura, Kenji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 406(Part B), p.456 - 459, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:37.06(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nakajima, Kaoru*; Kitayama, Takumi*; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Matsuda, Makoto; Sataka, Masao*; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Toulemonde, M.*; Bouffard, S.*; Kimura, Kenji*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 5, p.13363_1 - 13363_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.15(Multidisciplinary Sciences) impacts
impactsKitayama, Takumi*; Nakajima, Kaoru*; Suzuki, Motofumi*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Saito, Yuichi; Matsuda, Makoto; Sataka, Masao*; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Isoda, Shoji*; Kimura, Kenji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 354, p.183 - 186, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Hirayama, Hideo*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Mokhov, N.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.2055 - 2058, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)It is important to obtain neutron spectra and its intensity on shielding experiment. Deduction of high-energy neutron spectra were done using fitting and unfolding methods based on the shielding data obtained at the anti-proton (pbar) target station in Fermilab. The neutron spectra for fitting method is useful to be easily obtained and the values gave reasonable results compared with nuclear data. Therefore, that for unfolding methods included inconsistency. Furthermore, the deduced neutron spectra were verified through the calculation analyses by PHITS code.
Yashima, Hiroshi*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; Vaziri, K.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.48 - 51, 2011/02
The shielding experiment was performed at the anti-proton production target station in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. Aluminum, Bismath, Niobium, Copper and Indium samples were placed behind the shields. After irradiation, induced activities of samples were measured by using HPGe detector. The spatial distribution of reaction rate of samples which were placed behind the iron and concrete shields were obtained. The measured data shows that the reaction rates on the outer surfaces of the iron and concrete shields increases toward the downstream of the target. The obtained reaction rates were also fitted to Moyer's formula, and the attenuation lengths for iron and concrete shields were obtained.