Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Arakaki, Yu; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Murakami, Takahiko; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
New experiments simulating fuel debris in the new criticality assembly, STACY, are designed to contribute to the validation of criticality calculations for criticality control of the fuel debris in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. In the new STACY experiment, a two-region core consisting of a driver region and a test region was investigated in order to configure a debris-simulated core with under-moderation condition (lattice pitch 1.27-cm) having the constraint of available fuel rod number. The test region with a 1.27-cm lattice pitch is surrounded by the driver region, in which fuel rods are arranged in a checkerboard pattern on a 1.27-cm lattice plate, with a 1.80-cm lattice pitch. Neutron spectra and sensitivity were calculated by using MCNP6 and ENDF/B-VII. The core which has a 17 17 test region with 373 fuel rods is the largest two-region core under the constraint. It was found that the core which has a 17
17 test region with 373 fuel rods is the largest two-region core under the constraint. It was found that the core which has a 17 17 test region can simulate the neutron spectra of under-moderation condition in a 13
17 test region can simulate the neutron spectra of under-moderation condition in a 13 13 region inside the test region with the root-mean square percentage error of less than 5%. It was also confirmed that the sensitivity of
13 region inside the test region with the root-mean square percentage error of less than 5%. It was also confirmed that the sensitivity of  Si and
Si and  Ca (n,
Ca (n, ) reactions when the concrete simulant, was loaded could be simulated.
) reactions when the concrete simulant, was loaded could be simulated.
 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:48.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
 Zn
Zn probed by muon spin relaxation
probed by muon spin relaxationHigemoto, Wataru; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Saiga, Yuta*; Kosaka, Masashi*; Matsubayashi, Kazuyuki*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012039_1 - 012039_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.21(Physics, Applied)The cubic compound YbCo Zn
Zn has huge electronic specific heat coefficient and its ground state could be located in the vicinity of the quantum critical point. Indeed, a magnetic long-range order was observed under pressure above 1-2 GPa. To investigate magnetic ground state, we have carried out muon spin relaxation measurements and confirm non-magnetic ground state with fluctuating tiny magnetic moment.
has huge electronic specific heat coefficient and its ground state could be located in the vicinity of the quantum critical point. Indeed, a magnetic long-range order was observed under pressure above 1-2 GPa. To investigate magnetic ground state, we have carried out muon spin relaxation measurements and confirm non-magnetic ground state with fluctuating tiny magnetic moment.
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of European Research Reactor Conference 2020 (RRFM 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/10
Critical experiments of thermal neutron system are still expected to be playing an important role for wide technical issues. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is renovating the Static Experimental Critical Facility (STACY) to maintain the experimental capability. The new STACY is designed as a general-purpose criticality facility. Its core mainly consists of low enriched UO fuel rods, grid plates, and light water moderator. The first experiment campaign in the new STACY aims to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris, which will be used in validation of criticality analysis methods. The designs of the experimental core configurations are in progress.
fuel rods, grid plates, and light water moderator. The first experiment campaign in the new STACY aims to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris, which will be used in validation of criticality analysis methods. The designs of the experimental core configurations are in progress.
Shimada, Koji; Kametaka, Masao*; Nakayama, Kazuhiko; Seshimo, Kazuyoshi; Tanaka, Yoshihiro; Hayashi, Toshio*; Tanaka, Yukumo; Shimogama, Kota*; Okazaki, Kazuhiko*
Chishitsugaku Zasshi, 119(11), p.727 - 731, 2013/11
Staples for a stapler can be used as a frame of a small oriented sample taken from fragile and scarce fault gouge. The fault gouge was slotted for staples of an insert. Staples are a group of about ten or less ones holding right-angled three small surfaces. Pre-oriented staples set the slot would remove then presented for the SEM observation. Only a knife, some glues and simple equipment are needed for the method in the field or laboratories.
 melt by two-dimensional detector at 1 kHz
melt by two-dimensional detector at 1 kHzKumar, M. V.*; Kuribayashi, Kazuhiko*; Nagashio, Kosuke*; Ishikawa, Takehiko*; Okada, Jumpei*; Yu, J.*; Yoda, Shinichi*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Applied Physics Letters, 100(19), p.191905_1 - 191905_4, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.9(Physics, Applied) identification of metastable phases formed from the undercooled LuFeO
identification of metastable phases formed from the undercooled LuFeO melt under controlled oxygen partial pressure
melt under controlled oxygen partial pressure  o
o was studied by X-ray diffraction measurements at a synchrotron radiation source. Real-time observation of the formation and growth of individual phases during the single recalescence of Lu
was studied by X-ray diffraction measurements at a synchrotron radiation source. Real-time observation of the formation and growth of individual phases during the single recalescence of Lu Fe
Fe O
O and LuFe
and LuFe O
O phases at
phases at  o
o of 1
of 1 10
10 Pa has been revealed by a high speed imaging system at 1 kHz. The obtained diffraction pattern of the metastable phase in the LuFeO
Pa has been revealed by a high speed imaging system at 1 kHz. The obtained diffraction pattern of the metastable phase in the LuFeO system was consistent with that of the metastable and stable phases reported in the Lu-Fe-O system.
system was consistent with that of the metastable and stable phases reported in the Lu-Fe-O system.
Li, M.*; Nagashio, Kosuke*; Ishikawa, Takehiko*; Mizuno, Akitoshi*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Watanabe, Masahito*; Yoda, Shinichi*; Kuribayashi, Kazuhiko*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Acta Materialia, 56(11), p.2514 - 2525, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:71.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Co-61.8 at.% Si (CoSe-CoSi ) eutectic alloys were solidified on an electromagnetic levitator (EML) and an electrostatic levitator (ESL) at different undercooling levels. The results indicated that there is only a single recalescence event at low undercooling with the CoSi intermetallic compound as primary phase, which is independent of processing facilities, on either an EML or an ESL. The microstructure, however, is strongly dependent on the processing facility. On high undercooling, double recalescence takes place regardless of levitation condition. In situ X-ray diffraction of alloys solidified on the EML demonstrates that the CoSi
) eutectic alloys were solidified on an electromagnetic levitator (EML) and an electrostatic levitator (ESL) at different undercooling levels. The results indicated that there is only a single recalescence event at low undercooling with the CoSi intermetallic compound as primary phase, which is independent of processing facilities, on either an EML or an ESL. The microstructure, however, is strongly dependent on the processing facility. On high undercooling, double recalescence takes place regardless of levitation condition. In situ X-ray diffraction of alloys solidified on the EML demonstrates that the CoSi compound becomes the primary phase upon the first recalescence, and the CoSi intermetallic phase crystallizes during the second recalescence. In addition to phase identification, real-time diffraction patterns can also provide additional evidence of the fragmentation of the primary phase.
compound becomes the primary phase upon the first recalescence, and the CoSi intermetallic phase crystallizes during the second recalescence. In addition to phase identification, real-time diffraction patterns can also provide additional evidence of the fragmentation of the primary phase.
Toida, Masaru*; Suyama, Yasuhiro*; Mori, Takayuki*; Inaba, Takeshi*; Sasakura, Takeshi*; Atsumi, Hiroyuki*; Masumoto, Kazuhiko*; Kobayashi, Ichizo*; Iwano, Keita*; Furuichi, Mitsuaki*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2007-065, 210 Pages, 2007/09
"Geoscientific research" at the Tono Area is developing site investigation, characterization and assessment techniques for understanding of geological environment. Their important goals are to establish a methodology for analyzing uncertainties in heterogeneous geological environment and to develop investigation techniques for efficiently reducing the uncertainties. The current study proposes a new approach where all the possible options in the models and data-sets, which cannot be excluded in the light of the evidences available, are identified. This approach enables uncertainties associated with the understanding at a given stage of the site characterization to be made explicitly using an uncertainty analysis technique based on Fuzzy geostatistics. This approach supports the design of the following investigation stage and reduces the uncertainties efficiently. In FY H16 the technique has been tested through geological modelling and groundwater analyses with Tono Area case based on current knowledge, to demonstrate its applicability and to compile the knowledge / information required to describe the H17 report. This report can be summarized as follows: (1) The knowledge / information required to describe the heterogeneous characteristics was compiled and connected to uncertainties associated with the characterization of a geological environment using a synthesis diagram. (2) Methodologies for assignment and screening of parameters were developed by using Evidential Support Logic (ESL). (3) Applicability of the techniques could be confirmed with Tono Area case. (4) This report proposed a new methodology that integrates the technique into JAEA ordinary technique to good advantage in the geoscientific research project.
Nagashio, Kosuke*; Nozaki, Kiyoshi*; Kuribayashi, Kazuhiko*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Applied Physics Letters, 91(6), p.061916_1 - 061916_3, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.4(Physics, Applied)The spontaneous dendrite fragmentation in solidification from undercooled Si melt was studeid by time-resolved 2D X-ray diffractometry using sinchrotron radiation. For the sample solidified at 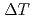 =261 K, several diffraction spots appeared at 1 ms after recalescence and the subsequent transition from spots to rings occurred within
=261 K, several diffraction spots appeared at 1 ms after recalescence and the subsequent transition from spots to rings occurred within  25 ms, which suggests that the fragmentation occurred after recalescence but just at the initial stage of the plateau period. Although the present experiment supported that the driving force for the fragmentation is a capillarity effect at the plateau period, the time scale for the fragmentation differed from the current quantitative prediction.
25 ms, which suggests that the fragmentation occurred after recalescence but just at the initial stage of the plateau period. Although the present experiment supported that the driving force for the fragmentation is a capillarity effect at the plateau period, the time scale for the fragmentation differed from the current quantitative prediction.
Takamura, Shuichi*; Kado, Shinichiro*; Fujii, Takashi*; Fujiyama, Hiroshi*; Takabe, Hideaki*; Adachi, Kazuo*; Morimiya, Osamu*; Fujimori, Naoji*; Watanabe, Takayuki*; Hayashi, Yasuaki*; et al.
Kara Zukai, Purazuma Enerugi No Subete, P. 164, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
 identification of the metastable phase during solidification from the undercooled YFeO
identification of the metastable phase during solidification from the undercooled YFeO melt by fast X-ray diffractometry at 250 Hz
melt by fast X-ray diffractometry at 250 HzNagashio, Kosuke*; Kuribayashi, Kazuhiko*; Vijaya Kumar, M. S.*; Niwata, Kenji*; Hibiya, Taketoshi*; Mizuno, Akitoshi*; Watanabe, Masahito*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Applied Physics Letters, 89(24), p.241923_1 - 241923_3, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:61.1(Physics, Applied)A time-resolved X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiment at 250 Hz using a synchrotron radiation source was carried out during the containerless solidification of ReFeO (Re=Y and Lu) in order to identify the metastable phase
(Re=Y and Lu) in order to identify the metastable phase  . The metastable phase solidified primarily from the undercooled YFeO
. The metastable phase solidified primarily from the undercooled YFeO melt finally transformed to the stable orthorhombic YFeO
melt finally transformed to the stable orthorhombic YFeO phase during the short period of recalescence (
phase during the short period of recalescence ( 0.035 s). Although the metastable phase could not be detected in the as-solidified sample by the powder XRD, the successfully obtained diffraction pattern of the metastable phase in the YFeO
0.035 s). Although the metastable phase could not be detected in the as-solidified sample by the powder XRD, the successfully obtained diffraction pattern of the metastable phase in the YFeO system was consistent with that of the metastable hexagonal LuFeO
system was consistent with that of the metastable hexagonal LuFeO phase.
phase.
Nagashio, Kosuke*; Adachi, Masayoshi*; Higuchi, Kensuke*; Mizuno, Akitoshi*; Watanabe, Masahito*; Kuribayashi, Kazuhiko*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Journal of Applied Physics, 100(3), p.033524_1 - 033524_6, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:47.09(Physics, Applied)Grain refined microstructure is often obtained spontaneously in the solidification of metals and semiconductors from the undercooled melt without any external forces. Although it has been reported that the grain refinement is mainly caused by the fragmentation of the dendrites, the dynamic process of the fragmentation of dendrites has not been fully understood because the microstructure after the solidification has been analyzed. Here, we present a time-resolved 2- dimensional X-ray diffraction experiment on the solidification of Si from the undercooled melt. The number of diffraction spots observed at low undercoolings (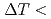 100K) did not increase at the plateau stage, while the diffraction pattern at medium undercoolings (100K
100K) did not increase at the plateau stage, while the diffraction pattern at medium undercoolings (100K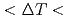 200K) changed from the spots with the tail to rings with the lapse of time. Both this result and high speed video imaging suggested that the high-order arms of the dendrites mostly detached from the main stems because nucleation could not be expected at the melting point after recalescence. The several spots observed at low undercoolings drastically changed to rings at high undercoolings (
200K) changed from the spots with the tail to rings with the lapse of time. Both this result and high speed video imaging suggested that the high-order arms of the dendrites mostly detached from the main stems because nucleation could not be expected at the melting point after recalescence. The several spots observed at low undercoolings drastically changed to rings at high undercoolings (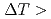 200K), which indicated the complete fragmentation of dendrite main stem as well as high-order arms. This complete fragmentation resulted in the grain refined microstructure.
200K), which indicated the complete fragmentation of dendrite main stem as well as high-order arms. This complete fragmentation resulted in the grain refined microstructure.
Toida, Masaru*; Sasakura, Takeshi*; Atsumi, Hiroyuki*; Masumoto, Kazuhiko*; Tanaka, Toshiyuki*; Suyama, Yasuhiro*; Kobayashi, Ichizo*
JNC TJ8400 2004-023, 146 Pages, 2005/02
To establish sealing technique suitable for geological environmental conditions of Japan, it is necessary to obtain data related with this sealing function through laboratory tests and in-situ tests. It also is necessary to put these data to practical use and to establish the estimating method of the sealing technique.Tunnel sealing experiment, which has been carried out as collaboration between JNC and AECL at URL of AECL Canada, is progressing in the final stage and fundamental data relating with the sealing function has almost obtained. This report deals with the total data processing and interpretation of the sealing experiment, as well as the numerical analysis and interpretation on tracer test results. Conceptual plans of the experiment to confirm the performance of tunnel sealing technique in a sedimentary rock are also discussed.
Higuchi, Kensuke*; Kimura, Kakuryo*; Mizuno, Akitoshi*; Watanabe, Masahito*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Kuribayashi, Kazuhiko*
Measurement Science and Technology, 16(2), p.381 - 385, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:87.03(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)X-ray diffraction and density measurements have been simultaneously performed to investigate the atomic structure of molten silicon in wide temperature range including undercooling region by using the electromagnetic levitation technique. The density was obtained from the mass and the shape of levitated sample by non-contact method based on the image analysis technique. X-ray diffraction experiments were performed by using the synchrotron radiation at SPring8, Japan. From structural analysis of undercooled molten silicon, first nearest neighbour coordination numbers and interatomic distances were about 5 and 2.48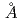 with no dependence on temperature in the range of 1900-1550 K. We conclude as a result that the short-range order based on tetrahedral bonds of undercooled molten silicon does not change with the degree of undercoolings but medium-range order changes by the degree of undercoolings.
with no dependence on temperature in the range of 1900-1550 K. We conclude as a result that the short-range order based on tetrahedral bonds of undercooled molten silicon does not change with the degree of undercoolings but medium-range order changes by the degree of undercoolings.
 ray from fuel of High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor; Method of measurement and results
ray from fuel of High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor; Method of measurement and resultsFujimoto, Nozomu; Nojiri, Naoki; Takada, Eiji*; Yamashita, Kiyonobu; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Kojima, Takao; Umeta, Masayuki; Hoshino, Osamu; Kaneda, Makoto*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2001-002, 64 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Tanai, Kenji; Iwasa, Kengo; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Miura, K.*; Okutsu, Kazuo*; Kobayashi, Masaaki*
JNC TN8400 99-046, 177 Pages, 1999/11
For the construction of underground facilities comprising access tunnels, connecting tunnels, main tunnels and disposal tunnels, a large number of tunnels will be excavated in deep rock formations. These excavations will extend hundreds kilometers in total length. Therefore, special attention must be paid, to transporting large volume of debris, ventilation, emergency escape routes in case of accident, and other factors. In addition, special attention must also paid to potential accidents which might in underground excavations, including unstable facing phenomena (such as collapse and swelling of facing at weak layer sections), spring water flow resulting collapse of rock, gas eruption, and rock burst. While considering these factors to be emphasized during the construction of geological disposal facilities, the investigation reviewed the existing working methods on individual construction technologies of access tunnels, main tunnels, connecting tunnels, disposal tunnels, and disposal pit, based on the recognition that the present state deals with a wide range of geological environments, and conducted investigation about the construction methods for each tunnel on the basis current technologies, and described the outline of these methods. Furthermore, for the items to be particulaly emphasized on site characterization koko and siting data such as ground pressure and spring water, the investigation reviewed the current countermeasure works, and made survey on the phenomena appeared during actual tunnel construction works and their countermeasres, and carried out a study on effectiveness of these countermeasures. This constructing of disposal site in deep geological formations is basically possible by applying, or confirming, current excavation technologies for tunnels and underground facilities, A systematic construction system combines separate technologies relating to construction, (excavation technology, tunnel support work method, etc.). Such systems ...
 Al superconductors for International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER)
Al superconductors for International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER)Yamada, Yuichi*; *; *; *; *; *; *; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Ando, Toshiro; Matsui, Kunihiro; et al.
Cryogenics, 39(2), p.115 - 122, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.96(Thermodynamics)no abstracts in English
Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Hada, Kazuhiko; Hayashi, Koji
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 41(3), p.250 - 257, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Hada, Kazuhiko; Hayashi, Koji
Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-7) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Saito, Shinzo; Tanaka, Toshiyuki; Sudo, Yukio; Baba, Osamu; Shindo, Masami; Shiozawa, Shusaku; Mogi, Haruyoshi; Okubo, Minoru; Ito, Noboru; Shindo, Ryuichi; et al.
JAERI 1332, 247 Pages, 1994/09
no abstracts in English