Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oshima, Katsumi; Oda, Yasuhisa; Takahashi, Koji; Terakado, Masayuki; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kajiwara, Ken; Sakamoto, Keishi
JAEA-Technology 2015-061, 65 Pages, 2016/03
In JAEA, an ITER relevant control system for ITER gyrotron was developed according to Plant Control Design Handbook. This control system was developed based on ITER CODAC Core System and implemented state machine control of gyrotron operation system, sequential timing control of gyrotron oscillation startup, and data acquisition. The operation of ITER 170 GHz gyrotron was demonstrated with ITER relevant power supply configuration. This system is utilized for gyrotron operation test for ITER procurement. This report describes the architecture of gyrotron operation system, its basic and detailed design, and recent operation results.
Narita, Ayumi; Kaminaga, Kiichi; Yokoya, Akinari; Noguchi, Miho; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Usami, Noriko*; Fujii, Kentaro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 166(1-4), p.192 - 196, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.85(Environmental Sciences)For the knowledge about irradiation effects of mammalian cells depending on the cell cycle, most of them had been analyzed by statistical approches. Our purpose is to establish the method for real-time observation of irradiated cells under a microscope. Fluorescent ubiquitination-based cell cycle indicator (FUCCI) human cancer (HeLa) cells (red indicates G1; green, S/G2) were exposed to a synchrotron X-ray microbeam. Cells in either G1 or S/G2 were selectively irradiated according to cell color observed in the same microscopic field in a culture dish. Time-lapse micrographs of the irradiated cells were acquired for 24 h after irradiation. The cell cycle was strongly arrested by irradiation at S/G2 and never progressed to G1. In contrast, cells irradiated at G1 progress to S/G2 with a similar time course as non-irradiated control cells. These results show single FUCCI cell exposure and live cell imaging are powerful methods for studying radiation effects on the cell cycle.
Oda, Yasuhisa; Oshima, Katsumi; Nakamoto, Takashi*; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 90(7), p.365 - 373, 2014/07
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Masao*; Autsavapromporn, N.*; Usami, Noriko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Plante, I.*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Muto, Yasuko*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Ikeda, Hiroko; Hattori, Yuya; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 55(Suppl.1), P. i54, 2014/03
Autsavapromporn, N.*; Suzuki, Masao*; Funayama, Tomoo; Usami, Noriko*; Plante, I.*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Muto, Yasuko*; Ikeda, Hiroko; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; et al.
Radiation Research, 180(4), p.367 - 375, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:89.88(Biology)We investigated the role of gapjunction intercellular communication (GJIC) in the propagation of stressful effects in confluent normal human fibroblast cultures wherein only 0.036-0.144% of cells in the population were traversed by primary radiation tracks. Confluent cells were exposed to graded doses from X ray, carbon ion, neon ion or argon ion microbeams in the presence or absence of an inhibitor of GJIC. After 4 h incubation, the cells were assayed for micronucleus (MN) formation. Micronuclei were induced in a greater fraction of cells than expected based on the fraction of cells targeted by primary radiation, and the effect occurred in a dose-dependent manner with any of the radiation sources. Interestingly, the inhibition of GJIC depressed the enhancement of MN formation in bystander cells from cultures exposed to high-LET radiation but not low-LET radiation. The results highlight the important role of radiation quality and dose in the observed effects.
Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Tanaka, Yutaka*; Kawai, Mikito*; Akino, Noboru; Kazawa, Minoru; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Usui, Katsutomi; Sasaki, Shunichi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083049_1 - 083049_8, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:88.4(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hydrogen negative ion beams of 490 keV, 3 A and 510 keV, 1 A have been successfully produced in the JT-60 negative ion source with three acceleration stages. These successful productions of the high-energy beams at high current have been achieved by overcoming the most critical issue, i.e., a poor voltage holding of the large negative ion sources with the grids of 2 m for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m
for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m ). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60SA and ITER.
). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60SA and ITER.
Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Tanaka, Yutaka*; Kawai, Mikito*; Akino, Noboru; Kazawa, Minoru; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Usui, Katsutomi; Sasaki, Shunichi; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Hydrogen negative ion beams of 490keV, 3A and 510 keV, 1A have been successfully produced in the JT-60 negative ion source with three acceleration stages. These successful productions of the high-energy beams at high current have been achieved by overcoming the most critical issue, i.e., a poor voltage holding of the large negative ion sources with the grids of  2 m
2 m for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m
for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m ). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60 SA and ITER.
). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60 SA and ITER.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Yokoya, Akinari; Cunniffe, S. M. T.*; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Kobayashi, Katsumi*; O'Neill, P.*
Radiation Research, 172(3), p.296 - 305, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:60.53(Biology)To characterize the DNA damage induced by K-shell ionization of phosphorus atom in DNA backbone on the level of hydration, the yields of DNA strand breaks and base lesions arising from the interaction of ultrasoft X-rays (USX) with energies around the phosphorus K-edge were determined using dry and fully hydrated pUC18 plasmid DNA samples. Base lesions and bistranded clustered DNA damage sites were revealed by post-irradiation treatment with the base excision repair proteins, Nth and Fpg. The complex types of damage, prompt and enzymatically induced DSB are preferentially induced by phosphorus K-resonance at 2153 eV rather than simple SSB and isolated base lesions particularly in hydrated conditions. It is concluded that not only the phosphorus K-resonance and resulting emission of low energy LMM-Auger electrons ( 120 eV) but also the level of hydration plays an important role in the induction of complex damage in plasmid DNA.
120 eV) but also the level of hydration plays an important role in the induction of complex damage in plasmid DNA.
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Konishi, Teruaki*; Imaseki, Hitoshi*; Yasuda, Keisuke*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Takagi, Keiichi*; Hatori, Satoshi*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(Suppl.A), p.A29 - A47, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:72.75(Biology)Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Hanada, Masaya; Kamada, Masaki; Kobayashi, Kaoru; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Inoue, Takashi; Honda, Atsushi; Kawai, Mikito; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1519 - 1529, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:41.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The JT-60SA N-NBI system is required to inject 10 MW for 100 s at 500 keV. Three key issues should be solved for the JT-60SA N-NBI ion source. One is to improve the voltage holding capability. Recent R&D tests suggested that the accelerator with a large area of grids may need a high margin in the design of electric field and a long time for conditioning. The second issue is to reduce the grid power loading. It was found that some beamlets were strongly deflected due to beamlet-beamlet interaction and strike on the grounded grid. The grids are to be designed by taking account of beamlet-beamlet interaction in three-dimensional simulation. Third is to maintain the D- production for 100 s. A simple cooling structure is proposed for the active cooled plasma grid, where a key is the temperature gradient on the plasma grid for uniform D- production. The modified N-NBI ion source will start on JT-60SA in 2015.
Nagoshi, Masayasu*; Kawano, Takashi*; Makiishi, Noriko*; Baba, Yuji; Kobayashi, Katsumi*
Surface and Interface Analysis, 40(3-4), p.738 - 740, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:7.02(Chemistry, Physical)Grazing incidence X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) has been applied to mirror-polished stainless steel sheets and Si-wafer using incident X-ray with high energy from synchrotron radiation. Monochromatized X-ray with the energy of 1.8 keV to 3.6 keV was irradiated to the sample surfaces with various incident angles. Total reflection condition with the high-energy incident X-ray provides us X-ray photoelectron spectra having remarkably low background intensity. The results will be compared with background calculations in previous researches and discussed in terms of the penetration depth of X-ray and inelastic mean free path of photoelectrons. We also discuss the depth information of the obtained spectra.
Masukawa, Fumihiro; Abe, Teruo*; Hayashi, Katsumi*; Handa, Hiroyuki*; Nakashima, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2006-024, 98 Pages, 2006/11
We have developed SHINE3, simple code for high energy neutron skyshine dose evaluation, for the shielding designs of high energy accelerator facilities. This code uses the 4-parametric fitting function to the skyshine dose response by neutron and secondary  -ray, which were predicted by PHITS, the general-purpose Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Monte Carlo code system. This code can be applied for skyshine dose evaluation of neutron up to 3 GeV in energy, and distance ranging between 10 and 2000 meters from source point, with equivalent accuracy as those by Monte Carlo Method.
-ray, which were predicted by PHITS, the general-purpose Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Monte Carlo code system. This code can be applied for skyshine dose evaluation of neutron up to 3 GeV in energy, and distance ranging between 10 and 2000 meters from source point, with equivalent accuracy as those by Monte Carlo Method.
Sasa, Toshinobu; Umeno, Makoto*; Mizubayashi, Hiroshi*; Mori, Keijiro*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Saito, Shigeru; Kai, Tetsuya; Nakai, Kimikazu*; Zako, Akira*; Kasahara, Yoshiyuki*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2005-021, 114 Pages, 2005/03
To perform the research and development for accelerator-driven system (ADS), Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) plans to build a Transmutation Experimental Facility under the JAERI-KEK joint J-PARC program. Transmutation Experimental Facility consists of two buildings, Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility to make reactor physics experiment with subcritical core, and ADS Target Test Facility for the preparation of irradiation database for various structural materials. In this report, purpose to build, experimental schedule, and design study of the ADS target test facility with drawer type spallation target are summarized.
Oyama, Hidenori*; Takakura, Kenichiro*; Nakabayashi, Masakazu*; Hirao, Toshio; Onoda, Shinobu; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Simoen, E.*; Claeys, C.*; Kuboyama, Satoshi*; Oka, Katsumi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 219-220, p.718 - 721, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Tayama, Ryuichi*; Hayashi, Katsumi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.30 - 33, 2004/03
The construction of Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) is planned under the framework of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) project. A liquid lead-bismuth (Pb-Bi) spallation target with beam power of 600MeV-200kW will be installed into the TEF. Analyses were performed to determine the effective thickness of biological shield for Pb-Bi target by using both MCNPX and ATRAS code system. Thickness of around 6m should be required to decrease the radiation level. The streaming analyses through the proton injection beam duct and the primary cooling circuit piping were also performed. The result of the beam duct streaming shows good agreement between the results of MCNPX and DUCT-III. The additional shield must be installed to suppress the activation of accelerator components. In the case of streaming through the primary cooling circuit piping, it is proved that the radiation level at the exit of the shield is allowable. The radiation level can be much more reduced by optimizing the bending position and length of the piping.
Nakano, Hideo*; Masukawa, Fumihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sasamoto, Nobuo*; Tayama, Ryuichi*; Handa, Hiroyuki*; Hayashi, Katsumi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.50 - 53, 2004/03
In order to estimate accuracy of the various calculation methods for the neutron streaming through a maze and duct in proton accelerator facilities, we performed benchmark analyses by using the radiation shielding design codes. According to the results of the benchmark analyses, it is concluded that NMTC/MCNP, MCNPX and DUCT-III are applicable to actual calculation of the duct-streaming radiations for J-PARC.
Masukawa, Fumihiro; Nakano, Hideo*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sasamoto, Nobuo; Tayama, Ryuichi*; Hayashi, Katsumi*; Shin, Kazuo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.46 - 49, 2004/03
A simple design code for duct-streaming radiations, DUCT-III was applied to the analyses of the streamed neutron spectra measured at TIARA labyrinth with two bends. The code satisfactorily reproduced the measured neutron energy spectra and the Monte Carlo calculations, except that every calculation overestimated the measured thermal components by factor of 2 or 3.
Masukawa, Fumihiro; Nakano, Hideo*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sasamoto, Nobuo; Tayama, Ryuichi*; Handa, Hiroyuki*; Hayashi, Katsumi*; Hirayama, Hideo*; Shin, Kazuo*
JAERI-Tech 2003-018, 42 Pages, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Usami, Noriko*; Yokoya, Akinari; Ishizaka, Shozo*; Kobayashi, Katsumi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 42(3), p.317 - 331, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:28.36(Biology)The characteristics of DNA lesions produced by the phosphorus K-shell absorption in yeast cells were studied using monochromatized soft X-rays tuned to the phosphorus K-edge peak (2153 eV) and below the peak energy (2147 eV). The repaired fractions of DNA double-strand breaks (dsb) were measured relatively by using both a mutant, (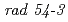 ), which shows the temperature-sensitive dsb repair-deficient, and a wild-type strain. The repaired fraction of lesion in
), which shows the temperature-sensitive dsb repair-deficient, and a wild-type strain. The repaired fraction of lesion in 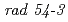 , which corresponds to the relative yield of dsb reparable by the
, which corresponds to the relative yield of dsb reparable by the 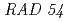 pathway, was not affected by the phosphorus photoabsorption. Repair of the produced lesions in the wild-type cells was also measured by comparing the surviving fraction of the immediately plated cells to that of those cells plated after holding in a non-nutrient medium for 80 hrs. The recovery of the surviving fraction after the holding treatment was dependent upon the soft X-ray energy. These results suggest that irrepairable lesions are produced by the inner-shell photoabsorption of phosphorus in DNA, although its yield is small.
pathway, was not affected by the phosphorus photoabsorption. Repair of the produced lesions in the wild-type cells was also measured by comparing the surviving fraction of the immediately plated cells to that of those cells plated after holding in a non-nutrient medium for 80 hrs. The recovery of the surviving fraction after the holding treatment was dependent upon the soft X-ray energy. These results suggest that irrepairable lesions are produced by the inner-shell photoabsorption of phosphorus in DNA, although its yield is small.