Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hayashi, Takao; Sakurai, Shinji; Sakasai, Akira; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Kono, Wataru*; Onawa, Toshio*; Matsukage, Takeshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 101, p.180 - 185, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Remote pipe welding tool accessing from inside pipe has been newly developed for JT-60SA. Remote handling (RH) system is necessary for the maintenance and repair of in-vessel components such as lower divertor cassettes in JT-60SA. Cooling pipes, which connects between the divertor cassette and the vacuum vessel with bellows are required to be cut and welded in the vacuum vessel by RH system. The available space for RH system is very limited inside the vacuum vessel, especially around the divertor cassettes. Thus, the cooling pipes are required to be cut and weld from the inside in the vacuum vessel. The inner diameter, thickness and material of the cooling pipe are 54.2 mm, 2.8 mm and SUS316L, respectively. An upper pipe connected to the divertor cassette has a jut on the edge to fill the gap between pipes. Owing to the jut and two-times welding, the welding tool achieved the maximum allowable gap of 0.7 mm.
Hayashi, Takao; Sakurai, Shinji; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Sakasai, Akira
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(9-10), p.2299 - 2303, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:67.4(Nuclear Science & Technology)Remote handling (RH) system is necessary for the maintenance and repair of in-vessel components of JT-60SA. Design study of RH system, focusing on the deployment of remote pipe cutting tool for JT-60SA divertor cassette is reported in this conference. Some cooling pipes on the outboard side in the divertor cassette should be cut and welded in the vacuum vessel. The outer diameter, thickness and material of the cooling pipe is 59.7 mm, 2.7 mm and SUS316L, respectively. Cutting tool head equips a disk cutter blade and rollers which are subjected to the reaction force. The cooling pipe is cut by rotating the cutting tool head with pushing out the disk cutter blade. Newly developed cutting tool indicates that the cooling pipe is cut by pushing out the disk cutter blade up to 30.5 mm in radius, i.e. 61 mm in diameter.
Yoshida, Masafumi; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Adachi, Ayumu*; Hayashi, Takao; Nakano, Tomohide; Fukumoto, Masakatsu; Yagyu, Junichi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Masaki, Kei; Itami, Kiyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 438, p.S1261 - S1265, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fuel retention rates and carbon re-deposition rates in the plasma shadowed areas in JT-60U were measured. Distributions of the fuel retention as well as the carbon re-deposition in the whole in-vessel of a large tokamak were clarified for the first time in the world. The fuel retention in the plasma shadowed areas was about two times larger than that in the carbon re-deposited layers on the plasma facing surface, although the amount of the carbon re-deposited on the plasma shadowed areas were about a half of that on the plasma facing surface, because of relatively lower temperature in the shadow areas causing higher hydrogen saturation concentration in the carbon re-deposited layers. The total fuel retention rate in JT-60U, including previously measured for all plasma facing areas, was evaluated to be 1.3 10
10 H+Ds
H+Ds , which was lower than that in other devices, due to probably to higher temperature operation in JT-60U.
, which was lower than that in other devices, due to probably to higher temperature operation in JT-60U.
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Hayashi, Takao; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Fukumoto, Masakatsu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 438, p.S659 - S663, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dust generated by the plasma-wall interaction is a potential source of the tritium retention in a fusion reactor. Dust samples were collected at 3, 5 and 3 different toroidal locations of the first wall, divertor surface and exhaust route under the divertor, respectively. On the tile surface, large number of dust was found, in particular, at the inner divertor rather upper area of the deposition layers, where recycling neutrals are increased during discharges. On the other hand, significant amount of dust (20-50 times larger) was generally accumulated at the bottom divertor, in particular, the plasma-unexposed area (remote area). It was found that the poloidal distribution is relatively symmetrical in the toroidal direction within a factor of three. Recently, analysis of dust spatial and size distributions, and evaluation of fuel retention in dust have been progressed. The total amount of the hydrogen isotope contained in the dust was estimated.
Ashikawa, Naoko*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Fukumoto, Masakatsu; Hayashi, Takao; Ueda, Yoshio*; Muroga, Takeo*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 438, p.S664 - S667, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:57.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, W concentrations of dusts at P-8 section and hydrogen isotope retentions in dusts are analyzed. Compositions of C including W material dusts were observed in JT-60U. For an enhanced resolution of the XPS measurement to analyze quantitatively the composition of the dust flakes, the new analysis using XPS with indium foil was done and showed that the dust flakes contains about less than 1% of tungsten in carbon. Compositions of tungsten-carbon mixed dusts at different poloidal positions are reported. Produced areas of dust including W is estimated on the outer doom wing by IMPGYRO code. Relative intensities at low temperature regions were smaller than bulk divertor target, which may be caused by the high baking/operation temperature. Amounts of retained Hydrogen/Deuterium in dust particles depend on internal defects and carbon composition of dusts.
Yoshida, Masafumi; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Hayashi, Takao; Nakano, Tomohide; Fukumoto, Masakatsu; Yagyu, Junichi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Masaki, Kei; Itami, Kiyoshi
Fusion Science and Technology, 63(1T), p.367 - 370, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, the retentions of hydrogen isotopes (H and D) in the gaps in JT-60U are clarified. Carbon tiles used in 1992-2004 were poloidally and toroidally taken out from outboard first wall in JT-60U to measure the retentions. The H and D retentions in the samples were measured by thermal desorption spectrometry (TDS). The H+D retention in the top side was higher than that of the bottom side, which might be due to thicker re-deposited carbon layers on the surface of the top side. The retentions in the surface of the side surfaces were slightly lower than that in the plasma facing surface where the retention was saturated to be 3-4e22 atoms/m . The retention rate was evaluated to be 3e17 H+D atoms/m
. The retention rate was evaluated to be 3e17 H+D atoms/m /s from the measured retentions in two different discharge times by assuming the retention to increase linearly with the discharge time.
/s from the measured retentions in two different discharge times by assuming the retention to increase linearly with the discharge time.
Sakasai, Akira; Masaki, Kei; Shibama, Yusuke; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Nakamura, Shigetoshi; Ozaki, Hidetsugu; Yokoyama, Kenji; Seki, Yohji; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
The JT-60SA vacuum vessel (VV) and divertor are key components for the performance requirements. Therefore the manufacturing and development of VV and divertor are in progress, inclusive of the superconducting magnets. The vacuum vessel has a double wall structure in high rigidity to withstand electromagnetic force at disruption and to keep high toroidal one-turn resistance. In addition, the double wall structure fulfills originally two functions. (1) The remarkable reduction of the nuclear heating in the superconducting magnets is made by boric-acid water circulated in the double wall. (2) The effective baking is enabled by nitrogen gas flow of 200 C in the double wall after draining of water. Three welding types were chosen for the manufacturing of the double wall structure VV to minimize deformation by welding. Divertor cassettes with fully water cooled plasma facing components were designed to realize the JT-60SA lower single null closed divertor. The divertor cassettes in the radio-active VV have been developed to ensure compatibility with remote handling (RH) maintenance in order to allow long pulse high performance discharges with high neutron yield. The manufacturing of divertor cassettes with typical accuracy of *1 mm has been successfully completed. Brazed CFC (carbon fiber composite) monoblock targets for a divertor target have been manufactured by precise control of tolerances inside CFC blocks. The infrared thermography test of monoblock targets has been developed as new acceptance inspection.
C in the double wall after draining of water. Three welding types were chosen for the manufacturing of the double wall structure VV to minimize deformation by welding. Divertor cassettes with fully water cooled plasma facing components were designed to realize the JT-60SA lower single null closed divertor. The divertor cassettes in the radio-active VV have been developed to ensure compatibility with remote handling (RH) maintenance in order to allow long pulse high performance discharges with high neutron yield. The manufacturing of divertor cassettes with typical accuracy of *1 mm has been successfully completed. Brazed CFC (carbon fiber composite) monoblock targets for a divertor target have been manufactured by precise control of tolerances inside CFC blocks. The infrared thermography test of monoblock targets has been developed as new acceptance inspection.
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Hayashi, Takao; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Hatae, Takaki; Nakano, Tomohide
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(4), p.1572 - 1575, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)Dust research has been performed in JT-60U in order to predict the plasma performance and the tritium retention in a fusion reactor. Laser scattering measurement showed, in specific discharge after disruptions, both the size and number were peaked in the far-SOL and they decreased near the separatrix. This result shows that sublimation of dust is dominant in the SOL. Dust collection after the experiment campaign showed that large weight of the dust was cumulated on the exhaust route of gas flow under the divertor. The total amount of the hydrogen isotope contained in the dust were estimated for the cases with deposited in the volume and near the surface.
Hayashi, Takao; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Nakano, Tomohide
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(4), p.1548 - 1551, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)A real mass densities of carbon dust collected in the baffle and divertor regions of JT-60U were investigated. On the plasma-exposed surface, large areal density of 610 mg/m is found at the upper tile of the inner divertor, which is much larger than other areas due to the soft deposition. On the other hand, as for the plasma-shadowed area, largest areal density of 5,100 mg/m
is found at the upper tile of the inner divertor, which is much larger than other areas due to the soft deposition. On the other hand, as for the plasma-shadowed area, largest areal density of 5,100 mg/m was found underneath the dome structure. The total dust weights at the plasma-exposed surface and the shadowed areas were estimated to be 1.3 g and 22.2 g, respectively, assuming the toroidal symmetry. Count-based size distributions were also investigated. The average dust size of the main population is less than 20
was found underneath the dome structure. The total dust weights at the plasma-exposed surface and the shadowed areas were estimated to be 1.3 g and 22.2 g, respectively, assuming the toroidal symmetry. Count-based size distributions were also investigated. The average dust size of the main population is less than 20  m for both the plasma-exposed surface and the shadowed area.
m for both the plasma-exposed surface and the shadowed area.
Hayashi, Takao; Sakurai, Shinji; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Sakasai, Akira
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(2), p.549 - 553, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Design study of RH system, especially the expansion of the RH rail and replacement of the lower divertor cassettes, was described in this paper. The dimensions and weight of the divertor cassette, which is 10 degrees wide in toroidal direction, are 1.62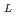
 0.57
0.57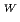
 1.25
1.25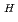 m and 800 kg, respectively. The RH system can use four horizontal ports whose inside dimensions are 0.66
m and 800 kg, respectively. The RH system can use four horizontal ports whose inside dimensions are 0.66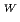
 1.83
1.83 m. The space for RH system is very limited. The RH rail is installed before transporting divertor cassettes. The RH rail can cover 180 degrees in toroidal direction. A divertor cassette can be replaced by heavy weight manipulator (HWM) consists of an end effector, a telescopic arm and a vehicle. The HWM brings the divertor cassette to the front of another horizontal port, which is used for supporting the rail and/or carrying in and out equipments. Then another RH device, which is installed from outside the vacuum vessel, receives and brings out the divertor cassette.
m. The space for RH system is very limited. The RH rail is installed before transporting divertor cassettes. The RH rail can cover 180 degrees in toroidal direction. A divertor cassette can be replaced by heavy weight manipulator (HWM) consists of an end effector, a telescopic arm and a vehicle. The HWM brings the divertor cassette to the front of another horizontal port, which is used for supporting the rail and/or carrying in and out equipments. Then another RH device, which is installed from outside the vacuum vessel, receives and brings out the divertor cassette.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi*; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nishitani, Takeo; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-019, 194 Pages, 2010/08
This report describes the results of the conceptual design study of the SlimCS fusion DEMO reactor aiming at demonstrating fusion power production in a plant scale and allowing to assess the economic prospects of a fusion power plant. The design study has focused on a compact and low aspect ratio tokamak reactor concept with a reduced-sized central solenoid, which is novel compared with previous tokamak reactor concept such as SSTR (Steady State Tokamak Reactor). The reactor has the main parameters of a major radius of 5.5 m, aspect ratio of 2.6, elongation of 2.0, normalized beta of 4.3, fusion out put of 2.95 GW and average neutron wall load of 3 MW/m . This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
. This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
Sakurai, Shinji; Higashijima, Satoru; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Masuo, Hiroshige*; Ozaki, Hidetsugu; Sakasai, Akira; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 85(10-12), p.2187 - 2191, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)JT-60SA tokamak project has just started construction phase under both the Japanese domestic program and the Japan-EU international program "ITER Broader Approach". All of plasma facing components (PFC) shall be actively cooled due to high power long pulse plasma heating. Lower single null closed divertor with vertical target (VT) will be installed at the start of experiment phase. Each divertor module covers a 10-degree sector in toroidal direction. PFCs such as VTs, baffles and dome shall be assembled on a divertor cassette, which provides integrated coolant pipe connection to coolant headers in the VV. Static structural analysis for dead weight, coolant pressure and EM loads shows that displacement and stress of the divertor module are generally small but a part of support structure of PFC requires improvement.
Hayashi, Takao; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Arai, Takashi; Sato, Masayasu
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(2-6), p.908 - 910, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)The residual gas analysis has been conducted by high-resolution mass spectrometry which can discriminate between D and He gas species during helium glow discharge cleaning (He-GDC) in JT-60U in order to investigate the effect of He-GDC. The residual gas analyzer was able to distinguish between D
and He gas species during helium glow discharge cleaning (He-GDC) in JT-60U in order to investigate the effect of He-GDC. The residual gas analyzer was able to distinguish between D and He peaks during He-GDC. Since the He-GDC started, the partial pressure of D
and He peaks during He-GDC. Since the He-GDC started, the partial pressure of D gas increases with time and reached its highest pressure (3.8
gas increases with time and reached its highest pressure (3.8  10
10 Pa), which is about ten times larger than that before the He-GDC (3.5
Pa), which is about ten times larger than that before the He-GDC (3.5  10
10 Pa). The total amount of D
Pa). The total amount of D , which was released during the He-GDC (7 hours), was evaluated as 4 Pa m
, which was released during the He-GDC (7 hours), was evaluated as 4 Pa m . The pressure of D
. The pressure of D (5.7
(5.7  10
10 Pa) about 7 hours after the He-GDC (7 hours) is significantly lower than before the He-GDC, which indicates the He-GDC is effective to remove the deuterium from plasma facing components.
Pa) about 7 hours after the He-GDC (7 hours) is significantly lower than before the He-GDC, which indicates the He-GDC is effective to remove the deuterium from plasma facing components.
Yoshida, Masafumi; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Nobuta, Yuji*; Hayashi, Takao; Masaki, Kei; Sato, Masayasu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.635 - 638, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.3(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have investigated hydrogen isotopes retention in the outboard first wall tiles of JT-60U by means of TDS, SIMS and SEM. The outboard first wall tiles of JT-60U are mostly eroded. The total retention (H+D) normalized by a unit area and integrated NBI time in the eroded first wall tiles and the eroded divertor tiles were nearly the same, in spite of the lower temperature of the first wall. Differently from divertor tiles, in which H retention was dominated owing to HH discharges preformed after DD discharges, deuterium is dominated in hydrogen isotopes retention and penetrates deeper from the surface. This is attributed to injection of high energy D and difficulty of isotopic replacement owing to their lower temperature. The integrated amount over the whole surface could be appreciably large. This type of hydrogen retention could be also possible for the metallic wall.
Hayashi, Takao; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Mayer, M.*; Krieger, K.*; Masaki, Kei; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Sato, Masayasu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.667 - 670, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Absolute concentrations and the depth profiles of D in plasma-facing graphite tiles used in JT-60U were determined by means of the D( He, p)
He, p) He resonant nuclear reaction. The analyzed samples were not exposed to H discharges before air ventilation. The maximum depth of analysis is about 1.4
He resonant nuclear reaction. The analyzed samples were not exposed to H discharges before air ventilation. The maximum depth of analysis is about 1.4  10
10 carbon (C) atoms/m
carbon (C) atoms/m , corresponding to a linear depth of 16
, corresponding to a linear depth of 16  m for the density of 1.7
m for the density of 1.7  10
10 kg/m
kg/m . The highest D concentration was found at the inboard mid-plane of first wall area. The maximum D concentration is D/C=0.13, and the concentration decrease with the depth. The D retention within 16
. The highest D concentration was found at the inboard mid-plane of first wall area. The maximum D concentration is D/C=0.13, and the concentration decrease with the depth. The D retention within 16  m is 1.9
m is 1.9  10
10 D atoms/m
D atoms/m . The D retentions in this paper were about 2
. The D retentions in this paper were about 2 9 times larger than previous samples, which were located on the same area and exposed to the hydrogen discharges. This indicates the H plasma discharges were effective to remove the D (and T) from graphite tiles in the first wall area.
9 times larger than previous samples, which were located on the same area and exposed to the hydrogen discharges. This indicates the H plasma discharges were effective to remove the D (and T) from graphite tiles in the first wall area.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Enoeda, Mikio; Isono, Takaaki; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Tsuru, Daigo; Suzuki, Satoshi; Hayashi, Takao; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 386-388, p.888 - 892, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:83.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)SlimCS is the conceptual design of a compact fusion DEMO plant assuming technologies foreseeable in 2020s-2030s. Considering continuity of blanket technology from the Japanese proposal on ITER-TBM, the prime option of blanket is water-cooled solid breeder with Li TiO
TiO and Be (or Be
and Be (or Be Ti). A reduced-activation ferritic-martensitic steel and pressurized water are chosen as the structural material and coolant, respectively. Toroidal coils produce the peak magnetic field above 16 T using the RHQT processed Nb
Ti). A reduced-activation ferritic-martensitic steel and pressurized water are chosen as the structural material and coolant, respectively. Toroidal coils produce the peak magnetic field above 16 T using the RHQT processed Nb Al conductors. The structure and materials of the conducting shell and divertor are also presented.
Al conductors. The structure and materials of the conducting shell and divertor are also presented.
Hayashi, Takao; Tobita, Kenji; Nakamori, Yuko*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 386-388, p.119 - 121, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:80 Percentile:98.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Neutron transport calculations have been carried out to assess the capability of zirconium borohydride (Zr(BH )
) ) and zirconium hydride (ZrH
) and zirconium hydride (ZrH ) as advanced shield materials, because excellent shields can be used to protect outer structural materials from serious activation. The neutron shielding capability of Zr(BH
) as advanced shield materials, because excellent shields can be used to protect outer structural materials from serious activation. The neutron shielding capability of Zr(BH )
) is lower than ZrH
is lower than ZrH , even though the hydrogen density of Zr(BH
, even though the hydrogen density of Zr(BH )
) is slightly higher than that of ZrH
is slightly higher than that of ZrH . High-Z atoms are effective in neutron shielding as well as hydrogen atoms. The combination of steel and Zr(BH
. High-Z atoms are effective in neutron shielding as well as hydrogen atoms. The combination of steel and Zr(BH )
) can improve the neutron shielding capability. The combinations of (Zr(BH
can improve the neutron shielding capability. The combinations of (Zr(BH )
) + F82H) and (ZrH
+ F82H) and (ZrH + F82H) can reduce the thickness of the shield by 6.5% and 19% compared to (water + F82H), respectively. The neutron flux for Zr(BH
+ F82H) can reduce the thickness of the shield by 6.5% and 19% compared to (water + F82H), respectively. The neutron flux for Zr(BH )
) is drastically reduced in the range of neutron energy below 100 eV compared to other materials, due to the effect of boron, which can lead to a reduction of radwaste from fusion reactors.
is drastically reduced in the range of neutron energy below 100 eV compared to other materials, due to the effect of boron, which can lead to a reduction of radwaste from fusion reactors.
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.86(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Takao; Nishitani, Takeo; Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Ishikawa, Masao; Shinohara, Koji
Review of Scientific Instruments, 79(10), p.10E506_1 - 10E506_3, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.32(Instruments & Instrumentation)In D-D or D-T operation fusion devices, the fusion neutron yield is the most important parameter to estimate the fusion power. We have conducted calibrations of a microfission chamber, 14 mm in diameter and 200 mm in length, by both Cf-252 neutron source and real plasmas in JT-60U. The detector employs both pulse counting and Campbelling modes in the electronics to cover 10 dynamic range of the neutron source strength. The efficiencies were influenced by the various components. The point efficiencies can be integrated and averaged with angle to provide toroidal line efficiencies. The line efficiencies of microfission chamber and the nearest neutron monitor of U-235 fission chamber was 5.38
dynamic range of the neutron source strength. The efficiencies were influenced by the various components. The point efficiencies can be integrated and averaged with angle to provide toroidal line efficiencies. The line efficiencies of microfission chamber and the nearest neutron monitor of U-235 fission chamber was 5.38  10
10 and 1.77
and 1.77  10
10 , respectively. Then the calibration using real plasma was also performed. The detection efficiency in Campbelling mode was about three-tenth of the nearest neutron monitor, which is consistent with the calibration result using Cf-252 neutron source.
, respectively. Then the calibration using real plasma was also performed. The detection efficiency in Campbelling mode was about three-tenth of the nearest neutron monitor, which is consistent with the calibration result using Cf-252 neutron source.
Hayashi, Takao; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Tamai, Hiroshi; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Matsukawa, Makoto
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 2(2), p.522 - 529, 2008/00
The JT-60SA aims to contribute and supplement ITER toward demonstration fusion reactor based on tokamak concept. One of the features of JT-60SA is its high power long pulse heating, causing the large annual neutron fluence. Because the expected dose rate at the vacuum vessel (VV) may exceed 1 mSv/hr after 10 years operation and three month cooling, the human access inside the VV is prohibited. Therefore a remote handling (RH) system is necessary for the maintenance and repair of in-vessel components. A divertor cassette, which is 10 degrees wide in toroidal direction and weighs 500 kg itself due to the limitations of port width and handling weight, can be exchanged by heavy weight manipulator (HWM). The HWM brings the divertor cassette to the front of the other RH port, which is used for supporting the rail and/or carrying in and out equipments. Then another RH device receives and brings out the cassette by a pallet installed from outside the VV.