Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Higuchi, Yuki*; Yoshimune, Wataru*; Kato, Satoru*; Hibi, Shogo*; Setoyama, Daigo*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Harada, Masashi*; et al.
Communications Engineering (Internet), 3, p.33_1 - 33_7, 2024/02
Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Hiroki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Setoyama, Daigo*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Sasaki, Tsuyoshi*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.22082_1 - 22082_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yoshimura, Nobuyuki*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Nakamura, Takeshi*; Omi, Kazuhito*; Kobayashi, Aine*; Okada, Masashi*; Sato, Yoichi*; Nakaya, Tsuyoshi*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.260 - 264, 2023/11
The J-PARC main ring (MR) will be increased to 1.3 MW. To cope with the increase in beam intensity, the intra-bunch feedback system (IBFB) needs to be upgraded to handle higher frequencies up to about 200 MHz. To evaluate the performance and understand the optimal parameters after this upgrade, we are developing a particle tracking simulation that includes the necessary components. The recoherence period induced by chromaticity between tracking simulations and experiments are compared and it cannot be discribed by the simple simulations, and we investigate what mechanisms explain this result. The shift of synchrotron tune caused by longitudinal wakes using tracking simulations are calculated and it find that introducing the effect of longitudinal wakes only does not explain the recoherence period in the experimental results.
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Urata, Shingo*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.18721_1 - 18721_12, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:45.8(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The first sharp peak diffraction peak (FSDP) in the structure factor of amorphous materials is thought to reflect the medium-range order structure in amorphous materials, and the structural origin of the FSDP has been a subject of ongoing debate. In this study, we employed machine learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) with nearly first-principles calculation accuracy to investigate the structural origin of the FSDP in high-density silica glass. First, we successfully reproduced various experimental data of high-density silica glass using MLMD. Furthermore, we revealed that the development (or reduction) of the FSDP in high-density silica glass is characterized by the deformation behavior of ring structures in Si-O covalent bond networks under compression.
Yoshimune, Wataru*; Higuchi, Yuki*; Kato, Akihiko*; Hibi, Shogo*; Yamaguchi, Satoshi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kato, Satoru*
ACS Energy Letters (Internet), 8(8), p.3485 - 3487, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:66.84(Chemistry, Physical) O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.26(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
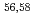 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:64.66(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 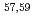 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the  decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for  level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 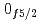 and
and 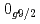 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:83.53(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:48.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:93.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
 Fe
Fe O
O grown on Al
grown on Al O
O ; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCD
; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCDNonaka, Yosuke*; Wakabayashi, Yuki*; Shibata, Goro; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Ikeda, Keisuke*; Chi, Z.*; Wan, Y.*; Suzuki, Masahiro*; Tanaka, Arata*; Tanaka, Masaaki*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(4), p.044413_1 - 044413_10, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kobayashi, Keita; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Materia, 62(3), p.175 - 181, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
 Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5
Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5Kunieda, Satoshi; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Konno, Chikara; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Ikeda, Yujiro*
Journal of Neutron Research, 24(3-4), p.329 - 335, 2023/01
We have evaluated double-differential cross-sections (DDX) of the  Be(p,xn) reaction based on the function proposed by Wakabayashi et al. up to 12 MeV. Through compilation in the ENDF-6 format file, data processing, and neutronics analysis with MC simulation codes MCNP and PHITS to thick target yield (TTY) measurements, the function was re-confirmed to give more reasonable DDX data than those in our previous library JENDL-4.0/HE and ENDF/B-VIII.0. We finally decided to reduce the absolute cross-sections by 15% for our new nuclear data library JENDL-5 since the prediction ability of neutronics simulation was much better than that based on the original function. Through comprehensive comparisons of the simulation results on TTY at different proton energies and neutron emission angles, we conclude that JENDL-5 gives the best estimation in the world.
Be(p,xn) reaction based on the function proposed by Wakabayashi et al. up to 12 MeV. Through compilation in the ENDF-6 format file, data processing, and neutronics analysis with MC simulation codes MCNP and PHITS to thick target yield (TTY) measurements, the function was re-confirmed to give more reasonable DDX data than those in our previous library JENDL-4.0/HE and ENDF/B-VIII.0. We finally decided to reduce the absolute cross-sections by 15% for our new nuclear data library JENDL-5 since the prediction ability of neutronics simulation was much better than that based on the original function. Through comprehensive comparisons of the simulation results on TTY at different proton energies and neutron emission angles, we conclude that JENDL-5 gives the best estimation in the world.
Kobayashi, Aine*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nakamura, Takeshi*; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Ishii, Koji*; Tomizawa, Masahito*; Takeuchi, Yasunao*; Sato, Yoichi*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.19 - 23, 2023/01
In the J-PARC main ring, density modulation due to longitudinal beam instability occurs during the debunching process of coasting beams. This leads to the generation of an electron cloud, which in turn causes transverse beam instabilities. The transverse beam instability causes beam loss and the electron cloud is assumed to cause vacuum degradation, both of which hinder the beam intensity enhancement, so it is essential to clarify the causes and countermeasures. In particular, the longitudinal impedance of several hundred MHz has been investigated as relevant, and measures to reduce the impedance of individual devices are underway. The Eddy-current type septum magnet, newly installed this year, was found to have a large impedance by simulation. Therefore, we are investigating a method to reduce the impedance by a flange loaded with SiC radio wave absorber, which can be applied to locations where there is no spatial margin to install a taper. In this report, we will discuss the characterization of SiC to be used in actual devices, impedance simulation reflecting the results of SiC evaluation, and evaluation of the effect of impedance countermeasures by impedance measurement using the wire method, and progress in evaluating the effect on the beam by beam simulation and beam study.
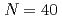 island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in
island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in  V and
V and  V
VElekes, Z.*; Juh sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064321_1 - 064321_10, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:49.92(Physics, Nuclear)The low-lying level structure of  V and
V and  V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for
V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for  V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for
V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for  V. Four and five new transitions were determined for
V. Four and five new transitions were determined for  V and
V and  V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed
V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed  rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2
rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2 and 9/2
and 9/2 levels. The (
levels. The ( ,
,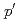 ) excitation cross sections for
) excitation cross sections for  V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,
V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,  V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
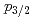 neutron orbital and the
neutron orbital and the 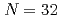 shell closure in
shell closure in  Ca
CaEnciu, M.*; Liu, H. N.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Poves, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 129(26), p.262501_1 - 262501_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:65.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The one-neutron knockout from  Ca was performed at
Ca was performed at  230 MeV/nucleon combined with prompt
230 MeV/nucleon combined with prompt  spectroscopy. The momentum distributions corresponding to the removal of
spectroscopy. The momentum distributions corresponding to the removal of 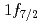 and
and 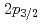 neutrons were measured. The cross sections are consistent with a shell closure at the neutron number
neutrons were measured. The cross sections are consistent with a shell closure at the neutron number 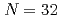 , found as strong as at
, found as strong as at 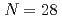 and
and 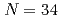 in Ca isotopes from the same observables. The analysis of the momentum distributions leads to a difference of the root-mean-square radii of the neutron
in Ca isotopes from the same observables. The analysis of the momentum distributions leads to a difference of the root-mean-square radii of the neutron 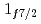 and
and 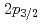 orbitals of 0.61(23) fm, in agreement with the modified-shell-model prediction of 0.7 fm suggesting that the large root-mean-square radius of the
orbitals of 0.61(23) fm, in agreement with the modified-shell-model prediction of 0.7 fm suggesting that the large root-mean-square radius of the 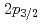 orbital in neutron-rich Ca isotopes is responsible for the unexpected linear increase of the charge radius with the neutron number.
orbital in neutron-rich Ca isotopes is responsible for the unexpected linear increase of the charge radius with the neutron number.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
 K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringSuzuki, Hakuto*; Zhao, G.*; Okamoto, Jun*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Shibata, Goro; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Cooper, M. W. D.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.9808_1 - 9808_11, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:76.65(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Nasu, Mitsunori*; Yanai, Hiroshi*; Hirayama, Naoki*; Adachi, Hironori*; Kakizawa, Yu*; Shirase, Yuto*; Nishiyama, Hiromichi*; Kawamoto, Teppei*; Inukai, Junji*; Shinohara, Takenao; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 530, p.231251_1 - 231251_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:89.58(Chemistry, Physical)