Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tominaga, Masahide*; Nagayasu, Yukari*; Sasaki, Motoharu*; Furuta, Takuya; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Oita, Masataka*; Nishiyama, Yuichi*; Haga, Akihiro*
Radiological Physics and Technology, 14(4), p.381 - 389, 2021/12
Due to recent advance of diagnostic radiology, the increase of diagnostic radiation exposure to patient becomes problem. Diagnostic Reference Levels has been released to optimized the radiation exposure to patients in Japan recently. The evaluation of entrance surface dose (ESD) is recommended to assess the dose level for general X-ray examination. The ESD can be easily evaluated by multiplying the backscatter factor of the patient body on the free-in-air air kerma. The air kerma free-in-air value used to estimate ESD may contain X-rays scattered from obstacles located at the time of measurement, which may induce non-minor error in assessments. We therefore studied the influence of scattered X-rays on air kerma measurement under various environments (distances, field sizes, and materials). It was found that the dependence on the X-ray energy and field size was different for different materials. The X-ray contamination can be ignored for all the materials when the distance to the scatterer exceeds 35 cm.
Fukuda, Kenji; Watanabe, Yusuke; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Hayashida, Kazuki*; Aosai, Daisuke*; Kumamoto, Yoshiharu*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-021, 76 Pages, 2019/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been investigating groundwater chemistry to understand the influence of excavation and maintenance of underground facilities as part of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in Mizunami, Gifu, Japan. In this report, we compiled data of groundwater chemistry and microbiology obtained at the MIU in the fiscal year 2017. In terms of ensuring traceability of data, basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling time, sampling method and analytical method) and methodology for quality control are described.
Hayashida, Kazuki; Kato, Toshihiro*; Kubota, Mitsuru*; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Chikyu Kagaku, 52(1), p.55 - 71, 2018/03
In this study, the simulated experimental drift was constructed in the granite of 500 m depth at Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory, and the hydrochemical process after the drift closure was observed. The groundwater chemistry around the drift changed with the change of the groundwater flow in the fractures when the gallery was constructed. The redox potential increased due to the infiltration of oxygen from the drift into the rock. After closing the drift, the redox potential of the groundwater plunged due to microbial activity, while the groundwater became alkalized conditon due to the influence of cement material such as shotcrete. The amount of cement material consumed for this alkalization was small, and it was considered that its influence would last long in accordance with the amount of cement used.
Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kokami, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kirishima, Akira*; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Mizuno, Takashi; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Miyakawa, Kazuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(3), p.373 - 381, 2017/03
Trace amounts of natural thorium and uranium in deep groundwater were investigated at two underground research laboratories situated at Horonobe and Mizunami, Japan. The groundwater was sampled from underground boreholes, and the colloid contribution was checked by in situ two size-fractionated ultrafiltration systems. A decrease in the concentration after in situ filtration suggested the presence of natural colloids and suspended matter that were carriers of a portion of the elements. The result of the Th and U concentrations in groundwater after 10 kDa filtration was analyzed thermodynamically using existing hydrogeological and geochemical data such as the mineral components in the groundwater at a given pH, ionic strength, concentration of co-existing ions, redox potential, and solid phase assumed. A crystalline solid phase made the solubility very low compared with that of the amorphous phase, and the solubility agreed well with the concentrations measured.
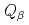 measurements of neutron-rich nuclei far from the
measurements of neutron-rich nuclei far from the  -stability line
-stability lineHayashi, Hiroaki*; Shibata, Michihiro*; Asai, Masato; Osa, Akihiko; Sato, Tetsuya; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kimura, Atsushi; Oshima, Masumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 747, p.41 - 51, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.98(Instruments & Instrumentation)To measure  -decay energy
-decay energy 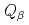 of short-lived fission products with good accuracy and high efficiency, we have developed a new total absorption clover detector and demonstrated its performance. Using a large-volume clover-type Ge detector having a through-hole in its center, we could measure total absorption spectra of
of short-lived fission products with good accuracy and high efficiency, we have developed a new total absorption clover detector and demonstrated its performance. Using a large-volume clover-type Ge detector having a through-hole in its center, we could measure total absorption spectra of  +
+  rays with extremely high efficiency and high energy resolution, and could determine
rays with extremely high efficiency and high energy resolution, and could determine 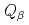 values with
values with  30 keV accuracy. Using this detector, we have determined the
30 keV accuracy. Using this detector, we have determined the 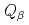 values of
values of 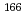 Eu and
Eu and 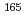 Gd for the first time, and of
Gd for the first time, and of 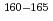 Eu and
Eu and 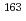 Gd with better accuracies. In addition, we have observed a new isomeric state in
Gd with better accuracies. In addition, we have observed a new isomeric state in 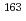 Gd, and determined its half-life and excitation energy.
Gd, and determined its half-life and excitation energy.
Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Furuta, Kazuki*; Kinoshita, Takeshi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Asano, Takahiro*; Sasaki, Yoshito; et al.
FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 86(3), p.532 - 543, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:36.72(Microbiology)Anaerobic microbial activity has a major influence on the subsurface environment, and should be considered in subsurface activities including the construction of radioactive waste repositories. We investigated denitrification and methanogenesis in anoxic groundwater from 140 m depth in two boreholes, where the redox potential fluctuated. The average maximum potential denitrification rates, measured under anaerobic conditions in the two boreholes using an  N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
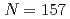 nucleus
nucleus  No
NoAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakama, Minoru*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Physical Review C, 87(1), p.014332_1 - 014332_6, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.66(Physics, Nuclear)The spin-parity and neutron configuration of the ground state of  No have been identified through
No have been identified through  -decay spectroscopy. The
-decay spectroscopy. The  No is the nucleus with the largest neutron number whose spin-parities and single-particle configurations have ever been identified. The neutron 9/2
No is the nucleus with the largest neutron number whose spin-parities and single-particle configurations have ever been identified. The neutron 9/2 [615] configuration was assigned to the ground state of
[615] configuration was assigned to the ground state of  No as well as to the 231.4 keV level in
No as well as to the 231.4 keV level in  Fm. This allowed us to establish energy spacings and order of the neutron single-particle orbitals in such heaviest nuclear region. The appearance of the 9/2
Fm. This allowed us to establish energy spacings and order of the neutron single-particle orbitals in such heaviest nuclear region. The appearance of the 9/2 [615] ground state at
[615] ground state at  =157 implies that the order of the neutron orbitals between the
=157 implies that the order of the neutron orbitals between the  =152 and 162 deformed shell gaps should change considerably with increasing neutron number.
=152 and 162 deformed shell gaps should change considerably with increasing neutron number.
 N(n,
N(n, )
) N reaction as a
N reaction as a  -ray intensity standard up to 11 MeV
-ray intensity standard up to 11 MeVMiyazaki, Itaru*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Takayama, Hirokazu*; Kasaishi, Masafumi*; Tojo, Akinori*; Furuta, Masataka*; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Suematsu, Osamu*; Narasaki, Hiromichi*; Shimizu, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(6), p.481 - 486, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.07(Nuclear Science & Technology)The intensities of the prompt  rays from the
rays from the  N(n,
N(n, )
) N reaction have been precisely measured. As the samples, a liquid nitrogen target and a deuterated melamine (C
N reaction have been precisely measured. As the samples, a liquid nitrogen target and a deuterated melamine (C D
D N
N ) were used. The previous values widely used as intensity standards agreed with those obtained in this study within 4-5% in the 2-11 MeV region, however, showed a monotonous decrease with the increase of
) were used. The previous values widely used as intensity standards agreed with those obtained in this study within 4-5% in the 2-11 MeV region, however, showed a monotonous decrease with the increase of  -ray energy.
-ray energy.
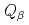 measurements of
measurements of 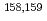 Pm,
Pm, 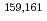 Sm,
Sm, 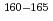 Eu,
Eu, 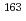 Gd and
Gd and 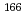 Tb using a total absorption BGO detector
Tb using a total absorption BGO detectorHayashi, Hiroaki*; Akita, Yukinori*; Suematsu, Osamu*; Shibata, Michihiro*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Osa, Akihiko; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 34(4), p.363 - 370, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:71.35(Physics, Nuclear)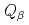 values of
values of 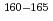 Eu and
Eu and 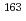 Gd were measured for the first time using a total absorption BGO detector, and the data of
Gd were measured for the first time using a total absorption BGO detector, and the data of 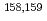 Pm,
Pm, 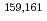 Sm, and
Sm, and 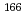 Tb obtained previously were reanalyzed. These nuclei were produced by the proton-induced fission of
Tb obtained previously were reanalyzed. These nuclei were produced by the proton-induced fission of  U at the JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator facility, and separated from the reaction products using an on-line isotope separator. The deduced mass excesses and two-neutron separation energies were compared with those of atomic mass evaluations and theoretical predictions.
U at the JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator facility, and separated from the reaction products using an on-line isotope separator. The deduced mass excesses and two-neutron separation energies were compared with those of atomic mass evaluations and theoretical predictions.
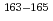 Eu
EuSato, Tetsuya; Osa, Akihiko; Asai, Masato; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Shibata, Michihiro*; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Kojima, Yasuaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -
- spectroscopy of
spectroscopy of  No
NoAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakama, Minoru*; Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka; Shibata, Michihiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
 -
- coincidence spectroscopy for the
coincidence spectroscopy for the  decay of
decay of  No has been performed at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility to study nuclear shell structure of superheavy nuclei. The decay scheme of
No has been performed at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility to study nuclear shell structure of superheavy nuclei. The decay scheme of  No has been established for the first time, and spin-parity and neutron single-particle configuration of the ground state of
No has been established for the first time, and spin-parity and neutron single-particle configuration of the ground state of  No have been identified. It was found that many theoretical calculations could not reproduce the ground-state configuration of the nuclei with 157 neutrons, which implies that the deformation of the nuclei with more than 157 neutrons would be substantially different from theoretical predictions.
No have been identified. It was found that many theoretical calculations could not reproduce the ground-state configuration of the nuclei with 157 neutrons, which implies that the deformation of the nuclei with more than 157 neutrons would be substantially different from theoretical predictions.
 -decay half-lives of four new neutron-rich isotopes
-decay half-lives of four new neutron-rich isotopes 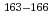 Eu and levels in
Eu and levels in 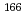 Gd
GdSato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Osa, Akihiko; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Shibata, Michihiro*; Kojima, Yasuaki*; Ichikawa, Shinichi
no journal, ,
 -decay half-lives of four new neutron-rich isotopes
-decay half-lives of four new neutron-rich isotopes 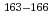 Eu produced in the proton-induced fission of
Eu produced in the proton-induced fission of  U have been determined, using an on-line isotope separator at JAEA. The measured half-life values are 7.7(4) s for
U have been determined, using an on-line isotope separator at JAEA. The measured half-life values are 7.7(4) s for 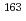 Eu, 4.6(7) s for
Eu, 4.6(7) s for 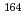 Eu, 2.7(6) s for
Eu, 2.7(6) s for 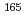 Eu and 1.7(4) s for
Eu and 1.7(4) s for 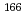 Eu. And we determined the
Eu. And we determined the 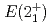 ,
, 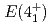 energies of
energies of 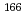 Gd
Gd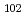 which is most neutron-rich Gd isotope to be 69.7(1) keV and 230.5(1) keV, respectively.
which is most neutron-rich Gd isotope to be 69.7(1) keV and 230.5(1) keV, respectively.
 spectroscopy of N = 155 and 157 nuclei using a gas-jet transport technique
spectroscopy of N = 155 and 157 nuclei using a gas-jet transport techniqueAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakama, Minoru*; Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
no journal, ,
Alpha- spectroscopy of
spectroscopy of 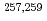 No and
No and  Rf nuclei with the neutron number N=155 and 157 have been performed for the first time at the JAEA tandem accelerator using a gas-jet transport technique. Spin-parities and neutron single-particle configurations of ground states of these nuclei as well as excited states in their daughter nuclei have been identified. On the basis of these experimental results, energy spacings and order of neutron single-particle orbitals between N=153 and 161 were evaluated. The result implies that the order of the neutron orbitals between N=153 and 161 should be inverted between lighter nuclei around
Rf nuclei with the neutron number N=155 and 157 have been performed for the first time at the JAEA tandem accelerator using a gas-jet transport technique. Spin-parities and neutron single-particle configurations of ground states of these nuclei as well as excited states in their daughter nuclei have been identified. On the basis of these experimental results, energy spacings and order of neutron single-particle orbitals between N=153 and 161 were evaluated. The result implies that the order of the neutron orbitals between N=153 and 161 should be inverted between lighter nuclei around 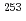 Fm and heavier ones around
Fm and heavier ones around 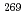 Hs.
Hs.
 -decay half-life of new neutron rich isotope
-decay half-life of new neutron rich isotope 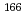 Eu and levels in
Eu and levels in 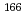 Gd
GdSato, Tetsuya; Osa, Akihiko; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Shibata, Michihiro*; Kojima, Yasuaki*; Ichikawa, Shinichi
no journal, ,
New neutron-rich rare-earth isotope 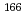 Eu produce in the proton-induced fisson of
Eu produce in the proton-induced fisson of  U were identified using the JAEA on-line isotope separator at the JAEA tandem accelerator and its half-life was determined to be 1.7(4) s. Excited state in
U were identified using the JAEA on-line isotope separator at the JAEA tandem accelerator and its half-life was determined to be 1.7(4) s. Excited state in 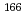 Gd was established for the first time.
Gd was established for the first time.
 -ray spectroscopy of the heaviest nuclei at JAEA tandem accelerator
-ray spectroscopy of the heaviest nuclei at JAEA tandem acceleratorAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakama, Minoru*; Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
no journal, ,
Recent results on the  -ray spectroscopic studies of the heaviest nuclei at the JAEA tandem accelerator are reviewed. The nuclei
-ray spectroscopic studies of the heaviest nuclei at the JAEA tandem accelerator are reviewed. The nuclei  No,
No,  No, and
No, and  Rf studied in the present work are the heaviest and the most neutron-rich nuclei that
Rf studied in the present work are the heaviest and the most neutron-rich nuclei that  -ray spectroscopic studies have ever been performed for. Excited-state energies, spin-parities, and single-particle configurations of those nuclei and their daughters have been established by means of
-ray spectroscopic studies have ever been performed for. Excited-state energies, spin-parities, and single-particle configurations of those nuclei and their daughters have been established by means of  -
- coincidence spectroscopy. The deduced energy spacings and order of neutron single-particle orbitals suggest that the higher-order deformations play an important role in level structure of the superheavy nuclei in this region.
coincidence spectroscopy. The deduced energy spacings and order of neutron single-particle orbitals suggest that the higher-order deformations play an important role in level structure of the superheavy nuclei in this region.
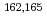 Gd using a total absorption detector
Gd using a total absorption detectorAsai, Masato; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Osa, Akihiko; Sato, Tetsuya; Otokawa, Yoshinori; Nagae, Daisuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Miyashita, Yuji*; Ouchi, Hiroyuki*; Izumi, Sayaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a new method to measure lifetime of long-lived isomers populated through the  decay, using a total absorption detector. Using this method, we have determined lifetime of the K isomers in
decay, using a total absorption detector. Using this method, we have determined lifetime of the K isomers in 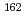 Gd and
Gd and 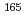 Gd for the first time. The short-lived neutron-rich nuclei
Gd for the first time. The short-lived neutron-rich nuclei 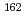 Eu and
Eu and 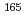 Eu were produced and mass-separated by the on-line isotope separator (ISOL) at JAEA tandem accelerator facility. Beta- and
Eu were produced and mass-separated by the on-line isotope separator (ISOL) at JAEA tandem accelerator facility. Beta- and  rays emitted by the
rays emitted by the  decay of
decay of 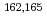 Eu were total-absorbed by the detector, and all the events were recorded with time stamps. This method enabled us to determine lifetime of the isomers with more than 100-
Eu were total-absorbed by the detector, and all the events were recorded with time stamps. This method enabled us to determine lifetime of the isomers with more than 100- s lifetime.
s lifetime.
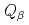 measurements
measurementsHayashi, Hiroaki*; Shibata, Michihiro*; Asai, Masato; Osa, Akihiko; Oshima, Masumi; Kimura, Atsushi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Sato, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
A new total absorption detector composed of a large Clover-type Ge detector and BGO Compton suppressors has been developed to measure 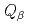 values of nuclei far from the
values of nuclei far from the  -stability line. The Clover detector has a through-hole with a 15-mm inner diameter at its center to put radioactive sources in it. Because of its high detection efficiencies for both
-stability line. The Clover detector has a through-hole with a 15-mm inner diameter at its center to put radioactive sources in it. Because of its high detection efficiencies for both  and
and  rays, the
rays, the 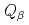 value can be directly determined from the endpoint of an observed total sum spectrum for
value can be directly determined from the endpoint of an observed total sum spectrum for  and
and  rays without information on the decay scheme. Using this detector,
rays without information on the decay scheme. Using this detector, 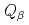 values of
values of 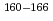 Eu and
Eu and 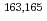 Gd produced in the proton-induced fission of
Gd produced in the proton-induced fission of  U and mass-separated by an on-line isotope separator at the JAEA-Tokai Tandem Accelerator have been determined with accuracies of 30-300 keV.
U and mass-separated by an on-line isotope separator at the JAEA-Tokai Tandem Accelerator have been determined with accuracies of 30-300 keV.
Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kokami, Takayuki*; Amamiya, Hiroki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Mizuno, Takashi; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kirishima, Akira*
no journal, ,
For thermodynamic analysis of the trace metals in groundwater, concentrations of Th, U, and rare earth elements (REEs) were investigated at Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. Groundwater was sampled in anaerobic condition directly from a packed section in the boreholes drilled to 140 m and 250 m depth in drift. The colloidal distribution was checked by an on-site batch ultrafiltration unit using 0.2  m or 10 kDa membranes. As the result, both Th and U concentrations could be estimated by thermodynamic calculations, assuming that the soluble solid phases are restricted to ThO
m or 10 kDa membranes. As the result, both Th and U concentrations could be estimated by thermodynamic calculations, assuming that the soluble solid phases are restricted to ThO (cr) and UO
(cr) and UO (cr), respectively. Meanwhile, the concentrations of REEs were also very low, and significant colloidal distribution for lighter REEs was observed. In the thermodynamic analysis where the lanthanide phosphate was assumed to be a solid phase, the experimental plots matched better with the calculated one, even though the changing trend differs from each other.
(cr), respectively. Meanwhile, the concentrations of REEs were also very low, and significant colloidal distribution for lighter REEs was observed. In the thermodynamic analysis where the lanthanide phosphate was assumed to be a solid phase, the experimental plots matched better with the calculated one, even though the changing trend differs from each other.
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Hayashida, Kazuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Watanabe, Yusuke
no journal, ,
Geochemical condition and solutes transport property in and around a simulated closure tunnel were studied by observing the behavior of REEs at Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. Results show that the REEs in the closure tunnel tend to be immobilized by absorbing to shotcrete and the colloidal flocculation.
Watanabe, Yusuke; Hayashida, Kazuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
In the geological disposal project of high-level radioactive waste, a disposal facility will be constructed in depths deeper than 300 m. In this study, the simulated experimental tunnel was constructed in the granite of 500 m depth at Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory, and the hydrochemical process after the tunnel closure was observed.