Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
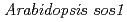 mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt tolerance
mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt toleranceAriga, Hirotake*; Katori, Taku*; Yoshihara, Ryohei*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei; Iuchi, Satoshi*; Kobayashi, Masatomo*; Tezuka, Kenji*; Sakata, Yoichi*; et al.
Plant Signaling & Behavior (Internet), 8(7), p.e24779_1 - e24779_5, 2013/07
Based on analysis of the salinity tolerance among 354  accessions, some accessions showed greater salt shock tolerance compared with a reference accession, Col-0 on a typical assay with drastic change in NaCl concentration from 0 mM to 225 mM. On the other hand, several accessions including Zu-0 exhibited marked acquired salt tolerance, which is induced after exposure to moderate salt stress (salt acclimation ability). It is likely that Arabidopsis plants have at least two types of tolerance abilities, salt shock tolerance and salt acclimation. To dissect the salt tolerance mechanisms of the salt tolerant accessions, we isolated a salt-sensitive mutant from ion beam-mutagenized Zu-0 seedlings. The mutant showed severe growth inhibition under salt shock stress due to a single base deletion in SOS1 gene as well-known salt shock tolerance gene, even more salt sensitive than Col-0. Nevertheless, the mutant was able to survive on the salt acclimation with 100 mM NaCl for 7 days followed with 750 mM sorbitol for 20 days (salt acclimation assay) as well as the Zu-0 wild type, whereas Col-0 showed apparent chlorosis under the condition. We propose that a gene for salt acclimation ability is different from a gene for salt shock tolerance and plays an important role in acquisition for marked salt- or osmotic tolerance.
accessions, some accessions showed greater salt shock tolerance compared with a reference accession, Col-0 on a typical assay with drastic change in NaCl concentration from 0 mM to 225 mM. On the other hand, several accessions including Zu-0 exhibited marked acquired salt tolerance, which is induced after exposure to moderate salt stress (salt acclimation ability). It is likely that Arabidopsis plants have at least two types of tolerance abilities, salt shock tolerance and salt acclimation. To dissect the salt tolerance mechanisms of the salt tolerant accessions, we isolated a salt-sensitive mutant from ion beam-mutagenized Zu-0 seedlings. The mutant showed severe growth inhibition under salt shock stress due to a single base deletion in SOS1 gene as well-known salt shock tolerance gene, even more salt sensitive than Col-0. Nevertheless, the mutant was able to survive on the salt acclimation with 100 mM NaCl for 7 days followed with 750 mM sorbitol for 20 days (salt acclimation assay) as well as the Zu-0 wild type, whereas Col-0 showed apparent chlorosis under the condition. We propose that a gene for salt acclimation ability is different from a gene for salt shock tolerance and plays an important role in acquisition for marked salt- or osmotic tolerance.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Parail, V.*; Koechl, F.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Wiesen, S.*; Lang, P. T.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 51(10), p.103030_1 - 103030_8, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.15(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Hoshino, Kazuo; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa; Fukuyama, Atsushi*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 6(Sp.1), p.2403065_1 - 2403065_8, 2011/08
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 51(7), p.073015_1 - 073015_7, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.28(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Parail, V.*; Koechl, F.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Wiesen, S.*; Lang, P.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa; JET-EFDA Contributors*
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi*; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nishitani, Takeo; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-019, 194 Pages, 2010/08
This report describes the results of the conceptual design study of the SlimCS fusion DEMO reactor aiming at demonstrating fusion power production in a plant scale and allowing to assess the economic prospects of a fusion power plant. The design study has focused on a compact and low aspect ratio tokamak reactor concept with a reduced-sized central solenoid, which is novel compared with previous tokamak reactor concept such as SSTR (Steady State Tokamak Reactor). The reactor has the main parameters of a major radius of 5.5 m, aspect ratio of 2.6, elongation of 2.0, normalized beta of 4.3, fusion out put of 2.95 GW and average neutron wall load of 3 MW/m . This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
. This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
Araki, Masanori; Hayashi, Kimio; Tobita, Kenji; Nishitani, Takeo; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nozawa, Takashi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Nakamichi, Masaru; Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Ozeki, Takahisa; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 86(4), p.231 - 239, 2010/04
The Broader Approach Activities, which support the ITER Project and implement activities to aim early realization of fusion energy, is an EU-Japan collaborative project to carry out various kinds of researches and developments during the period of the ITER construction phase. In this special topic, achievements and prospects of the projects on the International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) is described.
Ozeki, Takahisa; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Hoshino, Kazuo; Takizuka, Tomonori; Tokuda, Shinji
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.8, p.1138 - 1142, 2009/09
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa; Wiesen, S.*; Parail, V.*
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095015_1 - 095015_8, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:49.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Kawashima, Hisato; Kurita, Genichi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Honda, Mitsuru; Saito, Ai*; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(7), p.075029_1 - 075029_10, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:139 Percentile:97.7(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent design study on SlimCS focused mainly on the torus configuration including blanket, divertor, materials and maintenance scheme. For vertical stability of elongated plasma and high beta access, a sector-wide conducting shell is arranged in between replaceable and permanent blanket. The reactor adopts pressurized-water-cooled solid breeding blanket. Compared with the previous advanced concept with supercritical water, the design options satisfying tritium self-sufficiency are relatively scarce. Considered divertor technology and materials, an allowable heat load to the divertor plate should be 8 MW/m or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Urano, Hajime; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(5), p.055006_1 - 055006_9, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:89.51(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa; Wiesen, S.*; Parail, V.*
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Giruzzi, G.*; Park, J. M.*; Murakami, M.*; Kessel, C. E.*; Polevoi, A.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Bonoli, P.*; Budny, R. V.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Suzuki, Yoshio; Nakajima, Kohei; Kushida, Noriyuki; Kino, Chiaki; Aoyagi, Tetsuo; Nakajima, Norihiro; Iba, Katsuyuki*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ozeki, Takahisa; Totsuka, Toshiyuki; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(2-3), p.511 - 515, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.51(Nuclear Science & Technology)In collaboration with the Naka Fusion Institute of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (NFI/JAEA) and the National Institute for Fusion Science of National Institute of Natural Science (NIFS/NINS), Center for Computational Science and E-systems of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (CCSE/JAEA) aims at establishing an integrated framework for experiments and analyses in nuclear fusion research based on the Atomic Energy Grid InfraStructure (AEGIS). AEGIS has been being developed by CCSE/JAEA aiming at providing the infrastructure that enables atomic energy researchers in remote locations to carry out R&D efficiently and collaboratively through the Internet. Toward establishing the integrated framework, we have been applying AEGIS to pre-existing three systems.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa; Oyama, Naoyuki
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 48(1-3), p.196 - 200, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.15(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effect of the pressure profile on the energy loss caused by edge localized modes (ELMs) has been investigated by using an integrated simulation code TOPICS-IB based on a transport code with a stability code for the peeling-ballooning modes and a model for scrape-off-layer and divertor plasmas. The steep pressure gradient inside the pedestal top is found to broaden the region of the ELM enhanced transport through the broadening of eigenfunctions and enhance the ELM energy loss. The ELM energy loss in the simulation becomes larger than 15% of the pedestal energy, as is shown in the database of multi-machine experiments.
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Tokuda, Shinji; Ozeki, Takahisa
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 123, p.012008_1 - 012008_11, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:72.74(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We investigate numerically the effects of the equilibrium properties on the structure of the edge MHD modes in tokamaks. In particular, we focus on the effects of the plasma shape and the pressure profile inside the top of the pedestal. As the results of numerical analyses, we find that the structure of the unstable MHD mode expands to the plasma core region even when the width of the edge pedestal region, and the mode structure can expand deeply in strongly-shaped plasmas. This deeply expansion in strongly-shaped plasma is because the difference of the stabilizing effect of the ideal ballooning mode between the plasma edge region (including the edge pedestal region) and the region inside the pedestal in strongly shaped plasma is larger than that in weakly shaped plasma. This difference allows to destabilize the MHD mode whose structure extend from the edge pedestal region to the region inside the pedestal in strongly shaped plasma.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa; Oyama, Naoyuki
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 123, p.012025_1 - 012025_10, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:82.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Density dynamics effect on ELM has been studied by TOPICS-IB. The ELM particle loss is found to almost independent on the collisionality, as shown in experiments, due to the density profile before ELM and the increase of the SOL density during ELM. It is confirmed by varying the density and the temperature instead of artificially enhancing the collisionality that the collisionality dependence of the ELM energy loss is caused by the bootstrap current and the SOL transport. Additionally, ion convective and charge-exchange losses are found to enhance the collisionality dependence due to the equipartition effect.
Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Takizuka, Tomonori; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ozeki, Takahisa
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 49(12), p.1955 - 1969, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:40.3(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Hosoyama, Hiroki; Kamada, Yutaka; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Oyama, Naoyuki; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 933, p.229 - 236, 2007/10
no abstracts in English
Isayama, Akihiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takechi, Manabu; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Kamada, Yutaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.773 - 782, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:69.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Results from active control of neoclassical tearing modes (NTMs) by electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) in 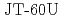 are described. Evolution of an NTM with the poloidal mode number
are described. Evolution of an NTM with the poloidal mode number 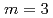 and the toroidal mode number
and the toroidal mode number 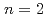 has been suppressed by ECCD inside the sawtooth inversion radius in the co-direction, showing the possibility of the coexistence of sawtooth oscillations and a small-amplitude
has been suppressed by ECCD inside the sawtooth inversion radius in the co-direction, showing the possibility of the coexistence of sawtooth oscillations and a small-amplitude 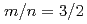 NTM without large confinement degradation. Stabilization of an
NTM without large confinement degradation. Stabilization of an 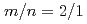 NTM by ECCD at the mode rational surface has been demonstrated with a small value of the ratio of the current density driven by electron cyclotron (EC) wave to the local bootstrap current density (
NTM by ECCD at the mode rational surface has been demonstrated with a small value of the ratio of the current density driven by electron cyclotron (EC) wave to the local bootstrap current density (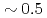 ). Also, dependence of the stabilization effect on ECCD location has been investigated in detail, and it has been clarified that an
). Also, dependence of the stabilization effect on ECCD location has been investigated in detail, and it has been clarified that an 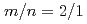 NTM can be completely stabilized with the misalignment of the ECCD location less than about half of the island width, and that the
NTM can be completely stabilized with the misalignment of the ECCD location less than about half of the island width, and that the 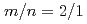 NTM is destabilized with the misalignment comparable to the island width. Time-dependent, self-consistent simulation of magnetic island evolution using the TOPICS code has shown that the above stabilization and destabilization of an
NTM is destabilized with the misalignment comparable to the island width. Time-dependent, self-consistent simulation of magnetic island evolution using the TOPICS code has shown that the above stabilization and destabilization of an 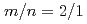 NTM are well reproduced with the same set of coefficients of the modified Rutherford equation. The TOPICS simulation has also clarified that EC wave power required for complete stabilization can be significantly reduced by narrowing the ECCD width.
NTM are well reproduced with the same set of coefficients of the modified Rutherford equation. The TOPICS simulation has also clarified that EC wave power required for complete stabilization can be significantly reduced by narrowing the ECCD width.