Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morishita, Yuki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Sato, Yuki; Oura, Masatoshi*
Radiation Measurements, 171, p.107064_1 - 107064_7, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0The detection of alpha and beta contamination locations is important for decontaminating nuclear facilities. In the high radiation dose rate environment at the decommissioning sites, the contamination measurement by the workers is not effective. Thus, we developed a remote automatic contamination measurement system using a new scintillator-based detector. A 50 mm
 100-
100- m-thick YAlO
m-thick YAlO (Ce)(YAP:Ce) scintillator was coupled with a flat panel-type multianode photomultiplier tube. The detector was installed downwards at the bottom of a robot. It has an energy measurement capability, and the energy measurement could discriminate the alpha particles from the beta and
(Ce)(YAP:Ce) scintillator was coupled with a flat panel-type multianode photomultiplier tube. The detector was installed downwards at the bottom of a robot. It has an energy measurement capability, and the energy measurement could discriminate the alpha particles from the beta and  Rn alpha particles. With the energy information, alpha and beta particles could be identified and mapped simultaneously. In addition, a slow-moving robot could be used to obtain statistically sufficient counts in a single run measurement, allowing the evaluation of surface contamination density using only alpha particles. The remote automatic contamination measurement system will be useful in visualizing the contamination distribution in environments that are inaccessible to workers.
Rn alpha particles. With the energy information, alpha and beta particles could be identified and mapped simultaneously. In addition, a slow-moving robot could be used to obtain statistically sufficient counts in a single run measurement, allowing the evaluation of surface contamination density using only alpha particles. The remote automatic contamination measurement system will be useful in visualizing the contamination distribution in environments that are inaccessible to workers.
Morishita, Yuki; Higuchi, Mikio*; Kaneko, Junichi*; Kitagawa, Yuichi*; Akedo, Jun*; Soma, Mitsugu*; Matsui, Hiroaki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1057, p.168702_1 - 168702_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)This paper describes the development of a large-area imaging detector capable of measuring the detailed distribution of alpha particles on hands and feet for use in entry/exit control monitors in decommissioning sites such as the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The detector was developed using a commercially available ZnS(Ag) scintillator and an electron multiplying CCD camera. The effectiveness of the detector was evaluated by measuring several types of radiation sources, and the results showed that it was possible to detect the position of alpha particles in a very short time, and contamination levels of up to 11 Bq/cm could be visualized. As a result of the minimal detectable surface activity concentration evaluations, 2.0 minutes or more is required to achieve 4 Bq/cm
could be visualized. As a result of the minimal detectable surface activity concentration evaluations, 2.0 minutes or more is required to achieve 4 Bq/cm , and 25.0 minutes or more is required to achieve 0.4 Bq/cm
, and 25.0 minutes or more is required to achieve 0.4 Bq/cm . The field of view of the detector was also checked, and it was confirmed that the setup had a field of view that could cover most of the hand and the sole of the shoe. This detector is expected to be useful for preventing internal uptake and decontamination.
. The field of view of the detector was also checked, and it was confirmed that the setup had a field of view that could cover most of the hand and the sole of the shoe. This detector is expected to be useful for preventing internal uptake and decontamination.
 -ray dust monitor for highly-concentrated airborne contaminants
-ray dust monitor for highly-concentrated airborne contaminantsSagawa, Naoki; Fujisawa, Makoto; Hosomi, Kenji; Morishita, Yuki; Takada, Chie
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 58(3), p.135 - 140, 2023/11
Radioactivity concentrations of airborne dust are important measurements because they are used to protect workers from intakes and to assess internal exposure doses. Therefore, we developed a portable  -ray dust monitor by using an ultra-thin plastic scintillator, which is designed for continuous monitoring of highly-concentrated airborne contaminants (
-ray dust monitor by using an ultra-thin plastic scintillator, which is designed for continuous monitoring of highly-concentrated airborne contaminants ( 10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm , equivalent to 30 times larger than the derived air concentration of
, equivalent to 30 times larger than the derived air concentration of  Sr) such as a decommissioning work in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. From the performance test results, it is evaluated that the developed portable
Sr) such as a decommissioning work in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. From the performance test results, it is evaluated that the developed portable  -ray dust monitor is functional in continuous monitoring with an airborne concentration of 1 Bq/cm
-ray dust monitor is functional in continuous monitoring with an airborne concentration of 1 Bq/cm .
.
 particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector
particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detectorMorishita, Yuki; Sagawa, Naoki; Takada, Chie; Momose, Takumaro; Takasaki, Koji
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(13), p.1376 - 1383, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)It is very important to evaluate the diameters (activity median aerodynamic diameter) of Plutonium dioxide (PuO ) particles for internal exposure dose evaluation. In this study, a method of evaluating PuO
) particles for internal exposure dose evaluation. In this study, a method of evaluating PuO particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector was developed. PuO
particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector was developed. PuO particles with different diameters were modeled by Monte Carlo simulation, and the change in the shape of the energy spectrum for each particle diameter was evaluated. Two different patterns were modeled, namely, the case of
particles with different diameters were modeled by Monte Carlo simulation, and the change in the shape of the energy spectrum for each particle diameter was evaluated. Two different patterns were modeled, namely, the case of  PuO
PuO and the case of PuO
and the case of PuO (including isotopic composition of Pu). Multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the PuO
(including isotopic composition of Pu). Multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the PuO particle diameter from the obtained parameters. The simulated diameters and the diameters obtained with the regression model were in good agreement. The advantage of using the alpha-particle imaging detector is to measure the alpha energy spectrum for individual particle, and this allows accurate measurement of particle diameter distribution.
particle diameter from the obtained parameters. The simulated diameters and the diameters obtained with the regression model were in good agreement. The advantage of using the alpha-particle imaging detector is to measure the alpha energy spectrum for individual particle, and this allows accurate measurement of particle diameter distribution.
Morishita, Yuki; Takasaki, Koji; Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Tagawa, Akihiro; Shibata, Takuya; Hoshi, Katsuya; Kaneko, Junichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*; Oura, Masatoshi*
Radiation Measurements, 160, p.106896_1 - 106896_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study proposes a newly developed phoswich alpha/beta detector that can discriminate alpha and beta particles emitted from the alpha and beta contaminations in the FDNPS site. The phoswich alpha/beta detector is made up of two layers of scintillators that detect alpha and beta particles. The pulse shape discrimination (PSD) method was used to detect alpha particles in high beta particle and high gamma-ray (comparable to gamma-ray dose rate near the FDNPS reactor building) environments. Due to a 23.3% full width at half maximum (FWHM) energy resolution for alpha particles, the detector can be used to distinguish between nuclear fuel materials such as plutonium and its radon progeny (Po-214). Moreover, the detector could distinguish alpha particles from  Cs gamma rays with a dose rate background up to 9.0 mSv/h. It is the first to demonstrate that the developed phoswich detector can be used to discriminate and measure alpha and beta particles of the actual contaminated FDNPS samples.
Cs gamma rays with a dose rate background up to 9.0 mSv/h. It is the first to demonstrate that the developed phoswich detector can be used to discriminate and measure alpha and beta particles of the actual contaminated FDNPS samples.
Morishita, Yuki
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1027, p.166258_1 - 166258_7, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:53.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)During the decommissioning process of nuclear facility sites, such as the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), radioactive contamination due to alpha, beta, and gamma nuclides is present. To accurately detect these nuclides, a new phoswich alpha/beta/gamma detector is proposed and developed. A portable alpha/beta/gamma radiation continuous air-monitoring system is also developed using the proposed phoswich detector for detecting unknown radioactive air contamination. The developed phowich detector features a 6 mm  6 mm
6 mm  6 mm-stilbene scintillator (first layer) and a 6 mm
6 mm-stilbene scintillator (first layer) and a 6 mm  6 mm
6 mm  6 mm-Gd
6 mm-Gd (Ga, Al)
(Ga, Al) O
O (Ce) (GAGG) scintillator (second layer). The bottom of the GAGG scintillator is optically coupled to a silicon photomultiplier (SiPM). The proposed phoswich detector is capable of successfully separating alpha, beta, and gamma nuclides by applying the pulse-shape discrimination (PSD) technique. The alpha energy resolution of the 5.5 MeV alpha particles using was 22.1% at the full width at half maximum (FWHM), whereas the gamma energy resolution of the 0.662 MeV gamma rays was 10.3% FWHM. The energy spectra obtained from the simulations agree well with those obtained from measurements. Continuous alpha-nuclide air measurements were conducted in the basement of a concrete building, where the
(Ce) (GAGG) scintillator (second layer). The bottom of the GAGG scintillator is optically coupled to a silicon photomultiplier (SiPM). The proposed phoswich detector is capable of successfully separating alpha, beta, and gamma nuclides by applying the pulse-shape discrimination (PSD) technique. The alpha energy resolution of the 5.5 MeV alpha particles using was 22.1% at the full width at half maximum (FWHM), whereas the gamma energy resolution of the 0.662 MeV gamma rays was 10.3% FWHM. The energy spectra obtained from the simulations agree well with those obtained from measurements. Continuous alpha-nuclide air measurements were conducted in the basement of a concrete building, where the  Rn concentration was approximately 200 Bq/m
Rn concentration was approximately 200 Bq/m , using the developed portable continuous air-monitoring system. The measured peaks, which correspond to
, using the developed portable continuous air-monitoring system. The measured peaks, which correspond to 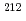 Bi (6.1 MeV),
Bi (6.1 MeV),  Po (7.7 MeV), and
Po (7.7 MeV), and 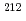 Po (8.8 MeV), were observed in the alpha spectrum by separating beta and gamma rays. Therefore, the developed monitoring system can be potentially efficient for the early detection of unknown released radioactive materials.
Po (8.8 MeV), were observed in the alpha spectrum by separating beta and gamma rays. Therefore, the developed monitoring system can be potentially efficient for the early detection of unknown released radioactive materials.
Morishita, Yuki; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Yamaji, Akihiro*; Hayashi, Masateru*; Sasano, Makoto*; Makita, Taisuke*; Azuma, Tetsushi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.5948_1 - 5948_11, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.78(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The internal exposure of workers who inhale plutonium dioxide particles in nuclear facilities is a crucial matter for human protection from radiation. To determine the activity median aerodynamic diameter values at the working sites of nuclear facilities in real time, we developed a high-resolution alpha imager using a ZnS(Ag) scintillator sheet, an optical microscope, and an electron-multiplying charge-coupled device camera. Then, we designed and applied a setup to measure a plutonium dioxide particle and identify the locations of the individual alpha particles in real time. Employing a Gaussian fitting, we evaluated the average spatial resolution of the multiple alpha particles was evaluated to be 16.2 umFWHM with a zoom range of 5 x. Also, the spatial resolution for the plutonium dioxide particle was 302.7 umFWHM due to the distance between the plutonium dioxide particle and the ZnS(Ag) scintillator. The influence of beta particles was negligible, and alpha particles were discernible in the alpha-beta particle contamination. The equivalent volume diameter of the plutonium dioxide particle was calculated from the measured count rate. These results indicate that the developed alpha imager is effective in the plutonium dioxide particle measurements at the working sites of nuclear facilities for internal exposure dose evaluation.
Morishita, Yuki
Radiation Measurements, 140, p.106511_1 - 106511_7, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Radon-222 ( Rn) is a naturally-occurring radioactive gas, and the measurement of this isotope and its progeny is of interest from the viewpoint of protection against internal exposure. We have developed a new alpha beta-imaging detector combined with a waveform digitizer capable of imaging alpha- and beta-particle locations simultaneously. This detector is used for
Rn) is a naturally-occurring radioactive gas, and the measurement of this isotope and its progeny is of interest from the viewpoint of protection against internal exposure. We have developed a new alpha beta-imaging detector combined with a waveform digitizer capable of imaging alpha- and beta-particle locations simultaneously. This detector is used for  Rn -progeny measurements. The thin-stilbene plate was optically coupled to a position-sensitive photomultiplier tube (PSPMT), and the analog signals from the PSPMT were transferred in parallel to the waveform digitizer. For 5.5-MeV alpha particles, the detection efficiency was 97.2% for 2
Rn -progeny measurements. The thin-stilbene plate was optically coupled to a position-sensitive photomultiplier tube (PSPMT), and the analog signals from the PSPMT were transferred in parallel to the waveform digitizer. For 5.5-MeV alpha particles, the detection efficiency was 97.2% for 2 steradians, and the energy resolution was 21.6% full width at half maximum (FWHM). The imaging detector was able to discriminate between alpha and beta particles via the pulse-shape-discrimination (PSD) technique, as well as being capable of alpha- and beta-particle imaging. When measuring the
steradians, and the energy resolution was 21.6% full width at half maximum (FWHM). The imaging detector was able to discriminate between alpha and beta particles via the pulse-shape-discrimination (PSD) technique, as well as being capable of alpha- and beta-particle imaging. When measuring the  Rn progeny, both
Rn progeny, both  Bi and
Bi and  Po are imaged simultaneously, and a correlation is found between the positions of
Po are imaged simultaneously, and a correlation is found between the positions of  Bi and
Bi and  Po. The developed detector will be useful as a
Po. The developed detector will be useful as a  Rn detector and in alpha-continuous-air monitoring for nuclear-fuel facilities.
Rn detector and in alpha-continuous-air monitoring for nuclear-fuel facilities.
 Si
Si O
O (GPS) scintillator-based alpha imaging detector for rapid plutonium detection in high-radon environments
(GPS) scintillator-based alpha imaging detector for rapid plutonium detection in high-radon environmentsMorishita, Yuki; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*; Torii, Tatsuo
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 67(10), p.2203 - 2208, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:71.58(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We developed a Gd Si
Si O
O (GPS) scintillator-based alpha imaging detector and demonstrated its effectiveness by evaluating actual Pu particle and
(GPS) scintillator-based alpha imaging detector and demonstrated its effectiveness by evaluating actual Pu particle and  Rn progeny. The GPS scintillator plate was prepared by a sintering method. The outer dimensions of the GPS scintillator plate were 5
Rn progeny. The GPS scintillator plate was prepared by a sintering method. The outer dimensions of the GPS scintillator plate were 5  5 cm, and the scintillator layer was approximately 50
5 cm, and the scintillator layer was approximately 50  m on a 3-mm-thick high-transparency glass. The plate was optically coupled to a position-sensitive photomultiplier tube with silicone grease. The developed imaging detector exhibited good uniformity. Pu particle activities were accurately evaluated at 14 different positions, and the difference in activity was within 6%. Radon-222 (
m on a 3-mm-thick high-transparency glass. The plate was optically coupled to a position-sensitive photomultiplier tube with silicone grease. The developed imaging detector exhibited good uniformity. Pu particle activities were accurately evaluated at 14 different positions, and the difference in activity was within 6%. Radon-222 ( Rn) progeny counts were reduced by 65.3% by applying an energy window. Although the Pu/
Rn) progeny counts were reduced by 65.3% by applying an energy window. Although the Pu/ Rn progeny activity ratio was 1/51, the Pu particle was successfully identified among
Rn progeny activity ratio was 1/51, the Pu particle was successfully identified among  Rn progeny within the 5 min-measurement time. The imaging detector has an excellent ability for detecting Pu among
Rn progeny within the 5 min-measurement time. The imaging detector has an excellent ability for detecting Pu among  Rn progeny. Thus, this detector is useful for alpha contamination monitoring in high-radon-background environments.
Rn progeny. Thus, this detector is useful for alpha contamination monitoring in high-radon-background environments.
Morishita, Yuki; Ye, Y.*; Mata, L.*; Pozzi, S. A.*; Kearfott, K. J.*
Radiation Measurements, 137, p.106428_1 - 106428_7, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have developed a compact, organic-scintillator-based alpha/beta spectrometer for radon measurements and have characterized it using a unique, small radon chamber. The spectrometer is composed of a through-silicon via (TSV) silicon photomultiplier (or SiPM) and a 6 mm  6 mm
6 mm  6 mm stilbene crystal cube. Analog signals from the SiPM are sent to a digitizer. The detector is housed in a light-tight box, with a stacked air filter installed in one side of the box to enable
6 mm stilbene crystal cube. Analog signals from the SiPM are sent to a digitizer. The detector is housed in a light-tight box, with a stacked air filter installed in one side of the box to enable  Rn gas to diffuse to the inside. We conducted one experiment with the spectrometer and an AlphaGUARD detector placed in a basement at the University of Michigan, and we conducted other experiments with both detectors placed in a small radon chamber together with
Rn gas to diffuse to the inside. We conducted one experiment with the spectrometer and an AlphaGUARD detector placed in a basement at the University of Michigan, and we conducted other experiments with both detectors placed in a small radon chamber together with  Ra sources. By applying a pulse-shape-discrimination technique, we were able to separate the alpha and beta spectra simultaneously and clearly and to measure them quantitatively. We found two peaks in the measured alpha spectrum: a lower-energy peak due to
Ra sources. By applying a pulse-shape-discrimination technique, we were able to separate the alpha and beta spectra simultaneously and clearly and to measure them quantitatively. We found two peaks in the measured alpha spectrum: a lower-energy peak due to 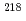 Po and a higher-energy peak due to
Po and a higher-energy peak due to  Po. We found a linear relation between the radon concentration y from AlphaGUARD and the counting rates from the stilbene-SiPM detector. The alpha/beta spectrometer is less than 10 mm thick, and we expect that it will be easy to increase the sensitivity with future device construction. Thus, this compact, organic-scintillator-based alpha/beta spectrometer shows promise for use in novel radon-detection systems.
Po. We found a linear relation between the radon concentration y from AlphaGUARD and the counting rates from the stilbene-SiPM detector. The alpha/beta spectrometer is less than 10 mm thick, and we expect that it will be easy to increase the sensitivity with future device construction. Thus, this compact, organic-scintillator-based alpha/beta spectrometer shows promise for use in novel radon-detection systems.
Morishita, Yuki; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 966, p.163795_1 - 163795_8, 2020/06
To date, alpha and high beta particle emitters have been detected in the reactor buildings of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). Since the beta radiation levels in the FDNPS buildings are extremely high, a commercial beta survey meter, such as a Geiger-Muller (GM) counter, would no longer have the ability to measure the beta contamination levels. In order to solve this issue, we utilized ultra-thin plastic scintillators to increase the detection rate of alpha and beta contamination. In this study, ultra-thin plastic scintillators with varied thicknesses of 7, 22, 24, 31, 39, and 55 um were prepared. To test their sensitivity, each scintillator was optically coupled to a glass plate and a 2-in square position-sensitive photomultiplier tube, and exposed to either an alpha, beta, or gamma source. Results from alpha spectrometry show that only the 55 um-thick plastic scintillator fully absorbed the alpha particles (5.5 MeV) with a 16.7% Full Width at Half Maximum. For alpha imaging under a high beta background, the 7 um-thick plastic scintillator was found to be the best choice, with an alpha to beta ratio of 652. This plastic scintillator also had the lowest sensitivity to beta particles, measuring only 41.74 cps when exposed to a 1 MBq  Sr/
Sr/ Y source in contact. It would therefore be possible to use the 7 um-thick plastic scintillator, to directly measure the surface contamination levels at the FDNPS site in real-time, where previous methods have fallen short. Thus, the developed detector would be a useful tool for the detection of alpha and beta contamination in the FDNPS.
Y source in contact. It would therefore be possible to use the 7 um-thick plastic scintillator, to directly measure the surface contamination levels at the FDNPS site in real-time, where previous methods have fallen short. Thus, the developed detector would be a useful tool for the detection of alpha and beta contamination in the FDNPS.
Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Aoki, Katsunori; Tsurudome, Koji; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(2), p.172 - 181, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)We developed a remote continuous air monitoring (RCAM) system. The RCAM system consisted of a personal air monitor and a robot. The personal air monitor (poCAMon, SARAD, Germany) had a 400 mm ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the
ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the  Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of
Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of 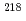 Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and
Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and  Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Morishita, Yuki
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 954, p.161708_1 - 161708_5, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.45(Instruments & Instrumentation)Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Torii, Tatsuo
Isotope News, (765), p.10 - 13, 2019/10
This paper reports the development of an alpha particle imaging detector to detect alpha emitters originating from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and the actual measurement of smear papers.
Morishita, Yuki; Di Fulvio, A.*; Clarke, S. D.*; Kearfott, K. J.*; Pozzi, S. A.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 935, p.207 - 213, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:82.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)We developed a prototype alpha/beta particle detector using a pulse shape discrimination (PSD) capable organic scintillator, a silicon photomultiplier, and a waveform digitizer. The charge integration PSD technique was used to separate alpha and beta particles. We compared the PSD figure of merit (FOM) values of two scintillators (EJ-299-33 and stilbene), and found that the stilbene (FOM =1.61) performance was superior to the EJ-299-33 (FOM = 0.56) performance, measured using an  Am source (5.5 MeV alpha particle emission) and a
Am source (5.5 MeV alpha particle emission) and a  Sr source. Additionally, the stilbene showed good energy resolution (23.6% FWHM for 5.5 MeV alpha particles). In the pulse height spectrum for the
Sr source. Additionally, the stilbene showed good energy resolution (23.6% FWHM for 5.5 MeV alpha particles). In the pulse height spectrum for the  Sr/
Sr/ Y source, the lower energy portion (
Y source, the lower energy portion ( Sr) and the higher energy portion (
Sr) and the higher energy portion ( Y) could be separated.
Y) could be separated.
Morishita, Yuki; Kaneko, Junichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*; Izaki, Kenji; Yajima, Tatsuo*; Matsuura, Mitsugu*; Tamura, Ken; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Measurements, 122, p.115 - 120, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:61.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)Morishita, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Usami, Hiroshi; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki*; Utsugi, Wataru*; Takahira, Shiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9, p.581_1 - 581_14, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:91.8(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Nakamura, Keisuke; Morishita, Yuki; Takasaki, Koji; Maehata, Keisuke*; Sugimoto, Tetsuya*; Kiguchi, Yu*; Iyomoto, Naoko*; Mitsuda, Kazuhisa*
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 193(3-4), p.314 - 320, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Morishita, Yuki; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Measurements, 112, p.1 - 5, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:85.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)To detect plutonium isotopes ( Pu,
Pu,  Pu, and
Pu, and  Pu) in a field of high beta and
Pu) in a field of high beta and  background, an alpha particle detector with low beta and
background, an alpha particle detector with low beta and  -ray sensitivity is required. Therefore, we optimized the thickness of the GAGG scintillator for alpha particle detection in a field of high beta and
-ray sensitivity is required. Therefore, we optimized the thickness of the GAGG scintillator for alpha particle detection in a field of high beta and  background. We prepared three GAGG scintillators with thicknesses of 0.05 mm, 0.07 mm, and 0.1 mm. Each of the GAGG scintillators was coupled optically to the SiPM array, which was used as the photodetector. Alpha, beta, and
background. We prepared three GAGG scintillators with thicknesses of 0.05 mm, 0.07 mm, and 0.1 mm. Each of the GAGG scintillators was coupled optically to the SiPM array, which was used as the photodetector. Alpha, beta, and  rays were irradiated onto the developed alpha particle detector, and their spectra were obtained. All GAGG scintillators used in this study were not sensitive to
rays were irradiated onto the developed alpha particle detector, and their spectra were obtained. All GAGG scintillators used in this study were not sensitive to  rays with a dose rate of 1 mSv/h. The beta count of the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG was only 1/100 that of the 0.1-mm-thick GAGG. Therefore, the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG scintillator is promising from the viewpoint of detecting plutonium contamination in a field with high beta and
rays with a dose rate of 1 mSv/h. The beta count of the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG was only 1/100 that of the 0.1-mm-thick GAGG. Therefore, the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG scintillator is promising from the viewpoint of detecting plutonium contamination in a field with high beta and  background.
background.
Morishita, Yuki; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Momose, Takumaro; Kaneko, Junichi*; Nemoto, Norio
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 178(4), p.414 - 421, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Plutonium dioxide (PuO ) is used to fabricate a mixed oxide fuel for fast breeder reactors. When a glove box containing PuO
) is used to fabricate a mixed oxide fuel for fast breeder reactors. When a glove box containing PuO fails, such as by rupture of a glove or a vinyl bag, airborne contamination of plutonium (Pu) can occur. If the worker inhale PuO
fails, such as by rupture of a glove or a vinyl bag, airborne contamination of plutonium (Pu) can occur. If the worker inhale PuO particles, they deposit in the lung and cause lung cancer. The nasal smear and nose blow methods are useful for checking workers for PuO
particles, they deposit in the lung and cause lung cancer. The nasal smear and nose blow methods are useful for checking workers for PuO intake in the field. However, neither method can evaluate the quantitative activity of Pu. No alpha-particle detector that can be used for direct measurements in the nasal cavity has been developed. Therefore, we developed a nasal monitor capable of directly measuring the activity of Pu in the nasal cavity to precisely evaluate the internal exposure dose of a worker. Prismatic-shaped 2
intake in the field. However, neither method can evaluate the quantitative activity of Pu. No alpha-particle detector that can be used for direct measurements in the nasal cavity has been developed. Therefore, we developed a nasal monitor capable of directly measuring the activity of Pu in the nasal cavity to precisely evaluate the internal exposure dose of a worker. Prismatic-shaped 2 2 acrylic light guides were used to compose a detector block, and a ZnS(Ag) scintillator was adhered to the surface of these light guides. Silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) arrays with 8
2 acrylic light guides were used to compose a detector block, and a ZnS(Ag) scintillator was adhered to the surface of these light guides. Silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) arrays with 8 8 channels were used as a photodetector. Actual PuO
8 channels were used as a photodetector. Actual PuO particles were measured using the nasal monitor. The nasal monitor could be directly inserted in the nasal cavities. The activity distribution of Pu was obtained by the nasal monitor. The average efficiencies in 4
particles were measured using the nasal monitor. The nasal monitor could be directly inserted in the nasal cavities. The activity distribution of Pu was obtained by the nasal monitor. The average efficiencies in 4 were 11.43% and 11.58% for the left and right nasal cavities, respectively. The effect of
were 11.43% and 11.58% for the left and right nasal cavities, respectively. The effect of  and
and  rays on the detection of the alpha particles of Pu was negligible. The difference in the measured Pu activity between the ZnS(Ag) scintillation counter and the nasal monitor was within 4.0%. The developed nasal monitor can solve the uncertainty problem encountered with the nasal smear and the nose blow methods. We expect this monitor to be useful for accurately estimating the internal exposure dose of workers.
rays on the detection of the alpha particles of Pu was negligible. The difference in the measured Pu activity between the ZnS(Ag) scintillation counter and the nasal monitor was within 4.0%. The developed nasal monitor can solve the uncertainty problem encountered with the nasal smear and the nose blow methods. We expect this monitor to be useful for accurately estimating the internal exposure dose of workers.